Pulmonary insufficiency, symptoms, treatment
By definition of pulmonary insufficiency is understood as the inability of the respiratory system to supply arterial blood with oxygen in sufficient quantity. In more detail, pulmonary insufficiency can be described as a pathological process in which the partial stress of CO2 is greater than 45 mm Hg. And oxygen pressure is less than 80 mm Hg. Art.
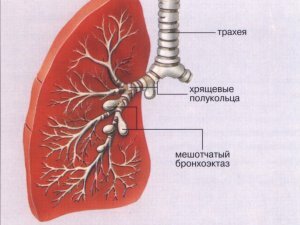
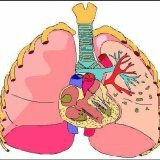
Pulmonary insufficiency usually develops when the work or function of respiratory organs and systems is disrupted. They are usually referred to as: thorax, upper respiratory tract, alveoli, lower respiratory tract, CNS( which regulates the coordination of the respiratory system), peripheral nervous system, pulmonary musculature. Pulmonary insufficiency can result in a wide variety of diseases, ranging from colds to acute bronchitis.
Classification of pulmonary insufficiency.
According to the mechanism of occurrence respiratory failure is divided into hypoxic, in which there is not enough oxygen in the tissues of the body;And hypercaptic - a large amount of carbon dioxide accumulates in the tissues.
The etiology of hypoxic pulmonary insufficiency is most often a violation of the functioning of the blood in our lungs. These disorders are observed in the case when the blood exchanges gases with alveoli, which do not exchange gases with the environment. With shunting, venous blood does not have time to be saturated with oxygen and, in such a composition, directly enters the arteries.
The etiology of hypoxemic pulmonary insufficiency lies in the presence of the following diseases:
- Pulmonary edema;
- Pneumoconiosis;
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome;
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, a frequent manifestation of which are emphysema and chronic bronchitis;
- Pulmonary alveolitis;
- Pneumonia;
- Pulmonary hypertension;
- Pulmonary fibrosis;
- Obesity;
- Pneumothorax;
- Bronchial asthma;
- Sarcoidosis;
- Embolism of the lungs;
- Kifoscoliosis;
- Broknoeectatic disease.
Pulmonary insufficiency. Symptoms and signs.
It should be noted that in some of these diseases mixed forms of pulmonary insufficiency are observed. Hypoxia or hypercapnia, for example, can be observed with obstructive chronic lung disease. When hypoxia or hypercapnia is usually impaired pumping function of the lungs.
The manifestation of pulmonary insufficiency is considered to be complaints of shortness of breath or choking. Both the reduction of oxygen in the blood, and the accumulation of carbon dioxide can lead to disruption of the CNS.These disorders usually manifest themselves as general anger, memory impairment, insomnia, poor sleep, confusion, loss of space. Accumulation of CO2 causes pain in the head, and in some cases even a loss of consciousness or even a coma. If suddenly the number of breaths is less than 12 per minute, then it's worth thinking about a possible respiratory arrest. Sometimes there is paradoxical breathing, which consists in a multidirectional movement of the chest and abdominal wall. With lung diseases during auscultation, wheezing and wheezing are noted.
The rate of formation of pulmonary insufficiency is divided into acute and chronic. Acute pulmonary insufficiency develops several days. And chronic - can develop up to several years.
Diagnosis of the disease with pulmonary insufficiency.
Diagnosis in acute or chronic pulmonary insufficiency can be based on anamnesis of the disease and clinical manifestations of the disease. It should be noted that complaints and clinical symptoms are different with pulmonary insufficiency. They usually depend on the disease, which is the reason for the development of pulmonary insufficiency. Symptoms, treatment are determined by the attending physician, a course of therapy is prescribed by the method of diagnostic observation. A key principle of diagnosis of pulmonary insufficiency is the study of the gas composition of arterial blood.
Predictions for patients with pulmonary insufficiency.
Mortality depends on the cause of the onset of the disease. The development of acute pulmonary insufficiency accounts for about a third of all cases. With progressive diseases, the appearance of pulmonary insufficiency can become an unfavorable sign. Without appropriate drug therapy, the average life span with pulmonary insufficiency is about a year. If you use special methods to support breathing, then this period increases. Mortality from pulmonary insufficiency in other diseases varies widely, but is considered one of the main factors that generally reduce the life span in patients.
Pulmonary insufficiency. Treatment and therapy.
Treatment of pulmonary insufficiency consists in the combined treatment of both the disease itself and the disease that caused the onset.
Treatment of acute pulmonary disease consists in the appointment of oxygen therapy. If breathing remains weak for a long time, non-invasive ventilation is prescribed. If further improvements are not observed, then invasive artificial ventilation is used in hospitals, since it is simply impossible to carry out artificial ventilation at home. In this case, it is necessary to intensively treat the underlying disease, for example, pneumonia. Inflammation of the lungs is treated with antibiotics. Ventilation of the lungs should be carried out until self-breathing stabilizes.
Treatment of chronic pulmonary disease consists in treating the very cause of the disease. Also, oxygen therapy and non-invasive ventilation of the lungs, and in some severe cases it is advisable to resort to artificial ventilation. In the case of the formation of large amounts of sputum in the lungs and the airway, the use of broncho-pulmonary drainage is required.