Dizziness: causes, methods of diagnosis and treatment

- is a visual analyzer;
- vestibular apparatus;
- proprioceptive device;
- brain structures.
The person sees surrounding objects and on the basis of the received information can realize the position in space.It is no accident that in pitch darkness there is sometimes instability in the vertical position.
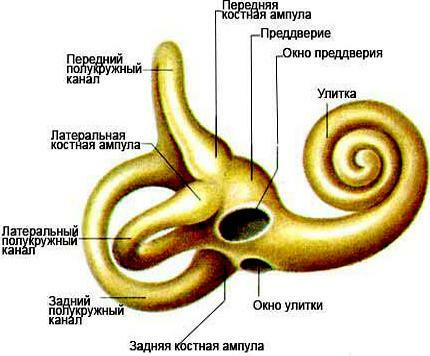
Vestibular apparatus( labyrinth)
Located in the skull in the cavity of the inner ear.Anatomically combined with an auditory analyzer.It consists of three hollow tubes( semicircular canals) located at an angle to each other, lined with a special shell with a mass of receptors and filled with liquid.When the position of the body changes( or rather, the head) in space, the fluid shifts, irritating the receptors.Transmission of information from them is carried out through the vestibular nerve, which sends pulses to the intracerebral structures
Proprioceptive( somatosensory) system
All organs, muscles, ligaments and bones of the body are permeated with millions of nerve endings.Some of them are equipped with sensitive receptors, from which the brain receives information about changes in the position of the body.Proof of this is the inability to maintain equilibrium with damage to the nerves of the extremities.
Intracerebral structures
The main center of equilibrium is in the cerebellum.However, there are several other structures( reticular formation, vestibular nuclei of the brainstem and cerebellum, extrapyramidal system) that perceive and process information coming from the receptor systems of the visual analyzer, the vestibular apparatus and the nerve endings of the body.
Violation of the functions of any of the parts of this incredibly complex mechanism leads to a distortion of the perception of patients in their position in space, which is manifested, among other things, by dizziness.There are two main types of dizziness:
- systemic, associated with impaired functions of the vestibular apparatus at different levels;
In turn, is divided into:
- central - with damage to brain structures;
- peripheral - with lesion of nerve nodes, nerves, semicircular canals;
- is a non-systemic one, which includes:
- imbalance associated with the uncoordinated action of all three equilibrium maintenance systems - visual analyzer, vestibular apparatus and proprioceptive mechanism;
- is a precancerous condition in which dizziness is caused by a sharp deterioration in the nutrition of any of the elements described above;
- is a psychogenic dizziness that occurs when anxiety or depressive conditions occur.
There is a separate form of vertigo - physiological dizziness.This type of symptom is not associated with any pathology and is caused by excessive irritation of the vestibular apparatus.Marine sickness is a classic example of such a vertigo.
Dizziness specificities depending on the cause
The reason for dizziness is the main factor that influences its characteristics.The nuances of the vertigo are determined by the level of damage to the balance maintenance system and the concomitant neurologic symptoms that are manifested in the underlying disease.
Systemic dizziness
30-50% of all patients complaining of vertigo suffer from its systemic form. Its cause is a number of diseases:
- Ménière's disease;
- vestibular neuronitis;
- benign positional paroxysmal dizziness( RVPG);
-
 neurinoma of the VIII pair of cranial nerves and other tumors;
neurinoma of the VIII pair of cranial nerves and other tumors; - craniocerebral trauma( CCT);
- toxic damage;
- vertebrobasilar insufficiency;
- Migraine;
- temporal lobe epilepsy;
- encephalitis;
- demyelinating diseases( usually - multiple sclerosis);
- anomalies in the development of the vertebrae of the cervical region, as well as the base of the skull.
With Ménière's disease , along with repeated attacks of dizziness, there are tinnitus, periodic hearing loss, marked autonomic disorders.Vertigo lasts from a few minutes to a day, the frequency of seizures is very diverse - from once a year to several times a day.Often before the attack there are feelings of stuffiness of the ears, a feeling of heaviness, noise in the head, disruption of coordination of movements.
Vestibular neuronite is an inflammation of the vestibular nerve, in which the most vivid symptom is intense dizziness for several hours.This pathology arises sharply, is caused by infectious causes or intoxication.Vestibular neuronitis is characterized by a complete absence of focal neurological and meningeal symptoms and complete hearing safety.
DPPG is a syndrome that occurs when crystals of calcium are formed in semicircular canals.A change in the position of the head causes their displacement and a strong stimulation of the receptors of the vestibular apparatus.At the same time, an attack of sweating arises, and the pulse rate decreases.Auditory phenomena( noise, hearing loss) and neurological symptoms are absent.
Tumors of the of the cerebellum, brainstem and cerebellum are often manifested by dizziness.This symptom may be the only sign of a volumetric process in the brain over time.
Dizziness occurring immediately after CCT , usually indicates a trauma to the labyrinth.Meningeal, focal symptomatology is absent, but there is a pronounced headache, often - nausea and vomiting.Sometimes the vertigo appears only a few days after the injury, and then you can suspect the development of the inflammation of the labyrinth - the serous labyrinthite.
The use of aminoglycoside antibiotics often provokes toxic damage to the auditory and vestibular apparatus.So, gentamicin first of all damages the structures of the labyrinth.This defeat is almost always irreversible.
Vertebrobasilar insufficiency is a disease in which there is a deterioration in the blood supply of both the labyrinth and the intracerebral structures.Simultaneously with dizziness other neurological symptoms are also revealed: motor and sensory disorders associated with damage to the cranial nerve nuclei, visual disturbances, coordination disorders of movements.The cause of this condition can be osteochondrosis, atherosclerosis, anomalies in the development of the main and vertebral arteries, that is, any conditions leading to a decrease in the lumen of these vessels.
The attack of dizziness with migraine is not a symptom of the disease, but a kind of aura - a condition that precedes the onset of headaches.
With temporal epilepsy, vertigo combines with powerful vegetative symptoms:
- with stomach pain;
- with nausea;
- with sweating;
- by increased salivation;
- loss of heart rate.
This form of epilepsy is not accompanied by convulsions, but other sensory disorders, for example, visual hallucinations, may occur.
Encephalitis is most often a viral inflammation of the brain that begins acutely or subacute with subsequent stabilization of the condition or gradual regression of the symptoms.Dizziness is accompanied by other, very diverse neurological symptoms.
 Vertigo often occurs with multiple sclerosis .The characteristic course of pathology, the multifaceted lesion and the results of instrumental and laboratory studies make it possible to fairly clearly determine the presence of the underlying disease.Difficulties can arise only then.When other symptoms are little expressed or dizziness is the first sign of multiple sclerosis.
Vertigo often occurs with multiple sclerosis .The characteristic course of pathology, the multifaceted lesion and the results of instrumental and laboratory studies make it possible to fairly clearly determine the presence of the underlying disease.Difficulties can arise only then.When other symptoms are little expressed or dizziness is the first sign of multiple sclerosis.
With anomalies in the development of the cervical vertebrae and the skull base, dizziness is caused by a mechanism similar to vertebro-basilar insufficiency.Usually there are other symptoms of the underlying disease, on the basis of which the final diagnosis is made.
Inconsistent dizziness
This includes types of dizziness that are not directly related to the work of the vestibular analyzer.
Equilibrium disturbances arising from the inconsistent operation of the three systems regulating the position of the body may result from:
- dysfunction of the vestibular system without affecting the semicircular canals;While the patient, closing his eyes, loses the ability to maintain balance;
- cerebellar lesions, in which the control of vision does not affect the severity of the symptoms;
- lesions of the subcortical nerve centers;
- impairment of impulse transmission from the visual analyzer, proprioceptors;
- taking some medications that affect nerve conduction.
In case of a presyncope, dizziness is often accompanied by a sensation of faintness, noise or ringing in the ears, instability, loss of balance, "darkening in the eyes".There are also emotional disorders - fear, anxiety, impotence, depression.Often after the onset of these symptoms, a syncope occurs, but it happens that they gradually disappear without losing consciousness to the sick.

Psychogenic dizziness occurs most commonly with depression, hypochondriac syndrome, hysteria, and also with some phobias( fear of open spaces).This type of vertego is distinguished by great persistence, expressed by emotional perception.
Treatment
Treatment of dizziness is performed according to the rules adopted for the treatment of the underlying disease:
- for disorders of cerebral circulation use nootropics, vasodilators, antiplatelet drugs;
- in Meniere's disease is limited to salt intake, diuretics are used, and surgical intervention is also carried out if necessary;
- vestibular neuronitis is treated with antiviral agents;
- benign paroxysmal positional dizziness is treated mainly non-drug;There are a number of techniques that allow the displacement of calcium crystals in the area of the vestibule of the labyrinth, where they will not irritate the receptors;
- with epilepsy apply special means that suppress the excessive electrical activity of the pathological focus in the brain.
Symptomatic agents are also used to interrupt the flow of impulses from the vestibular receptors( betagistin).

Some forms of dizziness show the use of meclosin, promethazine, cinnarizine.Widely used sedatives that do not eliminate dizziness, but which make it easier to carry it.
Treatment of psychogenic dizziness is accomplished by the appointment of psychotropic drugs - antidepressants, tranquilizers, sometimes - anticonvulsants, which have a sedative effect.Very effective and psychotherapy, since vertigo in this case is not an organic nature, but rather is a feature of perception of the surrounding reality.
Vertigo is just one of many neurological symptoms.Its appearance unambiguously testifies to inferiority in the body.That's why with repeated attacks of vertigo, you need to see a doctor as soon as possible for examination and quality treatment.
Bozbey Gennady, ambulance doctor



