Doubling of the uterus
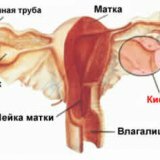
 Doubling of the uterus is a type of malformation of the uterus, in which partial or complete anatomical division of the uterine cavity occurs in two. At the origins of the formation of the doubled uterus there is always a violation of the normal development of the embryo. Intrauterine development of the fetus is a sequential process of laying and differentiation of cells and tissues, from which internal organs are gradually formed. The uterus of the fetus appears on the 10th to the 14th week of development, and at first it has two cavities separated by the septum, as it is formed by the fusion of two paramenezoneal( Müllerian) ducts. As these develop further, these channels merge together, and the septum is reduced. Similarly, a single vaginal cavity is formed.
Doubling of the uterus is a type of malformation of the uterus, in which partial or complete anatomical division of the uterine cavity occurs in two. At the origins of the formation of the doubled uterus there is always a violation of the normal development of the embryo. Intrauterine development of the fetus is a sequential process of laying and differentiation of cells and tissues, from which internal organs are gradually formed. The uterus of the fetus appears on the 10th to the 14th week of development, and at first it has two cavities separated by the septum, as it is formed by the fusion of two paramenezoneal( Müllerian) ducts. As these develop further, these channels merge together, and the septum is reduced. Similarly, a single vaginal cavity is formed.
Doubling of the uterus refers to a rather rare( 0.5 - 1%) pathology, as modern obstetrical service allows women to plan ahead in advance a normal pregnancy and prevent the appearance of a negative effect on the fetus.
Anomalies of the development of the uterus can arise when, during the period of formation of the genitals, the mother's organism is affected by negative factors. If the fusion of the two embryonic ducts occurs incorrectly, or does not occur at all, the uterine cavity remains divided.
Duplication of the uterus can be expressed unequally and depends on how it was formed. At the junction of the two mullerian ducts in the uterine cavity, there is sometimes a septum, dividing the uterus into two parts. If the two halves of the uterus developed completely isolated, a total doubling of the uterus and vagina eventually results.
Incomplete doubling of the uterus is characterized by the presence of a septum only in its upper part, and the lower third is a single enlarged cavity. There are situations when one half of the uterus and vagina with full doubling develops further, and the second stops forming and remains in an underdeveloped, embryonic state.
Clinically, doubling the uterus may not be apparent, especially if the doubling is incomplete. As a rule, all complaints of patients are reduced to reproductive dysfunction: infertility, miscarriage.
Anomalies in the structure of the uterus are diagnosed with the first gynecological examination, but their nature can only be established with an instrumental examination. Ultrasound scanning and hysterosalpingography very accurately determine the anomalies of the structure of the uterus.
An irregularly formed uterus does not always require surgical correction. Incomplete doubling of the uterus more often does not cause harm and does not interfere with pregnancy. It is necessary to speak about the need for treatment only in those situations when there is a pronounced clinical symptomatology( pain, menstrual dysfunction, infertility, miscarriage).Since doubling the uterus has many anatomical nuances, the method of eliminating the anatomical defect is chosen individually.
Reasons for doubling the uterus
It is well known that the anomalies of the formation of the uterus are associated with a distortion of the mechanisms of normal embryo development. Apparently, there are undesirable changes in environmental conditions( nutrition, gas exchange and the like) in which the fetus is formed, due to the negative impact of unfavorable factors on the pregnant woman's body.
Incorrect development of the embryo can provoke:
- pregnant infections, especially in the early stages, when the uterus develops in the embryo;
- malnutrition of the pregnant woman, when the fetus lacks the necessary nutrients for normal formation;
- the reception of teratogenic( that is, capable of harming the fetus) drugs;
- endocrine disorders( ovarian dysfunction, diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism of the thyroid gland);
- severe stress;
- severe toxicosis, manifesting as early as the beginning of pregnancy;
- intoxication( nicotine, occupational hazards, alcohol, drugs, radiation).
An essential role in the appearance of doubling of the uterus is played by a hereditary factor, therefore, pregnancy in women whose families have already experienced abnormal fetal development deserves special attention.
The close connection between the embryonic germs of the genital organs and the buds of the kidneys and the urinary tract explains the common common anomalies in the development of these systems, when the fetus simultaneously has a doubling of the uterus and doubling the kidney.
Symptoms and signs of uterine doubling
Doubling the uterus is a pathological division of it into two parts. This pathology has many anatomical variants that are classified into several groups:
1. Full duplication of the uterus, which we will discuss in more detail in the next chapter. There are two independent anatomical structures, that is, in fact - two uterus. Doubling of the uterus and vagina is considered an absolute doubling, when each of the halves has its own neck and its vagina.
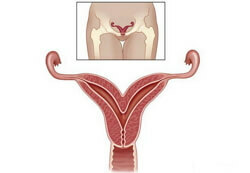
2. Incomplete doubling of the uterus. The uterus is partially divided by a septum in half, the formed halves resemble horns, therefore the term "bicorne uterus" is used. This anomaly is considered the most frequent( 62%) occurring. Both horns have one cervix and a single vaginal cavity. The degree of development of each half of the uterus can be unequal. In addition to symmetrical development, there are variants where among two there is one atresized( undeveloped) uterine horn or one closed but functioning horn.
The most common anatomical version is the saddle uterus, which is named because of its external similarity to the saddle. With this developmental anomaly, the septum in the uterine cavity is present only in the region of the uterine fundus, and in the rest the two-partedness is not expressed. In the bottom of the uterus, a saddle-shaped depression forms.
A doubled uterus with an open lumen is asymptomatic before the arrival of the first menstruation. Active complaints incomplete doubling of the uterus may not provoke. They appear only in case of violation of the outflow of menstrual blood. Most often, severe pains like a birth fights are provoked by a bicornic uterus with a functioning closed horn, when the accumulated blood can not be evacuated from the enclosed space, the additional horn accumulates and overstrains, that is, the hematometer is actually formed.
Contrary to popular belief among patients, infertility is not a frequent companion for doubling the uterus, since this defect is not associated with ovarian dysfunction and does not affect ovulation and fertilization. The fertilized egg can safely implant in one of the half of the uterus, but its further fate depends on the conditions under which the placenta and the fetus will be formed.
Diagnostic search for doubling the uterus includes gynecological examination, ultrasound scanning, metrosalpingography and hysteroscopy.
Palpation of the uterus more often provides information about the wrong form of the organ, but more detailed study of the pathology is possible only through instrumental diagnostic manipulation. Typical options for doubling the uterus are well visualized during ultrasound scanning. In parallel, the structure of the kidneys is studied to exclude the presence of a symmetrical pathology of development.
If doubling of the uterus is associated with the presence of severe clinical symptoms, and also requires surgical correction, a more detailed examination is needed: hysteroscopy and hysterosalpingography. They allow us to examine the inner surface of the uterus, determine the type of duplication, and also introduce a contrast agent and perform a series of X-rays to detail the information obtained.
Atypical forms of uterine duplication are rare, for their diagnosis it is preferable to perform MRI.
Complete doubling of the uterus
Full doubling of the uterus is considered if it is divided into two independently functioning departments( horns), each of them has its neck and is anatomically connected to only one located on the same side, the ovary. More often full duplication of the uterus is combined with the presence of a single vaginal cavity, but sometimes other anatomical variants are diagnosed: a vagina with a septum or a complete doubling of the vaginal cavity.
Symmetrically developed complete doubling of the uterus and vagina, which is sometimes referred to as absolute, rarely worries patients. More often the pathology is diagnosed accidentally with ultrasound scanning.
There is also an unequal development of doubled organs, when one half is fully developed, and the second is underdeveloped, or remains in its infancy( complete or partial aplasia).In situations where there is a partial aplasia of one of the vaginas, menstrual blood gradually accumulates in a confined space, and after 3-6 months after the start of the menstrual function provokes severe pain that can not be compensated for.
Sometimes a fistula-shaped aperture is formed in the septum between the two vaginal cavities, and the menstrual blood is partially thrown into the functioning vagina and evacuated in the usual way, and the remainder of the blood continues to accumulate in the closed cavity of the second vagina. In this situation, patients have signs of secondary infection - moderate pain and purulent leucorrhoea.
Complete doubling of the uterus and vagina is diagnosed during a primary examination, which reveals the presence of two vaginas and two necks of the uterus. In the course of further examination, two independent uterine cavities are defined.
Complete doubling of the uterus and absolute doubling do not interfere with the onset of pregnancy and allow bearing fetus. Pregnancy develops in one of the horns of the uterus and requires more detailed observation.
Treatment of doubling of the uterus
Uncomplicated typical forms of uterine doubling do not require treatment, since they do not affect menstrual function and do not interfere with conception or bearing.
If the abnormally developed uterus has negative clinical manifestations, the question of the possibility of surgical correction is being solved. The essence of any surgical technique is reduced to the formation of a single uterus. Reconstruction of the natural uterine cavity( metroplasty) can be performed through the abdominal cavity or laparoscopically. During the operation, the septum dividing the uterus into two is dissected. The dissection is made slowly along the midline using a special electrode( "electron knife") or a loop. When the surgical instrument reaches the bottom of the uterus, there is a slight bleeding, it indicates that the septum is completely dissected.
If as a result of the manipulations performed the uterine cavity becomes the only one, the operation is considered successful.
In order to avoid fusion( synechia) in the uterine cavity during the postoperative period, as well as to accelerate the processes of epithelialization of the wound surface in the first 2-3 cycles after the operation, it is recommended to take estrogens.
Sometimes the pathology can be eliminated with incomplete doubling of the uterus during diagnostic laparoscopy, when the instrument is inserted into the vagina, and then into the uterine cavity, where with it a thin and small septum is dissected.
An additional closed functioning uterine horn is always removed, but the fallopian tube and, accordingly, the ovary on its side are retained. Also requires mandatory surgical treatment for a full doubling of the uterus, when one of the vaginas is formed by the type of a closed bag( partial aplasia).In this situation, it is necessary to artificially form a single functioning vaginal cavity, therefore, the wall separating the vagina is dissected and a communication is formed between both vaginas. With the accumulation of blood in the closed cavities( neck, vagina), they are drained and then sanitized with antibiotics.
Doubling the uterus and anomalies in the development of the urinary system require joint treatment with urologists and nephrologists.
Regardless of the form of duplication of the uterus, pregnancy against this pathology has a higher risk in terms of complications, and therefore requires close attention. Independent births are rarely resolved, as it is not always possible to correctly predict their course and outcome.