Polycystic ovary
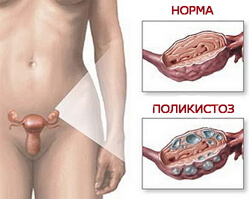 Polycystic ovary is a change in the anatomy and function of the ovaries on the background of impaired ovarian metabolism( steroidogenesis).Primary polycystic ovary is a genetically determined disease, is formed with the onset of ovarian function and manifests itself usually at pubertal age. Secondary polycystic ovary is not an independent disease and is presented as a set of symptoms, therefore it is called polycystic ovary syndrome( PCOS).Secondary polycystic is formed after a period of normal menstrual function.
Polycystic ovary is a change in the anatomy and function of the ovaries on the background of impaired ovarian metabolism( steroidogenesis).Primary polycystic ovary is a genetically determined disease, is formed with the onset of ovarian function and manifests itself usually at pubertal age. Secondary polycystic ovary is not an independent disease and is presented as a set of symptoms, therefore it is called polycystic ovary syndrome( PCOS).Secondary polycystic is formed after a period of normal menstrual function.
The use of the phrase "polycystic ovary syndrome" is not entirely correct, because the diagnosis of ovarian polycysticosis is made with primary anatomical and physiological changes, and polycystic ovary syndrome implies secondary disorders. The combination of polycystic ovarian syndrome seems to unite these states together and violates the meaning of the diagnosis formulation.
Ovary - a female female sexual gland. The consistency of the normal ovary is dense, the surface slightly bumpy, and in shape it resembles a peach bone. The ovary has a dense( white) shell and the underlying cortical layer. In the belly coat there are multiple follicles of different degree of maturity( primordial follicles).Together with the follicle, the egg also ripens. In the period of ovulation occurring at the middle of the cycle, the formed follicle bursts, the ovum leaves the ovary, and from the destroyed follicle is formed the so-called yellow body, capable of secreting the hormone progesterone. Two to three days before the onset of another menstruation, the function of the yellow body is completed. In the case of pregnancy, the yellow body begins to develop intensively and increase its hormonal activity, due to which it is called the "yellow body of pregnancy."After 3.5 - 4 months, the yellow body of pregnancy ceases to function and passes the baton to the formed placenta. After the first twenty weeks of pregnancy until the moment of its resolution, progesterone is produced by the placenta.
The size of the ovary depends on the age and phase of the menstrual cycle. The right ovary is usually larger and heavier than the left one. Ovaries of normal size during the examination usually can be palpated only in lean women.
Ovary belongs to three important functions:
1. Genital( generative) function of the ovary ensures the reproduction of eggs that are capable of fertilization.
2. Owing to hormones of the ovaries, genitalia develop and a female phenotype( "female" external appearance) is formed.
3. Hormonal function of the ovary along with a similar function of the endocrine glands is organically integrated into the general system of hormonal regulation, on which the condition of the entire female body depends.
A healthy ovary produces two "female" sex hormones - estrogen and progesterone. The entire process of steroidogenesis in the ovary is controlled by luteinizing( LH) and follicle-stimulating( FSH) hormones produced by the anterior pituitary gland.
Along with female sex hormones, the ovaries produce a small amount of androgens( male sex hormones).The decisive amount of androgen produces the adrenal cortex, and the androgen of the ovaries suffices only for the normal formation during pregnancy of the male fetus.
The basis for the development of polycystic ovaries is hormonal dysfunction followed by structural deformation of ovarian tissue and persistent infertility.
Causes of polycystic ovary
Girls with signs of primary polycystosis are born from mothers who have in the past infertility, miscarriage and other hormonal abnormalities. The hormonal "defect" is inherited from the mother and is transformed into polycystic ovaries in the daughter. Other causes of primary polycystosis are childhood infections, especially epidemic parotitis( "mumps").
Polycystic ovary syndrome occurs against a background of severe endocrine pathology, complications of normal pregnancy and / or childbirth, serious brain trauma, stress and intoxication.
In almost all( 40-70%) of women, polycystic ovary develops against the background of a decrease in the sensitivity of the body to insulin( insulin resistance), a pancreatic hormone that controls the level of sugar in the blood. As a result, a very large amount of insulin enters the bloodstream, and in male ovaries in excess quantities, male sex hormones( androgens) begin to be synthesized. Against the backdrop of hormonal dysfunction in the ovaries are disastrous changes.
Under the influence of excess androgens, the outer shell of the ovaries thickens. The ripened follicles present in it can not collapse to release the egg, instead they increase and fill with fluid, that is, they turn into cysts. Polycystic ovaries contain a large number of cysts, due to which they increase in size.
Increasing the level of androgens can trigger not only excessive insulin production. With normal body weight and physiological norm of the insulin content in the blood, a normal functioning of the hypothalamus-pituitary-ovary system may occur. In this case, the level of estrogen decreases, the production of growth hormone increases and the concentration of androgens increases.
Polycystic ovaries can cause endocrine diseases( diabetes mellitus, adrenal gland pathology), obesity, hereditary predisposition.
Thus, the basis of polycystic ovaries is always hormonal disorders.
Symptoms of polycystic ovary
The symptoms of polycysticosis are incredibly diverse, most of them are non-specific, as they can be present for any dyshormonal disorder. They can appear together with the first menstruation or a few years after the period of normal menstruation.
An adequate evaluation of all clinical, laboratory and instrumental data obtained helps to establish the correct diagnosis.
Diagnosis of polycystic ovaries starts with a general examination of the patient.
Often polycystic ovary companions as external signs of hyperandrogenism are:
- Hypertrichosis - increased growth of individual hair shafts in the chin, nipples, not thighs and neck. Always accompanies the primary lesion of the ovaries, indicates hyperandrogenism.
- Hirsutism - hair growth on forearms, legs and face. It is noted when the adrenal glands or "hormonal" tumors are affected.
- Virilism - male hair type, man's physique, low voice timbre. Accompany violations of the gonadotrophic function of the pituitary gland.
- Acne on the face.
Almost all patients with polycystic ovaries are overweight( most of the fat on their stomachs).Women with primary polycystosis are distinguished by their regular physique, developed mammary glands and hypertrichosis. In patients with secondary polycystosis, there is underdevelopment of the mammary glands, a narrow basin, hirsutism.
Menstruation with polycystic ovaries come on time( 12-13 years).The exception is polycystosis on the background of a violation of adrenal function. The nature of violations of menstrual function depends on the form and causes of polycystosis, is represented by meager( opsonomena) or rare( oligomenorrhea) menstruation, acyclic uterine bleeding or amenorrhea.
The most common reason for going to the doctor is primary or secondary infertility, since without proper( not always effective) treatment, ovulation with polycystic ovaries is almost impossible.
During gynecological examination, enlarged dense ovaries are defined.
Laboratory diagnosis of polycystic ovary includes a biochemical and general blood test, the determination of blood glucose and sensitivity to insulin, cholesterol, the study of the lipid profile of the blood.
An important diagnostic value is determining the level of hormones in the blood and their ratio. Hormonal examination is performed taking into account the phase of the cycle. An important criterion in the diagnosis of polycystic ovaries is an increase in the ratio of LH and FSH more than 2 - 2.5( at a rate of 1 - 1.5).It is not always the usual single study of the hormonal status of the patient enough for diagnosis, more often the study is conducted against the background of special hormonal samples( for example, a sample with Dexamethasone).
Ultrasound( ultrasound) is very informative about the diagnosis of polycystic ovary. Ultrasound - the criteria for polycystic ovary are:
- Symmetrical( bilateral) significant increase in the ovaries.
- The size of the ovaries should be such that their volume is greater than 9 cm³.
- Increase stromal density up to 25% of the volume.
- Thick capsule( a reliable sign of hyperandrogenia).
- Multiple, unevulated follicles( not less than 10) with a diameter of 8 to 10 mm are located at the periphery of the ovaries.
The diagnosis of polycystic ovary, delivered only on the basis of ultrasound signs, can not be reliable without corresponding clinical manifestations. This is especially true in the case of examination of women with regular ovulatory cycles and lack of characteristic symptoms. It is fair to talk about "ultrasound - signs of polycystosis", which implies the probability of the disease in the future. After conducting an additional survey for this category of women, it is advisable to establish surveillance.
Elevated levels of insulin in the blood of patients suggest a combination of polycystic ovary with type 2 diabetes. Systemic disorders in polycystic ovaries lead to early development of vascular pathologies, such as hypertension and atherosclerosis.
The most disturbing of all the consequences of polycystic ovary is endometrial hyperplasia( 19.5%), in 2.5% of cases it provokes the development of malignant disease( adenocarcinoma).In the presence of bleeding or persistent hyperestrogenism, diagnostic laparoscopy is sometimes performed.
Polycystic ovary and pregnancy
At a doctor's appointment, young women are interested in how to get pregnant with polycystic ovaries and how to maintain such a pregnancy. The answers to these questions can not be unambiguous and the only true ones.
In the vast majority of cases( 85%) infertility in polycystic ovary is primary and may be its only symptom. The number of spontaneous pregnancies in polycystic disease does not exceed 3 - 5%, and the probability of their successful outcome is negligible.
The result of hormonal dysfunction in polycystic ovaries is persistent anovulation and infertility. The exception is polycystic ovaries on the background of adrenal damage followed by the development of hyperandrogenism, when the onset of ovulation and pregnancy is possible. However, such situations are extremely rare and eventually result in premature termination of pregnancy.
Restoring the ability to conceive is one of the most difficult tasks of polycystic ovary therapy. It is performed only after elimination of the leading neuroendocrinal disorders and restoration of the normal menstrual cycle.
If the activities of the preparatory phase are successful, they begin to artificially stimulate ovulation. For this, the hormonal preparation Klomifen is used, it causes the egg to leave the ovary in time and prevents the formation of cysts. During the Clomifen administration, hormonal control tests and ultrasound monitoring are carried out.
If Clomifene does not give the desired result, the doctor may change the treatment regimen. Usually, a drug from the group of gonadotropic hormones containing LH and FSH is chosen.
Unfortunately, even the most competent infertility treatment in patients with polycystic ovary does not imply absolute success, and even restored ovulation in polycystic ovaries does not guarantee the onset of pregnancy. For example, after taking Clomifene in 60 out of 100 patients, ovulation returns, but pregnancy occurs in only 35 of them. Admission of gonadotropic hormones increases the chances of pregnancy up to 60%.
With unsuccessful infertility therapy for polycystic ovaries, surgical treatment is used.
If conservative and surgical treatment did not lead to the onset of a long-awaited pregnancy, and a woman is persistent in wanting to have a child, IVF( in vitro fertilization) is resorted to.
The risk of complications after infertility therapy is low, especially if the woman complies with all the necessary rules. These include ectopic pregnancy and early spontaneous miscarriages. The frequency of multiple pregnancy on the background of stimulation by hormones increases.
The course of pregnancy after the treatment of polycystic ovaries is associated with a risk of developing diabetes, pregnant women, toxicosis and premature birth. With a view to their prevention, special treatment is carried out at different periods of pregnancy.
Thus, the question of how to get pregnant with polycystic ovaries can only give one answer: be patient and follow the doctor's recommendations carefully.
Treatment of polycystic ovary
Polycystic ovary therapy is a complex multi-stage process of sequential restoration of physiological parameters of the whole organism. Polycystic ovary is not only a gynecological disease, so treatment should be directed to the elimination of those disorders that led to the development of ovarian pathology.
The scope of treatment is determined by taking into account the severity of the process and the desire of a woman to become pregnant.
At the first, preparatory, stage of treatment it is necessary to bring the weight of the patient to the physiological norm( in case of obesity).Dietotherapy contributes to the normalization of fat metabolism, and the necessary physical activity restores carbohydrate metabolism. An individual meal plan and a set of physical exercises are made for each patient, taking into account her physical data and the severity of the disease. It can not be said that this seemingly very uncomplicated stage of therapy can be managed without difficulties and disruptions. In the case of a positive effect, weight loss not only improves external data and overall well-being, but also contributes to a good psychological mood of patients for subsequent treatment.
The elimination of hormonal disorders is carried out at the second stage of the treatment of polycystic ovaries. At this stage, it is necessary to restore the normal menstrual cycle, eliminate hyperandrogenism( hirsutism, acne, and so on), lead to a physiological norm of carbohydrate and fat metabolism.
For the correction of the menstrual cycle in the treatment of infertility hormone preparations with a low content of estrogens are used, since anovulation with polycystic ovaries suggests hyperestrogenism. Modern combined oral contraceptives( COCs) are successfully used in the treatment of polycystic ovaries. Such drugs as Marvelon, Logest, Femoden, Zhanin and others, similar in composition, are prescribed by three-month courses with a subsequent monthly break. The treatment process is surely controlled by determining the level of hormones in the blood and ultrasound.
The third stage of conservative treatment of polycystic ovary is performed for women planning a pregnancy. The essence of the treatment is to stimulate ovulation.
Disorders of carbohydrate metabolism are successfully eliminated with the help of hypoglycemic drugs. A good effect is observed after the use of the drug Metformin. Usually, metformin in polycystic ovaries is prescribed for one to two weeks, after which the level of glucose in the blood of patients is reduced. It is established that metformin in polycystic ovaries slows down the absorption of glucose in the digestive tract, eliminates insulin resistance of tissues and inhibits the synthesis of glucose in the liver.
The elimination of the phenomena of hirsutism is carried out with the help of preparations of antiandrogenic action. Diane-35 is successfully coping with this task.
The use of antioxidants( Methionine, Accorbic acid and so on) and vitamins, physiotherapy and therapeutic massage is of additional importance.
It should be noted that the choice of treatment regimen, as well as drugs, depends on the purpose of therapy. If a woman complains of a menstrual disorder, hirsutism and other abnormalities, but does not plan a pregnancy, the treatment method chosen for her may differ from that in the case of a woman's desire to become pregnant.
No single regimen for the treatment of polycystic ovary is universal. All drugs are selected only for each patient. There are no guaranteed periods of recovery, nor is there a guarantee of the recovery itself.
Traditional medicine has no independent significance in the treatment of polycystic ovaries. However, some herbal preparations containing phytohormones can be used as an auxiliary therapy. These plants include the boron uterus, successfully used in the therapy of many gynecological diseases. The bovine uterus is used for polycystic ovaries and infertility in the form of alcohol tincture or water infusion. Some women claim that the boron uterus with polycystosis relieved them of the ailment. To confirm this statement or refute it is impossible, however, it can be assumed that in these women the diagnosis of polycystic ovary was made only on the basis of ultrasound - signs without other serious abnormalities. In this situation, phytotherapy could have a good preventive effect.
In case of unsuccessful conservative treatment of polycystic ovaries, the question of the possibility of surgical treatment, especially in women with infertility, is solved on an individual basis.
Operation with polycystic ovary
The indication for the surgical treatment of polycystic ovary is the lack of the effect of conservative therapy. The method of operation is determined depending on the disease pattern. In women with infertility, surgical treatment is an analogue of hormonal stimulation of ovulation.
All surgical procedures are performed with the participation of a laparoscope under general anesthesia. Most often, the following types of operations are used:
- Vaginal resection of the ovary is performed with a significant increase in the volume of the ovaries. The excessively overgrown tissue of the ovary( sometimes up to 2/3 of its volume) is removed, which is responsible for the excessive production of androgens. Against the background of the elimination of hyperandrogenia, the normal hormonal background is restored and ovulation occurs.
- Ovarian endothermocoagulation is used with a small increase in the size of the ovaries. The operation is not as traumatic as resection, and takes less time. The essence of the method lies in the point "cauterization" of ovarian tissue in order to eliminate the excessive production of androgens.
- Decortication of the ovary. It is performed to eliminate the altered( sclerotized and thickened) ovaries. It is removed with a scalpel, and the cystically altered follicles are pierced.
Sometimes, the choice of the method of surgery occurs during diagnostic laparoscopy, which allows for surgical treatment immediately after examination of the ovaries. Another advantage of laparoscopic surgeries is the ability to eliminate spikes and / or restore the patency of the fallopian tubes.
After surgical treatment, ovulation is usually restored within 6 to 12 months. The onset of ovulation is monitored by laboratory and hormonal tests( basal temperature measurement).If within two to three normal cycles ovulation does not occur, it is stimulated with the help of hormonal preparations. Absence of ovulation within a year after surgery is a bad sign, and further infertility treatment does not seem appropriate.
Unfortunately, it should be noted that in some cases, the recovery of ovulation is temporary, relapse of the disease usually occurs five years after the cure. In order to prevent recurrence of the disease, as well as to regulate the menstrual cycle, reduce hirsutism and prevent hyperplastic processes, COCs are monophasic or gestagens in the second phase of the cycle.
Diet for PCOS
The vast majority of patients with PCOS are overweight.
Adipose tissue has the ability to accumulate steroids, excess fat means excess steroids and dysfunction of the hypothalamus, which "manages" the menstrual cycle. Obesity leads to amenorrhea, infertility and many other serious consequences.
For successful treatment of hormonal disorders is necessary to eliminate the negative effect of adipose tissue on the body, so the treatment of polycystic ovaries start with correction of weight.
The program of dietary nutrition is made by a nutritionist. The recommended amount of food eaten depends on the degree of obesity, the growth of the patient, her profession, and also on the degree of physical activity.
There are many dietary options for obesity. All of them are based on the following basic principles:
- The body easily part with extra pounds if it lacks energy, that is, calories. If you reduce the calorie content of food and create an artificial energy deficit, the body will "burn" fat to replenish it. Limit caloric intake can be by eliminating from the diet of fatty foods, sugar and alcohol. Instead of rejecting any products, you can reduce their consumption, based on their calorie content. There are many options for low-calorie diets, which a nutritionist can recommend.
- To reduce weight recommended restriction of carbohydrate intake: potatoes, sugar, chocolate, bread, cereals, pasta. Sources of carbohydrates should be vegetables, legumes, dietary types of bread, low-sweet fruits and berries, buckwheat, oatmeal.
- The amount of protein in the diet of the patient should remain normal or elevated. Food should include meat, lean fish and cottage cheese, eggs and seafood.
- Meals should not be sparse. The optimal number of meals per day is 5-6 times. Between meals, raw vegetables and fruits are recommended for consumption. It is a mistake to believe that if there is little, then certainly you will lose weight. For weight loss, it is not the quantity of food eaten, but its quality that is important.
- The so-called unloading days with a limited list of permitted products are an integral part of therapeutic nutrition.
After the body weight returns to normal, the number and range of products used can be expanded. However, if the patient returns to the previous diet, overweight will return quickly. To permanently get rid of obesity, you need to consume foods in such quantities that the body weight remains in a stable physiological state.
Physical activities( fitness, gymnastics) are a good addition to a rational diet. In some patients, doing sports only two hours a week in conjunction with the diet produces a result similar to taking special tablets to reduce weight.
As in the case of dietary nutrition, intense exercise will help you get rid of excess pounds faster, but stopping physical exertion will return excess weight. It is enough to look at former athletes to make sure of this possibility. If a woman is not ready for constant physical exertion, it is better to choose the optimal mode of physical activity for oneself.
Tighter diets and increased physical activity help to quickly reduce weight, but can not hold it. This task can be successfully solved only by the right way of life, not imposed from the outside, but deliberately chosen by the woman herself.



