Bubble skidding
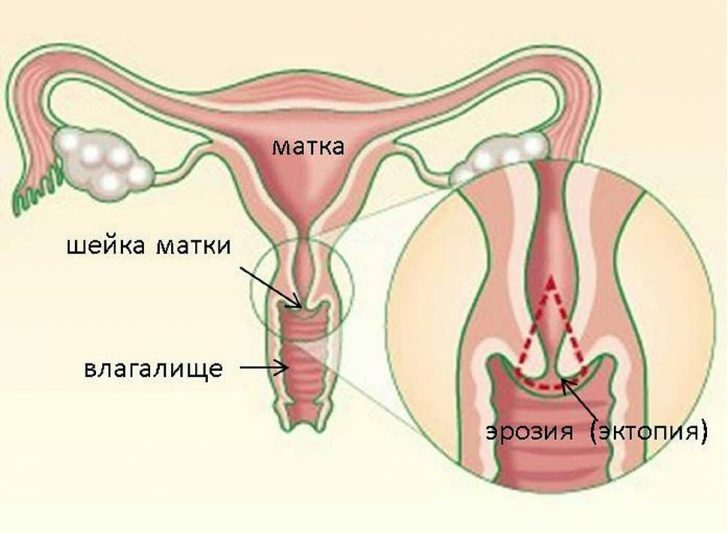
The bladder is a rare pregnancy pathology associated with an inferior ovum fertilization function that is incompatible with the development of pregnancy and the birth of a live fetus.
The result of a pathological process with a bubble drift is the formation in the uterus instead of a normal placenta of an unusual tissue, consisting of clusters of bubbles filled with liquid. The source of this transformation is the villus of the chorion. If the pathological growth fills the entire uterine cavity, the cystic caviar is classified as complete( classical).Partial bladder drift is localized only in a certain area of the fetal membrane.
Sometimes there is another name for a bubble drift - chorionadenoma.
There are reliable data on the possible malignant transformation of any form of bladder skidding. Malignant, and most severe, form of the disease is called destructive bladder drift.
To understand the pathogenesis of pathology, it is necessary to recall the events following fertilization. Recall that two sex cells - the ovum and the sperm - merge into one. At the same time, each of the "parent" cells assigns the future embryo with chromosomes - female( X) and male( Y) chromosomes, 23 chromosomes each. Of the 46 chromosomes belonging to the parents, a fertilized egg inherits only 23, and the "male / female" ratio determines the gender of the fetus.
A few hours after fertilization, the egg begins to divide, turning into a multicellular structure that gradually progresses toward the uterine cavity on the fallopian tube. After five days, the beginning of a new life reaches the uterus and is implanted( implanted) into its mucous layer.
As the embryo has to constantly develop and increase, its outer shell must be firmly fixed at the implantation site. For this purpose, the external embryonic membrane( chorion) at the place of attachment of the embryo to the uterine wall( the future placental platform) forms peculiar outgrowths - branched villi, which, like the roots of a tree, plunge deeply into the mucous membrane and connect to the bloody uterine vessels, Formation of the placenta. The remaining cells of the outer shell of the embryo are transformed into an umbilical cord and fetal membranes.
With a bubble drift, the naps surrounding the fertilized egg do not form the placenta, but degenerate into a completely unviable structure - an unusual, bubble-like tissue. The strom around the villi swells, they grow with the formation of bubble-like extensions( cysts).Connecting, these extensions become like grape clusters. Each cyst is filled with an iridescent yellowish liquid that secretes the hCG chorionic gonadotropin( pregnancy hormone), therefore, the hCG numbers with a bubble drift are of significant diagnostic significance.
The embryo, which requires oxygen and nutrition for development, gets a necessary placenta from normal pregnancy, and there is simply no such source in the case of a bubble drift, so inevitable degradation and death of the germ cells takes place.
The degenerated tissue is not limited to the place of its primary formation, it begins to expand, and the area of damage increases. This behavior of the tissues of the bladder drift makes it possible to compare it with the tumor.
Causes of bladder skidding remain unclear, but reliable studies have established a relationship between the development of pathology and the process of fertilization, when during the confluence of the sex cells there is a loss of maternal cells and a doubling of the male chromosomes.
Clinical symptoms of bladder skidding are ambiguous and depend on the behavior of the expanding chorion and gestational age. Often there are uterine pains, bloody leucorrhoea and a mismatch between the size of the pregnant uterus and the established term. The motor activity( stirring) of the fetus, of course, is not observed.
The presence of a bubble drift is well visualized during ultrasound scanning, since the modified tissue has characteristic features. The signs of embryo presence in the uterine cavity are not detected during scanning. The final diagnosis is carried out after evacuation of the bladder drift and examination of the tissues obtained in the histological laboratory.
Unfortunately, in the treatment of bladder drift, pregnancy is not envisaged, as the fetal's inability to live in complete isolation from the elements necessary for development is beyond doubt.
The removal of bladder skidding is the only method of therapy. Unpredictable behavior of the growing unusual tissue requires its complete elimination, therefore only surgical techniques are used. The uniqueness of this disease lies in the fact that with its aggressiveness, the process can be completely eliminated if it is correctly and timely to detect, without any consequences.
Pregnancy after bladder drift is possible, but it is necessary to be examined beforehand in order to prevent the repetition of a sad scenario. A clear pattern of recurrences of bladder skidding is not established, so the subsequent pregnancy can proceed and be completed properly.
The occurrence of bladder skidding is very small( less than 1%), but sometimes it appears in the conclusions of specialists in ultrasound diagnostics, which is very frightening for patients. Meanwhile, no conclusion of a functionalist is a diagnosis, because for correct diagnosis it is necessary to conduct several activities that unequivocally point to a certain pathology. Sometimes a bladder drift( especially partial) simulates other, less dangerous, pathologies that look very similar on the monitor, and the specialist writes a supposed, and not definitive, diagnosis of bladder drift, which, fortunately, is often not confirmed.
What is a bubble drift
Bubble skip is the result of chromosomal abnormalities. It is included in a special group of pathologies, united by the term "trophoblastic disease," which includes several states associated with anomalies of the trophoblast( the outer envelope of the embryo).
Trophoblastic diseases are always either tumors, or close to them in structure and behavior of a condition, which in the end in most cases provoke a tumor process. They are unique and very rare, because they have a unique way of development - they appear from the products of conception, that is, they are diagnosed only in pregnant women.
As a result of physiological fertilization, the egg has 46 chromosomes - 23 females and 23 males. A bladder skid can develop in full when the fertilized egg is completely devoid of maternal, female, genes, and instead of them there are duplicated father's genes, the male in the amount of 46. Also, it can become fertilized by two sperm cells deprived of the nucleus of the egg. Since the chromosomes of any cell are in its nucleus, a denuclearized egg does not contain them, and a doubled set of male chromosomes is provided by two spermatozoa.
Full bladder skidding does not involve the development of an embryo, only a significant increase in villi occurs.
Partial bladder drift is formed in a different way: the egg has the necessary core with female chromosomes( there are 23 of them), but there is a doubled set of male chromosomes( 46) in the fertilizing spermatozoon. As a result, 96( 46 + 23) chromosomes are present in the ovum, and the fetus, nevertheless, begins to develop, but has multiple malformations due to the large number of additional chromosomes, so it is also not viable.
Bladder drift tissues behave like a malignant tumor - they not only grow significantly, sprout through the uterine wall, but also can "spread"( metastasize) from the uterine cavity to the lungs. The degenerated trophoblast secrete the chorionic gonadotropin, and as the tissue excessively builds up the volume, the concentration of the hormone becomes excessive.
There are hypotheses about the effect of infectious processes on the degeneration of villus chorion, especially dangerous in this regard are called toxoplasmosis and viral infections.
It is impossible to reject the arguments of another popular theory of the origin of bladder drift, which links incorrect fertilization with hormonal dysfunction. As you know, for a full development of the ovum requires a sufficient number of estrogens, they provide the processes of folliculogenesis and subsequent ovulation. In the conditions of estrogen deficiency, according to some experts, the egg can grow inferior.
In re-pregnant women, as well as women who have undergone abortion, the chance of developing a cumulative drift increases threefold.
Symptoms and signs of bladder skidding
Bubble skid is classified as complete and partial. A more rare invasive( destructive) form is singled out separately.
The main criterion is the degree of degeneration of chorionic villi: if the area of their pathological transformation covers the whole chorion, the drift is considered complete, and if the chorion does not completely change, partial. Regardless of the form of the gall bladder, the fetus perishes, and the pathological process continues. Modified structures of the chorion proliferate fairly quickly, so the uterus also becomes larger. It is the inconsistency of its size to the expected duration of gestation that suggests the unfavorable development of pregnancy.
The timing of the formation of a bubble drift is very variable: early bladder skidding can be detected already on the 9th week of pregnancy, and sometimes it is detected only by the 34th week.
The clinic of bladder drift is more pronounced, the larger its area, therefore, in different forms, although it has similar symptoms, it differs somewhat.
1. Partial cirrhosis - early symptoms.
Partial bladder drifts, as it was said, do not affect the entire chorion. In the chromosome set, with this form, there are both male( Y) and female( X) chromosomes, but their number and ratio do not correspond to the norm: a single female chromosome has twice the number of male chromosomes. In the hypertrophied tissue of the expanding chorion contains fragments of the unmodified embryo and placenta, the villus of the chorion in the state of pronounced edema.
At the initial stages, the bladder skeleton mimics the symptoms of pregnancy, so it is difficult to diagnose it without additional examination.
Since the bladder drift does not cover the entire uterine cavity, the growth of the modified tissue occurs more slowly, the uterus retains the normal size for the gestation period or is slightly less than them. Therefore, at the beginning of the development of pathology, its symptoms may not be obvious, but suspicious changes can be detected during ultrasound scanning.
Incomplete bladder skidding does not exclude the development of pregnancy, as the pathological process starts after the third month of gestation and affects only part of the placenta. The fetus can die if the placenta is hit by more than a third.
2. Full bladder skidding - symptoms in the early stages.
Diagnosed on the 11th - 25th week of gestation. All available chromosomes are exclusively male. Signs of development of the embryo and embryo are absent completely, the uterus is filled with modified edematous naps and vesicles. Bubble skidding with this form grows quickly, so the uterus is already very early in the early stages.
3. Destructive form of a bubble drift. It occurs even rarer than its other two forms. It is characterized by aggressive germination of the villi to the full depth of the uterine wall with subsequent destruction of the surrounding tissues of the myometrium. It differs by severe internal bleeding.
Invasive bladder drift, in fact, is similar to the tumor process. Features of invasive bladder skidding are:
- a tumor usually local, with invasive( inward) growth;
- infrequently( 20-40%) metastasizes to the nearby vagina and vulva, less often metastases are "sent" to the lungs;
- much more often than other forms of drift is transformed into a malignant structure - chorion carcinoma;
- despite the aggressive course and the likelihood of malignant degeneration, responds very well to therapy and is cured 100%.
The sizes of the uterus that do not coincide with the period, with a bubble drift do not allow you to suspect this particular pathology without additional symptoms. It is especially difficult to determine, on this basis, the early bubble drift in partial form. The presence of chorionadenomas is indicated by several other symptoms:
- Bleeding. Has a specific feature - the presence in the bloody detachable typical bubbles of drift.
When the degenerated villus of the chorion grows, the excess tissue with the bubbles gradually separates from the uterine wall and "falls" into the uterine cavity, and from there it is evacuated outward along with the blood.
The blood loss provokes typical signs of anemia and worsens the state of health of the pregnant woman.
- Toxicosis. Depending on the term, they have a clinic of early toxicosis( nausea, vomiting, weakness and so on) or gestosis( preeclampsia and eclampsia).
- Absence of signs indicating the presence of the fetus. The fetus on the background of a bubble drift( if at all starts to form) dies very early, so all the studies conducted indicate its absence. Pregnant women note that they do not feel how the fetus moves.
Diagnosis of bladder skidding
The clinic for bladder skidding is not always obvious and can simulate other pathologies. Symptoms of bladder skipping, namely, asymmetric time of uterine enlargement, must be differentiated with those in multiple pregnancy, polyhydramnios and pregnancy against a background of fibroids. The bleeding that appears can indicate a spontaneous miscarriage.
The most reliable sign is the appearance in the vaginal discharge of typical vesicles, as a rule their appearance heralds the "expulsion" of the bladder drift.
Exterior examination does not allow to grope parts of the fruit and listen to his heart. Vaginal examination helps to palpate softening areas of the uterus, and also to establish that its size does not match the gestational age.
Ultrasound scan demonstrates a fairly typical picture for a bubble drift:
- uterine enlargement, not comparable with the gestation period;
- absence of the fetal egg on the early and fetus in later periods, with partial skidding, the stored parts of the fetus can be visualized;
- the presence of a homogeneous tissue of a fine-grained species( a symptom of a "snow storm") filling the uterine cavity;
- in every second pregnant woman and in the background of hormonal dysfunction, luteal cysts are recorded in the ovaries of large( more than 8 cm) sizes with a bubble drift, and in both ovaries symmetrically.
With the increase in the period of pregnancy, the ultrasound-picture of a bubble drift becomes more and more obvious.
Since bladder skipping provokes excessive accumulation of a pregnancy hormone, a laboratory determination of its concentration is of great diagnostic value. Concentration of hCG in case of pancreatic skidding changes not as in usual pregnancy: it exceeds 100 000 mIU / ml and does not decrease after one week period.
The presence of hCG after a bubble drift, or rather, its concentration, is also an important indicator in diagnosis. As a rule, after adequate treatment, the amount of hCG after bladder drift starts to decrease and is normalized by the 8th week. If such dynamics are not observed, and the amount of the hormone remains high, there is a possibility of a dangerous complication - a malignant tumor of the trophoblast.
Bubble skip can provoke a number of complications:
- toxicosis in the form of indigestible vomiting;
- early development of hypertension and pre-eclampsia;
- hyperthyroidism of the thyroid gland( hyperthyroidism);
- rupture of formed ovarian cysts;
- Infection of the contents of the uterus and subsequent septic process;
- bleeding, especially when invasive;
- trophoblastic embolization: penetration of bubbles from the uterine cavity into the pulmonary( through the vessels) and development of the embolism clinic;
- pronounced violations of the processes of blood clotting, leading to DIC syndrome.
Treatment of bladder skidding
Any chosen tactic of treatment of bladder drift is based on the need to remove pathologically overgrown trophoblast. The specialist is faced with the task of choosing the most acceptable pathway for the elimination of pathology.
The first stage of the treatment of cramps is analogous to abortion by vacuum aspiration. The method is suitable even for large sizes( up to 20 weeks) of the uterus. After the contents of the uterine cavity are aspirated, an additional control curettage is performed to remove those small villi that are too tightly attached to the mucosa. To uterus after the procedure as soon as possible returned to its original state, use uterotonics - uterine contracting agents( oxytocin, pituitrin).
Mechanical removal of the bladder drift is both therapeutic and diagnostic manipulation, as the study of the obtained tissues helps to clarify the diagnosis and to investigate the laboratory cellular composition of the obtained material. The presence of modified chorionic villi in the material indicates the reliability of the diagnosis of bladder skidding.
The presence of a rare and sometimes "dangerous" in the panel consequences of the diagnosis is very frightening for patients, especially if they are trying to obtain additional information from sources that are not entirely reliable. In addition, each of them is experiencing stress from the thought of a failed pregnancy and the death of a child. Therefore, before the beginning of therapy, a detailed discussion is needed that:
- this pregnancy began to develop incorrectly, and it has no chance of becoming "normal";
- even the most unfavorable course of bladder drift does not exclude complete cure;
- the next pregnancy after a bladder drift can be absolutely normal, provided the correct rehabilitation.
Often, self-exorcism of the bladder drift is possible, when the uterus, on the background of the introduction of reducing agents, evacuates the pathological contents independently.
The quality of the performed manipulation of skidding is controlled by ultrasonic scanning, it is performed several times with a two-week interval to ensure that the uterus and the surrounding tissues are "cleaned".
Radiography of the lung is indicated to all survivors of the procedure for the removal of bladder drift to exclude the presence of metastases.
After removal of the bladder drift, it is also necessary to control the dynamics of hCG.Laboratory monitoring is carried out weekly for the next two months.
A patient is considered healthy if:
- HCG after a bubble drift after two months does not exceed 15 MIU / ml;
- ultrasound does not detect tumors or metastases;
- X-ray lungs are "clean";
- menstrual function restored.
If the level of chorionic gonadotropin remains high eight weeks after the removal of the drift, there is reason to suspect the presence of trophoblast cells( in the uterus or other organs) that continue to secrete the gonadotropin or a malignant tumor of trophoblast, so that additional diagnostic measures are taken: examination, ultrasoundDiagnosis and radiography of the lungs. In such a situation, further treatment with chemotherapy is needed, methotrexate and dactinomycin are used separately or in combination with leukovirine. Treatment continues until complete diagnostic well-being, the criterion of which is absence of pathological foci and restoration of normal hCG parameters. In order to prevent recurrence, chemotherapy in the course dose is taken by two more courses.
Chemotherapy treatment allows 100%( all) patients with trophoblast pathology to be cured, and in 90% of the menstrual function returns to normal and does not need additional correction.
In the case when the pancreatic skid is complicated by threatening bleeding, preeclampsia or other dangerous conditions, the treatment tactics change: first they compensate for the threatening state, and then eliminate the bubble drift.
Destructive bladder drift can not be eliminated by aspiration, it literally grows into the uterine wall and the vagina. The high probability of dangerous bleeding and rupture of the uterus is the basis for using a more radical surgical technique - removal of the uterus( hysterectomy) along with pathological tissues is carried out.
In case of successful cure of the bladder drift, the patient still has a specialist for at least a year, and then must undergo a second examination. The subsequent pregnancy, if necessary, should be planned together with the doctor. As a rule, pregnancy after a bubble drift is recommended after the final control examination, that is, after a year or more, provided good results. This recommendation is explained by the fact that if during the year after the treatment, when the woman is under observation and passes the control tests, pregnancy occurs, the level of the chorionic gonadotropin begins to grow, and it becomes impossible to understand what is the reason for its growth - the returned tumor or real pregnancy.
Cumulative prevention of
Like any pathology, bladder skidding leaves a negative effect. Sometimes a woman who has experienced an episode of bladder drifting has problems with subsequent conception, menstrual dysfunction or amenorrhea develops, the risk of pathological course of subsequent births increases. In children born in pregnancies after bladder drift, pathologies are recorded more often. Also, the risk of pathology in childbirth increases in those who give birth after a bubble drift.
It should be remembered that after healing in place of the centers of the bladder drift, wherever they are( the uterus, the vagina, the lungs), small scars remain - the areas of connective tissue. They persist for a long time even after full recovery, but eventually dissolve, so do not refer to complications.
And, finally, the most adverse consequence of a bubble drift is the formation of malignant degeneration( up to 20%).
Bubble skid refers to rare and still poorly studied pathologies. Its main feature is a clear connection with pregnancy, so we can say that the lack of pregnancy is the only reliable measure for the prevention of ailment. However, such a measure, for obvious reasons, can be recommended only to those women who do not plan a desired pregnancy.
However, the lack of effective preventive measures does not preclude the elimination of factors that, in the opinion of specialists, can increase the risk of developing a bubble drift. These can be conditionally classified into those that are necessary for women planning a pregnancy, and those that are suitable for pregnant women.
When planning a pregnancy, women should first examine their state of health and find out how ready they are for a complex and long period of pregnancy, as well as for childbirth. Since there is evidence of a higher risk of bladder skipping in infectious diseases and hormonal dysfunction in patients, it is necessary to eliminate the source of infection and restore normal menstrual rhythm.
If the pregnancy has already occurred and is accompanied by a bubble drift, the diagnosis should be made as early as possible. In addition to timely diagnosis helps the patient's attentive attitude towards pregnancy and the implementation of all the doctor's recommendations.