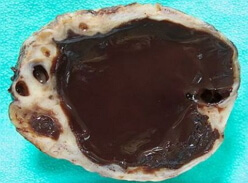
Piometer
 The pyrometer is a uterine cavity filled with purulent contents, formed as a result of a disturbed physiological process of purulent exudate evacuation. The accumulation of pus in the uterus occurs after infection of its contents. More often the pyometra is formed as a septic complication in patients on the background of postpartum or postabortion metroendometritis against a background of a sharp decrease in immunity indices. Less often, it occurs when infection with a disintegrating cancer of the uterus.
The pyrometer is a uterine cavity filled with purulent contents, formed as a result of a disturbed physiological process of purulent exudate evacuation. The accumulation of pus in the uterus occurs after infection of its contents. More often the pyometra is formed as a septic complication in patients on the background of postpartum or postabortion metroendometritis against a background of a sharp decrease in immunity indices. Less often, it occurs when infection with a disintegrating cancer of the uterus.
Pyometra is not always formed due to infectious inflammation. Sometimes, with the pathological occlusion of the cervical canal or a sharp decrease in the tone of the muscular wall from the uterine cavity, menstrual blood or bloody exudate can not be evacuated after abortion, diagnostic curettage or spontaneous premature birth( miscarriage).First, a large amount of blood accumulates in the uterus, which is unable to leave the uterine cavity, and a hematometer is formed. Then in the blood-filled uterus begins to develop an infection, it gradually turns its contents into purulent, and appears a pyometra.
In the first days after childbirth, a pyometra can also form, when the discharge( called lochia) accumulated in the uterine cavity due to atony of the uterus becomes infected and turns into pus. According to the name of postpartum secretions, the uterine cavity with pus is called a lychiometer.
The only reliable reason for the formation of pyometrics is the formation of an obstacle to free outflow of fluid from the uterus. This may be a blood clot, a polyp or myomatous node, a piece of the remaining placenta and so on.
Symptoms of pyometra sometimes correspond to the clinical signs of the infectious process and can be expressed in fever, pain, and poor health. Only 10% of patients with a pyometra have pus-shaped leucorrhoea with an unpleasant putrefactive odor, and they can also be bloody. As a rule, purulent or bloody-purulent leucorrhoea appear sporadically when the uterus manages to empty.
If a pyrometer emerged as a complicated metroendometritis, its symptoms may be "masked" by the clinical manifestations of an acute inflammatory process in the uterus.
In 50% of patients, the presence of piometers is not accompanied by a pronounced clinic, and it is difficult to establish a diagnosis without an appropriate survey.
Diagnostics of pyometers do not take much time. Sometimes( 17%) with palpation of the uterus can detect a tumor-like painful formation in the projection of the uterus. However, more often the diagnosis of pyometers is confirmed with a special probe or catheter, it is injected through the cervical canal into the uterine cavity, after which the contents accumulated in the uterus begin to be evacuated outside.
Laboratory diagnostics at a pyometra is designed to determine the presence of infection and its nature, and ultrasound scanning is necessary to clarify the condition of the pelvic organs.
In complex clinical situations it is possible to perform hysteroscopy, it allows to examine the uterine cavity and perform therapeutic manipulations.
Treatment of pyometers is only one - evacuation of pus from the uterine cavity. After emptying the uterus proceed to eliminate the infection. Antibiotics at a pyometra are appointed according to the bacteriological study data obtained by probing the uterus with leucorrhoea.
If there is an obstruction in the uterus or cervical canal for the outflow of uterine contents, the episode of pyometers may recur, and therefore all pathological formations( polyps, fetal or placenta remains etc.) are removed.
Reduced tone of the uterine wall is restored with drugs that enhance the contractile ability of the myometrium( uterotonics).
Pyometra is not an inoffensive condition. The prolonged presence of a large amount of pus in the uterine cavity threatens with severe septic complications and subsequent loss of the uterus.
Causes of pyrometers
Any obstacle to the normal outflow of the contents of the uterine cavity can be regarded as the reason for the formation of pyometers. It is assumed that initially there is an obstruction of the cervical canal, due to which the cervical and uterine secrets are not evacuated, but accumulate. Over time, secondary infection occurs and the subsequent transformation of the accumulated secret into purulent contents.
Cervical obstruction provoked by:
- Large cervical polyps, deforming the cavity of the cervical canal, create a mechanical obstruction in the way of serous secretion or menstrual blood draining from the uterine cavity. In this case, the uterus can periodically not completely empty, this explains the episodic purulent discharge after pyometras with putrefactive odor.
Cervical canal obstruction may be caused by small polyps with a long "leg", if they "descend" to the external throat and close it.
- Myoma of the uterus. If the myomatous node forms near the internal pharynx, as it grows, it is able to block partially or completely the cervical canal.
Also patchiness of the cervical can be threatened by "born" submucosal( submucous) myomatous nodes. Growing up, they tend to leave the uterus and along the way "clog up" it.
- Pathological narrowing of the cervical canal( stenosis).Cervical stenosis in young women is formed as a result of incorrect surgical manipulations, as well as after radiation therapy.
Aggressive instrumental intervention( abortion, diagnostic curettage, hysteroscopy and the like) can provoke the formation of coarse adhesions in the cervical canal zone, which deform and narrow the lumen of the canal.
A significant number of cases of diagnosis of pyometrics in elderly women is due to age-related stenosis of the cervical canal.
- Foreign bodies in the uterine cavity: a piece of placenta left after delivery;Part of the fetus not removed during the artificial termination of pregnancy;The intrauterine device that has shifted into the cervical canal.
However, the cases of development of pyometers without the involvement of the obstruction mechanism are not so rare, therefore among the reasons for its appearance are other physiological processes:
- Spastic state of the walls of the cervical canal. Leading among the causes of stenosis of the cervical canal after abortion.
- Decrease in contractility of the uterine wall( hypotension) or its complete absence( atony).Occurs in the background of prolonged or complicated delivery, and also after the birth of a large fetus."Tired" from excessive contractions, the uterus is not able to push out the accumulated blood after birth, which accumulates and becomes infected.
- Inflammatory processes in the endometrium. Often the result of incorrect therapy( or lack thereof) of endometriometritis is the pyometra. A large amount of inflammatory secretion literally "glues" the walls of the cervical canal, forming a cavity with pus.
Sometimes the reason for pyometers can not be reliably established. Probably, it was eliminated by the body itself, and the pyometra remained as a complication.
Symptoms and signs of pyrometers
Often the pyometra has no clinical signs. At half of patients it is diagnosed in the course of inspection in occasion of other pathology or casually.
Clinical manifestations of pyometrics are determined by the cause of its appearance.
Pyometra on the background of acute endometritis or metroendometritis is formed in the first few days after the artificial termination of pregnancy or childbirth. Violation of the outflow of blood from the uterus during this period can happen due to a violation of the contractility of the uterine wall, stenosis of the cervical canal, the accumulation of blood clots, or the presence of a piece of placental tissue. The accumulated blood in the uterus serves as a favorable environment for the propagation of pathogenic microorganisms, transforming the uterus into a pus filled with pus, a closed cavity. Most of the symptoms are associated with an acute infectious process: severe fever, intense pain, poor health, there may be puffy discharge with an unpleasant odor. The only reliable indication pointing to the piometer is the sudden decrease or complete cessation of discharge after abortion or childbirth, especially in the first three days.
Sometimes a pyometra is the result of a cluster of menstrual blood in the uterine cavity( hematomas) due to a mechanical or functional obstruction. Menstruation ceases or becomes very scarce and untimely, there are drawing pains. If the outflow of blood is not restored in a short time, local infectious inflammation develops, and the uterine cavity fills with pus.
To suspect the presence of pyometra it is possible after careful examination of the patient. When gynecological examination, if the painful formation of the testate consistency is palpable in the projection of the uterus against the background of an obvious obstruction of the cervical canal, diagnostic-medical sounding or catheterization of the uterine cavity is performed. When the probe neatly inserted into the cervical canal reaches the uterine cavity, its contents( blood and / or pus) flow outward. The resulting exudate is sent for examination to the laboratory to determine the nature of the infection and determine the most effective way to destroy it.
Isolations after piometers during probing can remain purulent until adequate antibiotic therapy begins, but after completion of treatment they should be correlated with the norm.
Ultrasound examination reveals the presence of fibroids, polyps or inflammation. Hysteroscopy provides the most accurate information about the uterine cavity and all processes occurring in it.
Treatment of pyrometers
The diagnosed pyometra is subject to mandatory treatment in a gynecological hospital. Initially, the uterus is freed from purulent contents and blood.
The further therapeutic tactics is influenced by the reason for the formation of pyometers. If it appeared against the background of delaying parts of the fetus after abortion or pieces of placental tissue after childbirth, scraping the uterus cavity is performed followed by washing the loosened cavity with solutions of antiseptics.
Antibiotic therapy is the leading method of therapy with pyometers. Antibiotics at a pyometra are selected according to the results of a bacteriological study, but they should be "connected" immediately after the patient enters the hospital, and waiting for a response from the baklaboratory takes time. Therefore, antibiotics( usually two kinds) are initially selected, capable of destroying as many pathogenic microorganisms as possible, and when the test results are ready, they either continue or are replaced.
Together with antibiotic therapy, drugs that relieve pain, restore the proper muscle tone, vitamins and immunostimulants are used.
Cervical polyps surgically removed, creating an obstacle to normal evacuation of uterine contents. It should be noted that any polyp of the cervical canal, even if it does not "interfere", in the future( in addition to other complications) can significantly increase and cork the cervical canal. Therefore, all cervical polyps are subject to removal.
A serious clinical situation is the combination of fibroids and pyometers. As a rule, more often the accumulation of pus in the uterus provokes a suppurated myomatous node or a myoma with a subserous arrangement. In young patients who did not reproduce the reproductive function, it is desirable to carry out sparing, preserving uterus, surgical manipulations, when only the myoma is removed. However, in the case of extensive purulent inflammation, when the tissues of the uterus literally melt, and save the organ is almost impossible.