Ovarian cyst
 Ovarian cyst is a mucinous or serous epithelial benign tumor that is a capsule whose cavity is filled with fluid. Kistoma in its origin is divided into primary( develops directly from the tissues of the ovary itself) and secondary( formed as a result of metastasis).In the course of the cystoma are distinguished into: benign, proliferating and malignant
Ovarian cyst is a mucinous or serous epithelial benign tumor that is a capsule whose cavity is filled with fluid. Kistoma in its origin is divided into primary( develops directly from the tissues of the ovary itself) and secondary( formed as a result of metastasis).In the course of the cystoma are distinguished into: benign, proliferating and malignant
Causes of
Initially, it is necessary to differentiate cystomas with ovarian cysts. Their differences are that the cystoma epithelial membrane, which produces its own secret( which is its content) and is capable of growth;And the cyst of the cyst is connective tissue, as a result of which it does not grow, but simply stretches due to the liquid accumulated in it, therefore it is very rare( unlike cystoma) to reach large sizes.
A teratoma or dermoid ovarian cyst( a single-chamber cyst full of bacon and hair) is formed due to malformations or genetic disorders from the embryonic tissue. Complaints in patients( aged 20 to 40 years) begin to occur only after the tumor reaches a sufficiently large size.
. Clinical manifestations of
. In most cases, small cystomas occur asymptomatically and are often detected quite accidentally with a planned gynecological examination or ultrasound of the pelvis. Very rarely, a dull minor pain in the lower abdomen can bother. As the cystoma increases in size, pains in the lower abdomen begin to appear, constipation and meager / frequent urination appear, which is directly related to the tumor squeezing of neighboring organs. A common symptom of cystaden is ascites( due to the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity a symmetrical increase in the abdomen is observed).If the cystoma has reached a very large size - there is asymmetry in the abdomen. Malignant menstrual irregularities or uterine bleeding
Diagnosis
The main methods of detecting a cyst are ultrasound of the pelvis and a standard gynecological examination. If it is necessary to clarify the nature of tumor formation and to differentiate it from malignant neoplasms of the ovaries, a puncture of the cystoma is done. In those cases when there are clinically valid doubts that the tumor is benign, diagnostic laparoscopy is performed, giving a 100% correct result. As additional diagnostic methods, magnetic resonance therapy and computed tomography are used. The malignancy of the process is also determined by the presence of the CA-125
on the blood. Treatment of the
cystoma. Regardless of the type of tumor, only surgical treatment is available, as there is a danger of a cystoma transition from benign to malignant( according to statistics in eight out of ten cases).At the moment, in most cases, 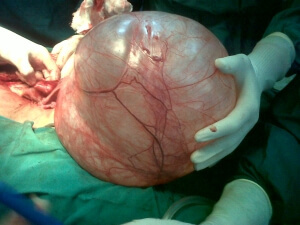 surgery is performed laparoscopically. The operation is also important to avoid twisting the leg of the tumor, which can occur during physical overstrain, heavy lifting, or as a result of sudden movements.
surgery is performed laparoscopically. The operation is also important to avoid twisting the leg of the tumor, which can occur during physical overstrain, heavy lifting, or as a result of sudden movements.
In addition to surgical treatment, with borderline and malignant tumors, chemotherapy is used with preparations: BenzoTEP, ThiotEP, etc. When choosing a specific drug for chemotherapy, the patient's weight, blood system state, overall health, type of cystoma, etc.
Treatment of ovarian cystoma is radiation therapy, used both for prophylactic purposes, and for the removal of tumor remnants after surgery. Also in the first days after surgery, hormone therapy with androgenic drugs is used, lasting for a long time.
The forecast of further life with a timely operation is quite favorable.