Hydrosalpinks
 Hydrosalpinx is one or two-sided dropsy of the fallopian tube, formed after the inflammatory process. Hydrosalpinx is a bag filled with serous fluid, and is a complication of acute salpingitis.
Hydrosalpinx is one or two-sided dropsy of the fallopian tube, formed after the inflammatory process. Hydrosalpinx is a bag filled with serous fluid, and is a complication of acute salpingitis.
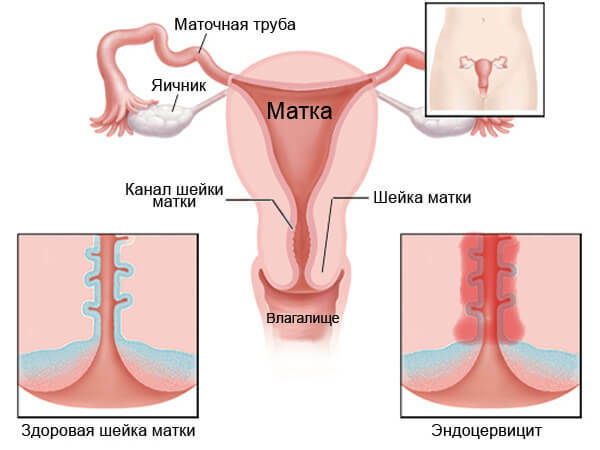
Fallopian tubes belong to the appendages of the uterus, due to which the reproductive function of the female body is realized. In appearance, each uterine tube looks like a hollow, thin tube 11 cm long, it begins at the upper corner of the uterus( uterine end) and opens into the abdominal cavity near the ovary, where it forms an ampoule( ampullar end).The wall of the fallopian tube is formed by three layers:
- A dense outer serous layer protects the tube from negative effects;
- The elastic middle muscle layer is formed by muscle fibers that are capable of peristaltic movements directed toward the uterine cavity;
- The inner mucous layer lining the cavity of the uterine tube, it forms many longitudinal folds and is covered with cells of the ciliated epithelium. These cells have on their surface special formations - cilia. Due to the movement of the cilia, the epithelium of the uterine tube can perform wave-like movements( flicker) in the direction from the ampullary end to the uterine. In the tubular epithelium there are glands capable of producing a serous secret.
Egg maturation occurs on the surface of the ovary. In the thickness of the outer( white) shell of the ovary is a lot of follicles, in each of them there is an egg at different stages of maturation. Maturation of the follicle and the egg is symmetrical, so when the mature follicle bursts, it releases the mature, ready to fertilize, ovum( ovulation).Then the egg enters the abdominal cavity. Her vitality lasts two days, and then she dies. In case of fertilization, the egg enters the fallopian tube and advances into the uterus due to contractions in the muscular tube of the tube, flickering of the epithelial layer, and also to the tubular glands that moisturize the surface of the epithelium and facilitate the movement process.
Peculiarities of the structure of the fallopian tubes are associated with the need to promote a fertilized egg from the abdominal cavity to the uterus for subsequent implantation and development of pregnancy. That is why the peristalsis of the fallopian tubes increases in a period that coincides with the time of ovulation and the subsequent, luteal, phase of the cycle.
Fallopian tubes have an abundantly developed network of blood vessels, due to which the inflammatory processes in this area develop rapidly and also spread quickly to surrounding tissues in the absence of good local immunity. Isolated inflammation of the fallopian tubes( salpingitis) is much less common in the combined inflammatory process in both the tubes and in the ovaries( salpingoophoritis).
The process of hydrosalpinx formation begins after an episode of acute inflammation in the uterus tube, acute salpingitis, and is its complication. Inflammatory effusion( exudate) accumulates in the tube of the uterus, glues its walls and forms a closed fluid formation.
Hydrosalpinx is a mechanical obstruction to the egg in the uterine cavity and causes tubal infertility. In a one-sided process, a single healthy mother-in-law remains in the woman and there is a chance of getting pregnant, and a bilateral hydrosalpinx makes pregnancy impossible.
Infertility in hydrosalpinx is often the only reason to call a specialist. The clinical picture with hydrosalpinx is similar to that of chronic inflammatory diseases of the uterine appendages. The brightest clinical picture of hydrosalpinx develops against the background of a pronounced adhesion process in the pelvic organs.
Medication removal of hydrosalpinx and elimination of its consequences is impossible. Hydrosalpinx therapy implies a consistent two-stage elimination of the pathological process in the area of the fallopian tubes. Initially, adequate anti-inflammatory treatment is performed, and then the hydrosalpinx is surgically removed. Preference is given to laparoscopic methods for the elimination of pathological education. The success of treatment is determined not by the quality of the surgical procedure performed, but by the possibility of the subsequent restoration of the proper function of the uterine tube.
Unfortunately, the insidiousness of the disease consists in the fact that even with the successful liquidation of the hydrosalpinx and complete restoration of the patency of the fallopian tubes, a woman often remains barren. Especially often this situation occurs in patients with a long-term chronic inflammation in the uterine appendages and a pronounced adhesion process in the abdominal cavity.
Modern women want to have as much information about their health and modern medical methods. Using the right terms help to quickly find the necessary information in all available sources. Sometimes patients use incorrect terms in the name of their illness. It is wrong to use the phrase "hydrosalpinks pipes" to find the necessary information."Hydro" means liquid, and "salpinx" is a pipe, and this means that the hydosalpinx pipe simply does not exist.
A similar situation occurs when the names of surveys. It is wrong to say laparoscopy of hydrosalpinx. Laparoscopy is an instrumental method of examining the internal organs, allowing you to see the abdominal or pelvic cavity from the inside. In addition to the fallopian tubes, the doctor sees all surrounding organs and tissues. Instead of laparoscopy hydrosalpinx, laparoscopy for hydrosalpinx is more correct.
Causes of hydrosalpinx
The process of hydrosalpinx formation is associated with occlusion of the ampullar part of the fallopian tube in the presence of a local infectious and inflammatory process.
Hydrosalpinx is formed after a nonspecific acute inflammatory process in the fallopian tube( salpingitis).The source of inflammation can be pathogenic microorganisms and representatives of opportunistic microflora. As a rule, the cause of acute salpingitis is not the only microorganism, but their association, which can contain streptococci, staphylococci, chlamydia, mycoplasma, E. coli and others.
Sources of infection often rise into the cavity of the tube from the lower parts of the vagina, cervical canal or uterus. The variants of the descending spread of the infection are infrequent, in this case the infection of the uterine tube is hematogenous( through the blood) due to the presence of infection in distant organs: the kidneys, the bladder, the tonsils, the intestine and others.
The causes of inflammation of the fallopian tubes are:
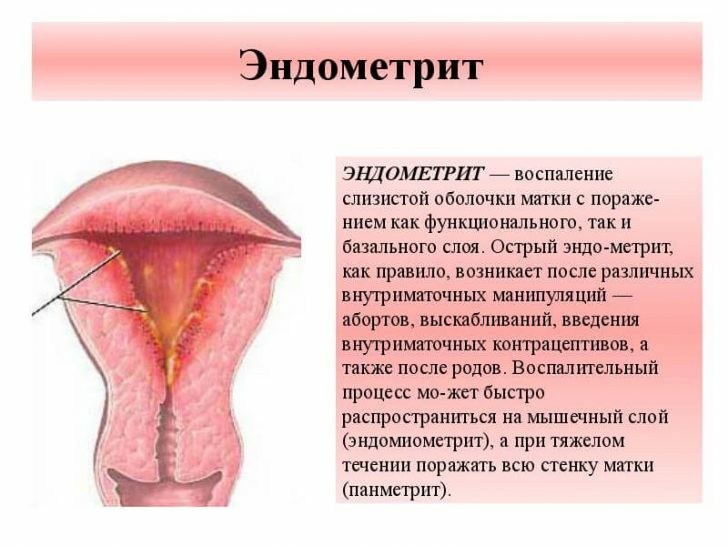
- Infectious-inflammatory diseases of the uterus( endometritis).
- Random sex life. In addition to the probability of contracting sexually transmitted diseases, it contributes to a change in the composition of the normal vaginal microenvironment. When undesirable microorganisms become too much, they become the cause of inflammation.
- Frequent hypothermia, which depletes the defenses of the body.
- Abortion, diagnostic manipulation and birth trauma of the genitals. Infection penetrates the genitals through a vast wound surface.
- Intrauterine device contraception. The introduction of the uterine spiral can be accompanied by the appearance of a focus of local noninfectious inflammation in the endometrium, under adverse conditions, an infectious process may develop on its background. Also, infection in the uterine cavity can rise from the vagina to the threads of the uterine spiral.
- Infectious and inflammatory lesions of the cervix: cervicitis and endocervicitis.
- Long-term inflammatory processes in the vagina significantly change the composition of normal microflora and deplete the mechanisms of immune protection of the mucous from infection. Excessively multiplying conditional-pathogenic microflora with time can become a source of inflammation in the cervical canal, and then rise into the fallopian tubes.
Factors predisposing to the development of tubal infection are: neglect of the rules of intimate hygiene, stress and overfatigue, dysbiotic disorders in the vagina.
Endocrine and hormonal diseases aggravate the course of salpingitis. Diabetes mellitus and thyroid diseases reduce the body's ability to resist infection.
The formation of hydrosalpinks is also facilitated by physiological defense mechanisms. When an inflammation occurs in the fallopian tube, the body tries to isolate it from surrounding tissues to prevent further infection of the pelvic cavity or uterus in case of a downward infection. Therefore, the ampullar section of the pipe is rapidly "closed", followed by the formation of a hydrosalpinx.
The episode of acute infectious inflammation in the fallopian tube does not always end with the formation of hydrosalpinx. With good immunity and timely treatment, adverse effects do not develop.
Symptoms and signs of hydrosalpinx
Regardless of the type of infection and the mechanism of its penetration into the fallopian tube, all types of infection affect its ampullar department.
If the infection gets into the fallopian tubes, the local inflammatory process begins to develop. The wall of the tube thickens due to pronounced edema, deforming its cavity. Inflammation causes the glands of the uterine tube to work hard, a lot of inflammatory fluid( exudate) is formed. As the exudate accumulates and the volume of the tube increases, the pressure on the superficial ciliate epithelium also increases, as a result, it becomes damaged and becomes unviable, and the quantitative ratio of ciliated and secretory cells shifts toward an increase in the latter. As a result, the ciliated epithelium atrophic at the site of inflammation development. As the symptoms of local inflammation increase, the exudate develops more and more, becomes thicker and more sticky. In places where the ciliated epithelium dies, the walls of the tube coalesce to form scars-adhesions. The spaces between the spikes are similar to the cells in which the inflammatory fluid accumulates. As a result of the sharply pronounced adhesion process, gross anatomical changes occur in the tube: the tube "seals" and turns into a saccular inflammatory pseudo-tumor formation - hydrosalpinx.
With a simple hydrosalpinx, the pipe looks like a closed expanded cavity filled with liquid contents. If the lumen of the tube is divided by adhesive septa into separate cavities, the hydrosalpinx is called follicular.
The external manifestations of both varieties of hydrosalpinx are the same: the pipe is similar to the retort due to the existing thickening site, its wall looks so thin due to overgrowth that through it you can see a clear, clear and clean liquid. Often the diagnosed bilateral hydrosalpinx does not always have a symmetrical structure, that is, the hydrosalpinx on the right may be simple, and the hydrosalpinx on the left may have a follicular structure, and vice versa.
Sometimes the contents of the hydrosalpinx pour out of the pipe. If the inflammatory fluid breaks through the abdominal opening of the tube into the pelvic cavity, it provokes a reciprocal inflammatory response. In case of evacuation of exudate into the uterus through the uterine opening of the tube, the patient develops abundant watery discharge and unilateral pains of a cramping character. This phenomenon is called a vented hydrosalpinx.
Inflammation in the fallopian tubes does not occur in all patients identically. When an infection enters the tubes, inflammatory exudate accumulates not always. In many patients with acute salpingitis, a small amount of inflammatory fluid is simply absorbed, and only in a small part of the patients inflammation spreads throughout the tube, followed by the formation of hydrosalpinx.
The clinical picture of hydrosalpinx is determined by a disease that provoked it. Most often, hydrosalpinx is formed after acute salpingitis, when the disease passes into a chronic form, and is accompanied by symptoms of chronic inflammation: unintentional abdominal( more often on the side of the lesion) disorders of the menstrual cycle, pathological discharge, and infertility.
If the hydrosalpinx is accompanied by an adhesive process in the surrounding tissues, the patients experience severe pelvic pain without clear localization. The clinic of the disease is sometimes similar to a surgical pathology, so the hydrosalpinx on the right can be confused with appendicitis, and the hydrosalpinx on the left has features of left-sided renal or intestinal colic.
In most cases, hydrosalpinks are diagnosed when examining patients with infertility. If the patient has one healthy tube, pregnancy is possible, then the available hydrosalpinx during pregnancy indicates the presence of infection and requires observation, and can be eliminated after childbirth. In the case of exacerbation of chronic salpingitis, hydrosalpinx during pregnancy has symptoms similar to those of non-pregnant ones.
The leading place in the diagnosis of hydrosalpinx belongs to instrumental methods of examination. In ultrasound, hydrosalpinx is defined as a thin-walled formation of an irregular shape filled with hypoechoic or anechogenous contents. From the cyst it is distinguished by the presence of its own thick capsule. In the cavity of the hydrosalpinx, septa can be detected, and the tube itself, with a pronounced inflammatory process, looks thickened and deformed. However, ultrasound can not always reliably determine the nature of pathological changes in the fallopian tubes, especially if the dimensions of the hydosalpinx are small and its contents are poorly visualized.
A more informative method for diagnosing anatomical abnormalities in uterine tubes is salpingography, in which a contrast fluid is injected into the uterus and fallopian tubes, followed by an X-ray examination. Contrast fills the cavity of the fallopian tubes and reveals all the defects inside. Through this survey, you can determine how much the fallopian tube is passable, and assess the patient's chances of pregnancy. Typically, if the contrast input appears in the pelvic cavity, it means that it was able to pass through the tube, that is - the uterine tube is passable. In the case of blockage of the tube, the contrast accumulates in the ampullar department.
Unlike all other diagnostic methods for hydrosalpinx, only diagnostic laparoscopy can provide absolute confidence in the diagnosis. In the event that removal of the hydrosalpinx and restoration of the patency of the fallopian tubes is required, laparoscopy becomes a therapeutic and diagnostic procedure.
Hydrosalpine treatment
Treatment of hydrosalpinx without surgery is almost impossible. The treatment program includes two stages.
At the first stage it is necessary:
- to establish the source of infection and to determine the appropriate antibacterial drug for its elimination.
- determine the nature of structural disorders in the affected tube( one or both);
- to find out how far the inflammatory process has spread, whether there are signs of inflammation in the ovaries or in the pelvic cavity;
- to identify concomitant infectious-inflammatory changes in the vagina, uterus and cervical canal;
- diagnose the existing dyshormonal disorders.
The complex of therapeutic measures at the first stage of hydrosalpinx therapy includes antibacterial, anti-inflammatory therapy and physiotherapy. Most often, the first stage of treatment is preparatory, and after it an operation is performed to remove the hydrosalpinx by the laparoscopic method.
Sometimes patients try to treat hydrosalpinx without surgery on their own using randomly chosen antibacterial agents or using traditional medicine recipes. This practice does not bring proper benefit or leads to an imaginary recovery, when the symptoms go away, and the chronic process continues to progress and can lead to the rupture of the fallopian tube.
The next stage of treatment involves not only removing the actual hydrosalpinx, but also restoring the patency of the uterine tube. Laparoscopy successfully copes with both tasks.
Laparoscopic removal of hydrosalpinx is the most effective method of infertility treatment, and it is also the most reliable diagnostic method that allows a doctor to see the occurring changes in their natural form. Before the beginning of the operation, carefully examine the area of the tube, assess the degree of inflammation and the level of damage. Proceeding from what he saw, the doctor determines further surgical tactics.
As a rule, the essence of the operation is to remove the hydrosalpinx, cut the adhesions and restore the lumen of the fallopian tubes. If the pipe is not recoverable, it must be removed.
Unfortunately, the successful restoration of the patency of the tubes of the uterus does not guarantee that the tube will function properly. Expressed inflammatory changes in the mucous membrane of the fallopian tube sometimes lead to complete death of the ciliated epithelium, and the egg can not move into the uterus. This kind of infertility is unpromising in terms of treatment, and the only way out for the patient is the method of in vitro fertilization( IVF).