Oophorectomy
 Single or bilateral ovaryectomy( ovariectomy) is not a common operation, as it is performed according to a limited number of indications. Sometimes the ovary has to be removed together with the fallopian tube, less often - with the uterus.
Single or bilateral ovaryectomy( ovariectomy) is not a common operation, as it is performed according to a limited number of indications. Sometimes the ovary has to be removed together with the fallopian tube, less often - with the uterus.
The importance of ovaries for the female body can not be overestimated. They are responsible for three main functions:
- Vegetative, thanks to which the sexual maturation of girls occurs, and the "female" appearance is formed. The ovaries are "switched on" during puberty and function until menopause.
- Hormonal. The ovaries secrete two determinant hormones cyclically: estrogen( in the first phase) and progesterone( into the second phase).Rhythmic production of ovarian hormones is regulated by the hypothalamus and pituitary in the brain.
- Generative( childbearing).Ovaries reproduce fertile eggs for the entire reproductive period.
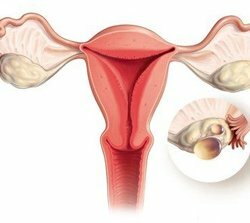
The full and adequate performance of all these functions with the ovaries provides the woman with health and maternity. Ovaries - the paired hormonal gland. The completely identical structure and functioning of the right and left ovaries testifies to the wisdom of nature, which prudently decided "just in case" to make this body paired. It is thanks to this decision that removal of the right ovary allows a woman to realize the function of childbearing at the expense of the remaining left ovary, and removal of the left ovary is compensated by the left right ovary.
Ovary( each) has a dense connective tissue outer shell, beneath it in the cortical layer there are many small undeveloped follicles containing the same undeveloped ovum. One of these follicles( they are called primordial) for a period equal to one menstrual cycle becomes fully ripe, and the inside of the egg reaches the necessary for fertilization development. The full development of the follicle and the ovum respectively provide estrogens. The ripe follicle( graafa vesicle) bursts into the middle of the cycle, and the ovum leaves it( ovulation), moving through the abdominal cavity to the fallopian tube - the place of potential fertilization. If fertilization does not happen, the egg dies in two days, and in the ovary, a yellow body is formed from the remnants of the bursting graafa vesicle that is capable of synthesizing progesterone. When the yellow body collapses( shortly before the menstrual period), under the influence of a sharp decline in hormones, the endometrium is rejected, and menstrual bleeding begins.
Thus, the conventionally menstrual cycle is divided by the period of ovulation into two phases of equal duration: follicular( first) and luteal( second).All the occurring changes in the follicular phase occur with the participation of FSH of the pituitary( follicle-stimulating hormone), and in the luteal phase the pituitary gland secretes LH( luteinizing hormone).
Similar cyclic structural and hormonal processes continue throughout the reproductive period.
The most common diagnosed pathology of the ovaries is hormonal dysfunction, when due to improper hormonal secretion the cycle is broken and / or infertility develops. As a rule, such violations are corrected by hormone therapy. Remove the ovary only in those situations when its presence is associated with life-threatening consequences, for example, with bleeding, septic complication, a large tumor and the like.
As a rule, unilateral removal of the ovaries leaves a woman a chance of motherhood. Pregnancy after removal of the ovary is possible, but its probability, for obvious reasons, decreases.
Serious consequences provoke bilateral ovariectomy, as the body loses the proper hormonal influence and enters the period of artificial premature menopause.
Therapy after removal of the ovaries is designed to correct hormonal disorders in order to eliminate climacteric disorders.
Reasons for ovarian excision
Any clinical situation in gynecology is considered by specialists from the position of organ preservation, especially in patients of the reproductive age. Therefore, every surgical intervention to remove the uterus or appendages has very clearly delineated indications.
The decision to remove the ovary is adopted:
- In case of an emergency, when the opportunity to maintain the health( and sometimes life) of the patient is directly related to ovariectomy.
To such, above all, are purulent processes in the appendages. In patients with weakened mechanisms of immune defense, infectious inflammation quickly spreads in the zone of the fallopian tubes and ovaries, followed by the formation of a delineated, pus-filled formation, the rupture of which may result in a septic shock. Eliminate such a purulent infiltrate is not always possible in isolation, so you have to remove the affected ovary.
Another indication for the removal of the ovary is the rupture of the ovarian cyst. More often it occurs with follicular, less often - with endometrioid and cysts of the yellow body. When the cyst ruptures, massive bleeding sometimes appears, which can not always be eliminated by more gentle methods.
Ectopic pregnancy, developing in the ovary, also often requires its removal.
- In the presence of a serious pathology that does not allow the ovary to function properly and can only be eliminated with it. These include extensive endometriosis without the presence of preserved ovarian tissue, ovarian and / or uterine tumor, including malignant tumors. Most experts are inclined to believe that any tumor is an indication for ovarian removal, since it is possible to reliably estimate the nature of education only after histological examination of its tissue.
Sometimes the ovary is removed due to the pathology of the fallopian tubes and / or uterus.
Statistically, the right ovary is removed more often.
Ovarian Removal Surgery
Removal of the left ovary and removal of the ovary to the right are not technically different.
In emergency situations, when there is no possibility for detailed diagnosis, the decision to remove the ovary is taken directly during the operation, when the situation is assessed visually.
The nature of the operation depends on the specific clinical situation that requires the surgeon to solve the main questions:
- To what extent the intervention will be performed, ie one ovary is removed or both;The uterus and tubes remain or are removed.
- Which surgical technique to choose.
In fact, all existing techniques are divided into sparing, laparoscopic, and cavitary. When the cavity technique( laparotomy), the abdominal cavity is opened layer by layer, and when laparoscopic - instead of a large incision, several small holes appear on the abdominal wall.
During the operation, the ovary is cut off from the supporting muscular-ligament skeleton, and the resulting abdominal defect is closed with a wide uterine ligament.
Depending on the method and volume, the operation time varies from one to four hours, and the subsequent number of days spent in the hospital does not exceed five days.
Early therapy after removal of the ovaries begins in the hospital. Usually it does not differ from that with other gynecological operations, but it has some peculiarities. Since the ovaries serve as a source of sex hormones, and their number depends on age, with bilateral ovariectomy, it is necessary to determine the degree of necessity of replenishing the hormone deficiency by medication. Hormonal rehabilitation after removal of the ovaries is necessary for patients who have not entered the climacteric period.
Consequences after removal of the ovaries
Negative consequences after removal of the ovaries can be conditionally classified into functional and organic.
Organic are associated with the removal of the organ as such, when its absence provokes the appearance of postoperative effects. One of them is a pain syndrome. Pain after removal of the ovary in the early period is associated with minor changes in the topography of the pelvic organs: they move slightly and fixing their apparatus "stretches", provoking pain. As a rule, after two weeks( or earlier), these pains cease.
Unfortunately, sometimes pain after removal of the ovary is provoked by a commissural process, which can not be completely eliminated. More often spikes form against the background of inflammatory phenomena, when inflammatory exudate appears in the pelvic cavity, eventually it becomes viscous and dense, therefore, literally "glues" adjacent tissues, disrupting their proper mobility. Early rehabilitation after removal of the ovaries suggests the prevention of inflammatory and, consequently, adhesive processes.
The most serious consequence of ovariectomy, especially in young patients, is a complex of functional disorders. Their severity is determined by the number of removed ovaries. One-sided ovariectomy leaves the patient with the opportunity to have her own sex hormones, and also to realize the reproductive function. More often after the removal of one ovary, dyshormonal malfunctions occur, which can be compensated.
If both ovaries are removed, the woman is artificially deprived of the necessary estrogenic influence, and a condition similar to the menopause, called post-stroke syndrome, sets in. In contrast to natural menopause, when the body has the ability to gradually adapt to the attenuation of the hormonal function of the ovaries, climacteric syndrome of artificial origin is quite difficult.
Life after removal of the ovaries
The most favorable clinical situation is observed after removal of only one ovary, since the remaining begins to compensate for the changes that have occurred.
Two or three weeks after bilateral ovariectomy, the first symptoms of an artificial climax appear: neurovegetative disorders( 72.8%), metabolic and endocrine disorders( 11.2%), psychoemotional abnormalities( 16%).The lack of a proper estrogenic effect on the mucous membranes of the genital tracts provokes premature "aging" with the development of atrophic changes.
Postastratsionny syndrome manifested tides, increased sweating( especially night), headaches, unstable blood pressure, chills, heart problems( arrhythmia).Deformation of the psychoemotional sphere also occurs( irritability, tearfulness, insomnia, decreased memory and attention, drowsiness and the like).
Because estrogenic influence extends to almost the entire female body, many systems respond to their absence, and the list of symptoms of artificial menopause can be very extensive.
The situation when a woman panics with a premature climax is understandable and understandable. However, it should be noted that although it is unpleasant, it is not a verdict. Moreover - not all women suffer this period severely, since its course is always individual and depends on the state of health in general and the gynecological - in particular. The greatest severity of negative symptoms occurs in the first two years after removal of the ovaries, and then the body is partially compensated.
Rehabilitation after removal of the ovaries suggests hormonal therapy. Preparations are selected in such a way as to imitate the natural hormonal background and keep it until the onset of natural menopause.
When a woman learns that she is going to have an ovariectomy, she is more often concerned about the question of whether pregnancy is possible after removal of the ovary. If only one ovary is removed, pregnancy is possible if the second ovary, tube and uterus are retained. With bilateral ovariectomy, natural conception, unfortunately, is impossible.