Omission of the uterus
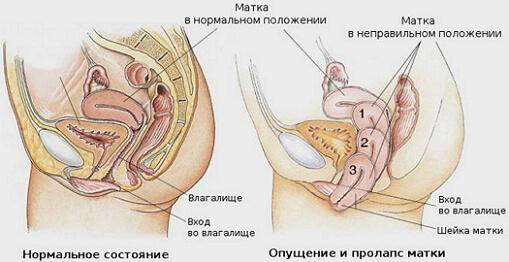 Omission of the uterus is the displacement of the uterus downward, followed by a "protrusion" into the vaginal cavity through the pelvic floor.
Omission of the uterus is the displacement of the uterus downward, followed by a "protrusion" into the vaginal cavity through the pelvic floor.
The exit of the female pelvis closes three powerful muscle layers forming the so-called "pelvic floor".The muscles forming this layer are arranged in the form of shingles, which provides the greatest strength to the entire muscular conglomerate. To increase the strength of muscle tissue, each muscle of the pelvic floor is strengthened by a fascia, which is a sheath of dense fibers of connective tissue.
The importance of the functions of the pelvic floor muscle can not be overestimated:
- The pelvic floor muscles provide a permanent arrangement of the internal genital organs, as well as the neighboring bladder and rectum.
- Physiological births take place with the active involvement of the pelvic floor muscles, which promote the fetus outward. After the end of labor, the pelvic floor returns to its original state.
- The pelvic floor is a support not only to the pelvic organs, but also to other internal organs. It is involved in the regulation of normal intra-abdominal pressure.
In its permanent place, the uterus also fixes its ligamentous apparatus - a round and broad ligament of the uterus.
Any processes associated with impaired muscle tone of the pelvic floor and weakening of the ligamentous apparatus of the uterus lead to a change in its normal location in the pelvic area.
There is a completely mistaken view that the omission of the uterus is present only in elderly women. Meanwhile, the statistics states that out of a hundred young women under the age of 30 each tenth has a different degree of ovulation, of a hundred women in 30-45 years, this pathology occurs in forty, and after 50 years it can be found already in half of a hundred. These facts suggest that age is not always the reason for the omission of the uterus, in some cases it contributes to the aggravation of the process that has arisen in the younger years.
Omission of the uterus is often hereditary and is found in close relatives of a female - mother, grandmother or sister.
Sometimes, along with the uterus, neighboring organs - the bladder, rectum or part of the intestine - drop.
Treatment of uterine prolapse depends on many factors and is selected for each patient individually. Prevention of the omission of the uterus at the initial stages of development of pathology is very effective. If you do not seek help in a timely manner, the process can progress up to the loss of the uterus.
Causes of omission of the uterus
With the weakening of the tone of the muscles and ligaments, which must keep the uterus in a certain constant position, it descends beyond the physiological boundaries. This is facilitated by the following reasons:
- Traumatic injuries of the pelvic floor muscles;
- Constitutional features( infantilism, asthenic constitution);
- Obstetric traumatic situations. During complicated births, very traumatic methods of delivery are sometimes used: imposition of obstetric forceps, manual extraction of the fetus with breech presentation, etc.;
- Postponed severe surgical operations on the genitals;
- Numerous births reduce the tone of the pelvic floor muscles;
- Deep ruptures of the perineum of any origin;
- Heavy physical labor associated with lifting weights;
- Increased intra-abdominal pressure caused by diseases of the abdominal cavity organs or chronic constipation;
- Congenital malformations in the pelvic area;
- Diseases of connective tissue, which is manifested by the presence of hernias or the descent of other internal organs;
- Violation of the production of sex steroids( mainly estrogens) affects the ability of muscle tissue to contract;
- The elderly. With age, muscle tissue loses its elasticity, atrophic changes occur. Estrogen deficiency in old age contributes to further weakening of the muscles and ligaments of the pelvic floor.
In the development of the process of ovulation of the uterus, not one of the provoking factors dominates, but their combination.
In any woman, slight omission of the uterus during pregnancy is not a pathology. Together with the growth and increase in the size of the fetus, the uterus also increases and can move somewhat downward. The exception is the omission of the uterus during pregnancy in women who have suffered from this ailment before. In this case, it is caused by other reasons, and pregnancy can aggravate it and break prematurely.
Thus, omission of the uterus is part of the general body disorders and should not be treated in isolation like a local process.
Symptoms of omission of the uterus
There are no typical symptoms of uterine omission. Each patient feels this condition individually. The process takes a long time, and small deviations in the state of health can not attract the attention of a woman. Much less often the omission of the uterus occurs quickly.
In most cases, women with abnormal genitals have abdominal pains, varying in intensity and duration, which can move to the waist and sacrum. Sometimes patients indicate the appearance of aching pain in the lower abdomen after a long stay on their feet. After changing the position of the body, the pain subsides. Often the omission of the uterus provokes pain during intimacy.
The shifting uterus presses on the surrounding tissues, which irritates the nerve endings of the vagina, causing a sensation of a foreign body.
Omission of the uterus may be accompanied by the appearance of leucorrhoea, bloody discharge and menstrual dysfunction( profuse and / or painful menstruation).
Sometimes women themselves in the conduct of hygiene procedures or after physical exertion detect an abnormal location of the genitals and consult a doctor in the absence of other symptoms.
Omission of the uterus provokes a change in the anatomically normal location of neighboring organs. Following the uterus, the bladder and / or rectum are shifted( in varying degrees), which leads to a change in their normal functioning - there are disorders of urination( dysuria, frequent urination) and defecation( constipation).Disorders of urination occur much more often than violations of the rectum. In severe cases, to a harmless inflammation in the urethra or bladder, a secondary pathogenic flora is added that can spread to the kidneys.
Long-existing displacement of the genital organs leads to the development of local inflammatory processes( colpitis, cervicitis, vaginitis and others).In the absence of proper treatment, inflammation ascending way extends to the pelvic area, and the genital descent clinic is supplemented with symptoms of endometritis, adnexitis, salpingoophoritis, etc.
The most reliable sign of the omission of the uterus is the result of a visual gynecological examination. During the examination, the woman is encouraged to strain( as during childbirth) to see how the position of the vaginal walls, cervix and uterus changes. The diagnosis of the omission of the uterus after examination in the mirrors does not cause difficulties.
The main diagnostic criterion for omission of the uterus is the localization of all anatomical changes within the vagina above the border of the genital gaps. If the pathological process goes beyond the sexual slit partially or completely, it is said about the prolapse of the genitals, which is evidence of the progress of the process of omission. However, the omission of the genitals does not always result in prolapse.
The downward shifting uterus causes changes in the position of the vaginal walls. In some patients, uterine prolapse is accompanied by the omission of the vagina, but such a scenario is not mandatory. The vagina is displaced unevenly. Distinguish only the anterior or only posterior wall of the vagina, and also the two walls together. During the examination in the mirrors, the uterus is visualized outside the entrance to the vagina, with the physical strain of the muscles( straining) it is not shown from the sexual slit.
The muscular skeleton of the small pelvis is organized in such a way that each individual organ participates in the maintenance of the other. The front wall of the vagina serves as a support for the bladder, when it moves down, it entrains it. The bladder descends and begins to bulge into the vaginal cavity, forming a cystocele. A similar process occurs with the participation of the back wall of the vagina and rectum, forming a rectocele.
Some patients get confused in terms and give incorrect names to this pathological process. The uterus is a hollow organ resembling a pear. It has a bottom, an anterior and a back wall. Omission of the uterus and omission of the walls of the uterus are different names of one process, but the omission of the walls of the uterus is not a competent term. Since the uterus descends together with its walls, talk about the omission of the anterior wall of the uterus and / or the lower back of the uterus is wrong - the uterus can not move down, leaving one of its walls in place. Therefore, the omission of the anterior wall of the uterus is impossible from the physiological and anatomical point of view, but there is an omission of the anterior wall of the vagina. Likewise, the omission of the posterior wall of the uterus does not exist as a medical term and implies the omission of the posterior wall of the vagina.
The process of ovulation of the uterus accompanies the descent of the cervix and / or its elongation( elongation).When gynecological examination, the descent of the cervix is well visualized.
Colposcopy, examination of swabs and sowings from the vagina is mandatory for all patients with omission of the genitals. With the displacement or prolapse of the uterus, hypertrophy( increase in volume) of the cervix, pseudo-erosion, endocervicitis, cervical canal polyps is often observed.
Ultrasonic examination specifies the location of the uterus and pelvic organs, diagnoses inflammatory processes.
The combination of pregnancy and ovulation of the uterus is not always harmless. If before the onset of pregnancy the expectant mother knew about her diagnosis and underwent appropriate examinations and treatment, pregnancy can proceed without serious complications. The course of pregnancy depends on the degree of omission of the genitals, the weight of the woman and the fetus and many other factors. The most common complication of pregnancy with the omission of the uterus is premature birth, so expectant mothers with this pathology are often placed in the hospital "for preservation".
A survey of women with genital depressions is carried out together with the urologist and proctologist as necessary, special examinations are conducted to establish a cystocele or a rectocele. Important in the diagnosis is the establishment of the presence of extragenital pathology in patients, as often the uterus descent occurs against the background of endocrine and metabolic pathologies.
If surgical treatment of genital descent is expected, the examination complex is expanded by additional diagnostic methods.
Degrees of ovulation of the uterus
When gynecological examination of patients with prolapse of the genitals, the degree of uterine prolapse is determined, which plays the role of an important diagnostic criterion.
It is very important to differentiate the omission of the uterus and / or the walls of the vagina from their loss( complete or partial).As a visual diagnostic border, the genital cleft is adopted. If the uterus is displaced downwards and does not go beyond the border of the sexual fissure, they speak of its omission, if this border is broken partially or completely - this is the prolapse of the uterus. Similarly regulate the process of displacement of the vagina and cervix. The degree of ovulation of the uterus clearly characterizes the process of moving the uterus to the genital gaps and is determined visually during a general gynecological examination.
The first degree of descent of the walls of the vagina and uterus can be observed at the very beginning of the process of their displacement. When examined, the uterus is displaced downwards, but the cervix remains within the vagina.
The second degree of omission is diagnosed if the cervix is located on the threshold of the vagina or below it, and the uterus body is visualized into the vagina.
Further development of the bias process leads to the fact that the uterus and a significant part of the vagina are located outside the genital cleft - the third degree.
Correctly establishing the degree of uterine omission is extremely important for determining further tactics of examination and therapy.
Treatment of ovulation of the uterus
It is not easy to choose the right treatment strategy for ovulation. It is necessary to consider:
- Age of the patient. Restoring normal muscle tone is much easier if the muscle tissue does not undergo age-related changes. In addition, complicated surgical manipulations are not always shown to elderly patients.
- At what stage is the pathological process, that is, to determine its degree.
- Presence of concomitant gynecological diseases.
- Is there a need to restore menstrual function in case of its violation?
- Does the patient plan to become a mother in the future?
- Features of bladder function and / or rectum( if any).
- In some cases, when combined with the omission of the uterus with extragenital pathology, the choice of the method of therapy is carried out jointly with physicians of other specialties.
If the displacement of the uterus is negligible and does not cause the woman any inconvenience, no specific treatment is required, and one can limit oneself to methods of preventing further progression of uterine displacement.
If the uterus is within the vagina, and the functioning of adjacent organs is not disrupted, you can begin therapy with conservative methods. Before the beginning of treatment it is necessary to lead to the physiological and age norm of the patient's lifestyle. Elimination of excessive physical exertion, balanced diet, weight loss and treatment of foci of chronic infection will have a beneficial effect on the body's ability to stop the progression of the disease.
Patients with hysterectomy are recommended enhanced hygiene measures in the intimate area, since the displacement of the genitals promotes the development of inflammatory and infectious processes in the vagina.
The goal of conservative methods of treating genital displacement is to strengthen the pelvic muscles and prevent further displacement. Treatment includes:
- Kegel exercises for the vaginal muscles. Increasing the tone of the muscles of the vagina prevents the worsening of the process of displacement of the uterus. Also appointed with a preventive purpose.
- Curative gymnastics with the lowering of the uterus according to the method of Yunusov.
- Lubrication of the vaginal mucosa with ointments with estrogens and metabolites to improve elasticity and weaken the processes of atrophy( used in menopause and postmenopause).
- Use of pessaries( uterine rings) in elderly women in the presence of contraindications to surgical treatment. Pessaries are rubber rings filled with air of various diameters. It is matched to the size individually. The pessary introduced into the vagina does not allow the uterus to move lower. The disadvantage of pessaries is the inability to introduce it for a long time. The high probability of development of bedsores and inflammation requires changing the uterine rings at least twice a month and doing regular syringing with herbs and antibacterial agents.
Rubber rings can be used in young women in a situation where they plan to give birth or have contraindications to surgical treatment.
- Special banadyazh at the lowering of the uterus for patients of any age. It is prescribed at the initial stages of the disease and is suitable for short-term use. Well-proven bandage when the uterus is lowered in pregnant patients.
- Gynecological massage restores blood circulation in the pelvic area, normalizes the intestinal function and eliminates inflammation and increases the tone of the vaginal muscles. Can be used as an independent method with minor changes in the position of the uterus or in the composition of complex therapy. Massage is performed only in a medical institution by a trained specialist.
If conservative therapy could not stop the process of displacement of the genitals, it is necessary to decide whether to perform surgical treatment. If the patient is diagnosed with a severe degree of ovulation or loss of the uterus, the operative treatment is started immediately.
The measures for preventing uterine prolapse are:
- Proper physical activity.
- Competent management of pregnancy and childbirth, as well as the restoration of normal muscle tone in the postpartum period.
- Therapeutic exercise for all women, predisposed to the omission of the uterus.
- Replacement hormone therapy( HRT) in menopause( only according to indications).
- Treatment of extragenital diseases, which are background for the displacement of the genitals.
The best prevention of the omission of the uterus is a timely visit to the doctor. Like any disease, the displacement of the uterus, found in the initial stages, is much easier to eliminate.
Surgery for ovulation of the uterus
Surgical treatment is an alternative for those already giving birth and elderly patients with uterine prolapse. It is also acceptable for those women who do not want or can not use other methods of treatment, have severe and / or complicated forms of prolapse of the genitals.
There is probably not a single gynecological pathology that has such a large number of methods of surgical treatment, like the omission( or prolapse) of the genitals. In the arsenal of modern surgery, there are several hundred ( !) treatment options for genital mutilation, each of which has its advantages and disadvantages. Unfortunately, none of the existing methods of surgical treatment does not exclude the omission of the uterus after the operation, regardless of the qualifications of the surgeons. Recurrences of the disease in 30-35% of operated patients appear, as a rule, in the first three years after the operation.
When choosing an operation method, many factors are considered:
- The degree of prolapse of the genitals. Severe forms( degrees) of the disease require more serious( radical) interventions.
- Age. In the elderly, hoping for conservative methods may not always be, the rejection of surgical treatment can be justified by the presence of serious contraindications or the initial degree of displacement of the genitals. The volume of surgical intervention in older women, as a rule, is expanding.
- Extragenital pathology. Before any surgical manipulation the patient should consult with doctors of adjacent specialties and get their consent for the operation.
- Combination of uterine dysfunction with concomitant cysto- and / or rectocele.
- The patient's opinion. In some cases, women refuse to do this or that type of surgery. Especially it concerns the removal of the uterus.
For all the variety of treatment methods, they can be divided into several groups according to the main feature - due to which anatomical formation( muscle, ligaments, etc.), the anomalous arrangement of the genitalia is eliminated.
The first group consists of operations aimed at strengthening the muscles of the pelvic floor. In some cases, they have an independent meaning, and sometimes are carried out as additional measures to other operations.
The second group of operations is performed to fix the uterus by shortening the uterine ligaments. For this, a round ligament of the uterus is used, it is shortened and ligated to the body of the uterus. Short ligaments do not allow the uterus to move downward and hold it in place.
Operations of the third group are more complex and more complex. To strengthen the fixation apparatus of the uterus, all available ligaments are used, which are sewn together. This group includes the most popular and effective "Manchester operation", characterized by high traumatism( deprives the patient of reproductive function).
Surgical methods of rigid fixation of the uterus to the bones of the pelvis belong to the fourth group of surgical treatment.
The fifth group of operations uses methods of plastic surgery. Their essence is to replace the ligaments and / or muscles with synthetic materials. This method was not widely used because of the large number of relapses of the disease and the presence of complications.
Operations to reduce the size of the vagina belong to the sixth group.
The seventh group of surgical interventions is formed by radical operations of uterine removal.
Combined surgical treatment using methods from different groups is considered to be the most appropriate.
All operations performed involve a risk of complications. The repeated omission of the uterus after the operation does not always indicate the shortcomings of the surgical technique used and may be due to the patient's poor health or the violation of her postoperative recommendations of the treating surgeon. The risk of developing other complications with a patient's strong health is low.
Successful operation does not exclude the presence of predisposition to the displacement of the uterus. Therefore, it is necessary to comply with all preventive measures and avoid visiting the doctor's office.
Exercises for omission of the uterus
Reducing the tone and elasticity of the pelvic floor muscles creates the conditions for possible displacement of the genitals. Specially designed gymnastics for this group of muscles can prevent unwanted processes of ovulation of the uterus and other genital organs, and in patients with ovulation of the uterus it is included in the composition of therapeutic measures.
Therapeutic gymnastics with the lowering of the uterus is aimed at increasing muscle tone, improving blood circulation and preventing inflammation.
The most popular among doctors and patients is the method of Kegel - a complex of exercises for pelvic muscles, named after its developer. The essence of the method consists in training the muscles surrounding the vagina, rectum and urethra( urethra) by maximal reduction for 3 seconds and subsequent relaxation.
To perform these therapeutic exercises, you do not need to visit a sports hall or a physiotherapy room, they are performed in any position, they can be repeated in the shower or at bedtime in bed.
Another popular Kegel exercise is related to the woman's ability to self-hypnosis: the patient is asked to present the muscular pelvic floor in the form of a kind of "elevator" on which she rises to the top and descends back. The climb starts from the "basement floor"( full relaxation), gradually the woman slightly strains the pelvic muscles, rises to the "first floor" and lingers for a couple of seconds in this position( elevator stop), then continues to move up, stopping at each improvised "floor".The higher the rise, the stronger the muscle tension. On the fifth "floor" it reaches a maximum. Movement "down" is accompanied by a gradual relaxation of muscles.
Each Kegel exercise is repeated throughout the day repeatedly, making a total of 50 to 100 cuts per day.
From the whole complex of exercises for each particular patient, several most suitable ones are selected, or the complex is recommended to be performed in full. The popularity of the Kegel system is explained by the fact that simple exercises can be performed at any time and any conditions, for example, sitting at work or in public transport.
The complex of therapeutic gymnastics with the lowering of the uterus includes strengthening the muscles of the abdominal press( anterior abdominal wall).A good condition of the abdominal muscles helps maintain normal intra-abdominal pressure, which prevents the displacement of organs.
Another popular method is exercise therapy by Yunusov's method. It includes voluntary contractions of the pelvic muscles during the act of urinating until the urine flow stops.
In women with a predisposition to omission of the uterus, therapeutic gymnastics acts as an effective prevention, and in the presence of an initial stage of the process, it can become the only treatment measure.
Regular swimming pool visits, cycling and physical exercise can replace a significant part of the exercise.



