Sinus tachycardia: causes and treatment
Sinus tachycardia: types and symptoms
Pharmacological sinus tachycardia is determined by the effect on the sinus node of the following substances: adrenaline, caffeine, alcohol, norepinephrine, isoproterenol, nicotine.
Pathological sinus tachycardia is either inadequate or adequate.
Sinus tachycardia adequate is caused by body temperature, anemia, hypoxemia, arterial hypotension, thyrotoxicosis, pheochromocytomy.
When sinus tachycardia is inadequate, there is a persistent symptomatic increase in the frequency of the sinus rhythm - in a waking state at rest, more than 100 beats per minute.
It is believed that the basis of the disease is an increase in the automatism of pacemaker cells belonging to the sinus node as a result of its primary damage, which is facilitated by an increase in the tone of the sympathetic region of the autonomic nervous system, and also by a decrease in the parasympathetic node.
Sinus tachycardia is inadequate - this is a rare enough, besides little studied phenomenon, found mainly in women, mostly at a young age. Patients complain of frequent dizziness, shortness of breath, persistent heartbeat, constant weakness. Despite the stable tachycardia at rest, increasing with exercise is disproportionate to the degree of its severity.
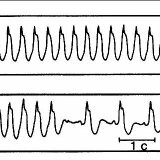
With this ailment, the CA-node systematically produces electrical impulses, which are traditionally performed by the ventricles and atria, while the ECG is practically no different from the norm, the only difference is the increase in heart rate. The ECG shows the correct alternation of the QRS-T complex and the P-wave, which is characteristic of the sinus rhythm.
The marked tachycardia can be accompanied by the oblique descending depression of the RS-T segment not exceeding 1 mm, a slight increase in the amplitude of the P and T teeth, by layering the P tooth at the T of the previous cycle.
Sinus tachycardia: causes of
Sinus tachycardia is most common in young people. And the cause of the development of this disease can be the immaturity of the nervous system. In the regulation of heart rate( heart rate) involved parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems.
Because of the release of adrenaline, the sympathetic nervous system is activated, resulting in increased heart rate and blood pressure. But the activation of the parasympathetic nervous system shows the opposite effect.
If these two systems are normal, they should be balanced, but admitted changes in a certain direction, if necessary. During sleep, for example, blood pressure and parasimatika prevails, and the heart rate decreases. But with physical exertion or stress the other way around.
This balance in young people is poorly maintained, the two parts of the nervous system constantly pull each other, so in most cases there is an inadequate regulation of heart rate, often in the form of tachycardia. A similar state was given the name - cardioneurosis.
It should be noted that there are other reasons for the development of tachycardia: stress, physical work, thyroid disease, fever, anemia, smoking.
Sinus tachycardia itself is not dangerous, but the cause of its development can be harmful to health.
Sinus tachycardia: the treatment
Before treat sinus tachycardia, a doctor must determine the cause of the disease, and then remove it: chronic foci of infection( eg, chronic tonsillitis) are treated primarily by reduction of hemoglobin levels, inspection and correction of the thyroid gland. In addition, it is advised to refrain from taking certain medications that only accelerate the sinus rhythm.
It does not matter what the reason for the tachycardia started, because the high pulse is no longer good, and if it also disturbs the patient, then he starts taking medications that slow the heart rate.
Often use beta-blockers. Less commonly used ivabradine, mainly if tachycardia is accompanied by low blood pressure. In addition, sedatives are used.
Special treatment is not required if the sinus tachycardia passes without symptoms and with a not very rapid pulse. But this is only if the tachycardia is not accompanied by symptoms of hemodynamic disturbances( dizziness, weakness, unconscious and even pre-occlusive conditions) and does not have a paroxysmal character. Similar attacks are sometimes observed with arrhythmia and are called sympathoadrenal paroxysms. With such an arrhythmia in young people, the prognosis is generally favorable.



