Aortic dissection: symptoms and first aid

Aortic dissection is a life-threatening condition, the basis of which is the partial or complete separation of the layers of this powerful blood vessel and their subsequent rupture.
Table of contents: Reasons for aortic dissection Types of aortic dissection Diagnosis and symptoms Treatment and first aid PreventionReasons for
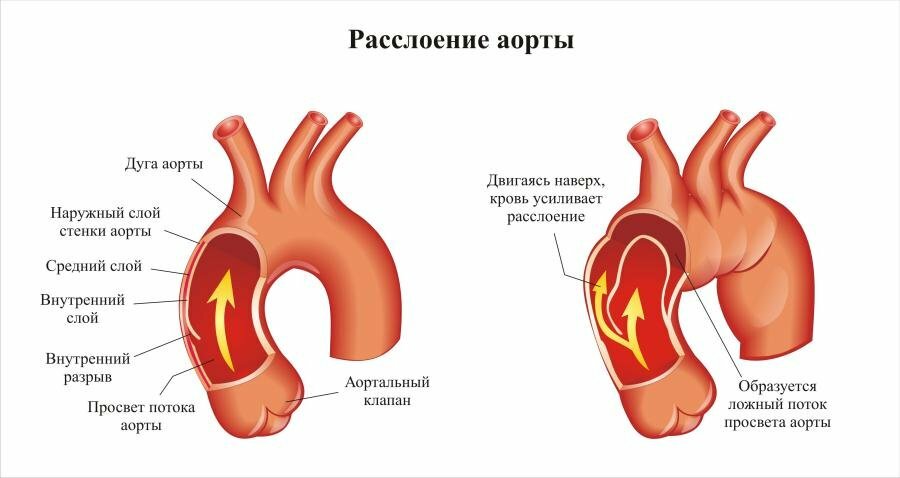
The main cause of aortic dissection is long-term arterial hypertension, especially if it is poorly adjusted.With prolonged high blood pressure, the aortic wall experiences a constant tension.There is a stretching, and the layers are stretched unequally.Over time, the inner shell of the aorta( intima) protrudes, forming an aneurysm - a kind of sac, under which the blood begins to flow.The second - the muscle layer - is unable to resist the pressure of the blood as intima, so the stratification progressively increases until the aortic rupture occurs.This is the last phase of this pathology.
The development of an aneurysm is promoted by factors that increase blood pressure( for example, smoking) and factors damaging the vessel wall:
- of dyslipidemia( atherosclerosis, etc.);
- connective tissue structure disorders:
- Marfan syndrome;
- bicuspid aortic valve;
- Ehlers-Danlos syndrome IV type;
- autoimmune lesions;
- Takayasu disease;
- Ormond disease;
- Behcet's disease;
- syphilis;
- injury;
- pregnancy in the third trimester;
- Use of psychoactive substances( amphetamines) and cocaine.
Mostly elderly people - 50-60 years old.Probably, this is due to the "experience" of hypertension, worsening of the state of connective tissue, the presence of a variety of concomitant diseases.Thirdly, aortic dissection is diagnosed in men.
Types of aortic dissection
There is a very deep classification of the aortic stratification that is used by specialists from all over the world - the DeBakey classification, according to which there are three types of disease:
- Type 1, in which the point of intimal rupture is in the ascending sectionAorta, and the stratification extends to its ventral part;
- type 2, in which the disruption of the intima is localized there, but the bundle ends with a blind sac above the brachiocephalic trunk;
- type 3, when the intimal rupture is located in the descending aorta.Specialists also highlight the specific forms of this pathology:
- intramural hematoma, which arises from a hemorrhage from capillaries that supply blood to the aortic wall;
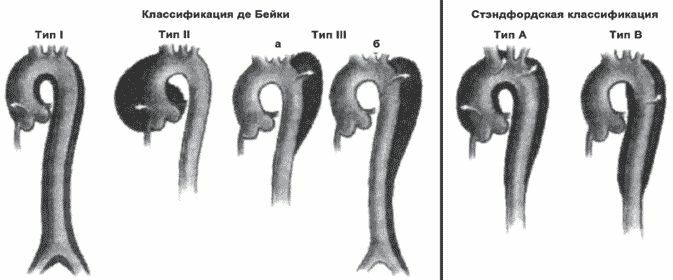
Both these forms eventually lead to aortic dissection.
Diagnosis and symptoms
The features of the development of the disease forced specialists to pay special attention to non-instrumental diagnostic methods.Sometimes there is simply no time to use a wide arsenal of diagnostic tools for a specialist, and there are no necessary equipment in the ambulance teams. Therefore, special attention is drawn to the history data:
- smoking;
- reception of drugs;
- Concomitant diseases( arterial hypertension, dyslipidemia, connective tissue and autoimmune pathologies, syphilis).
Note: for aortic dissection is characterized by a complaint of "special" pain.It arises suddenly, it is localized between the scapulae( as the distribution spreads, the bundle can shift), in intensity it is the strongest, tearing.There is a special term - "aortic pain" , which characterizes the patient's feelings in this pathology.
Additional symptoms may vary considerably depending on the level of the lesion:
- aortic arch - stroke, transient ischemic attack, syncope;
- intercostal branches - paraplegia;
- mesentery arteries - a pain in the abdomen, bearing a compressive nature;
- renal arteries - impaired urinary output up to anuria;
- iliac arteries - ischemia of the lower extremities.
If the entire wall of the vessel ruptures, hypovolemic shock may develop, and with a hemorrhage from the initial sections, a cardiac tamponade arises in the pericardial cavity.
With prolonged dissection, the patient gradually develops congestive heart failure.
When collecting objective data, most patients have a severe condition, unstable hemodynamics. At this stage, the main symptoms of aortic dissection are noted:
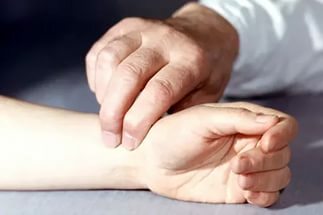
- difference in blood pressure on both hands of 20 or more mm Hg.St;
- lack of pulse on one of the radial arteries;
- is a noise of aortic regurgitation, heard over the heart.
Important! The laboratory data do not provide useful information for diagnosing, but they exclude other causes of chest pain( for example, myocardial infarction, pleurisy, cholecystitis).
Among the instrumental methods, the most important is the chest X-ray, which allows to reveal the expansion of the shadow of the mediastinum or aorta.An electrocardiogram with aortic dissection is poorly informative, but ECG monitoring helps to exclude acute myocardial infarction and life-threatening arrhythmia.
There is a triad known to doctors of the main symptoms of aortic dissection:
- aortic pain;
- enhanced mediastinal shadow on X-ray;
- disappearance of the pulse on one of the arms or a difference in blood pressure of more than 20 mm Hg.Art.On both hands.
With all three symptoms, the diagnosis of aortic dissection is 83%.
With the medical facilities available to the patient, special examinations can be conducted to the patient:
- ultrasound;
- computer and magnetic resonance imaging;
- aortography.
Treatment and first aid
 All patients with aortic dissection are subject to mandatory admission to the intensive care unit or resuscitation.With aortic dissection, medical and surgical treatment is used.
All patients with aortic dissection are subject to mandatory admission to the intensive care unit or resuscitation.With aortic dissection, medical and surgical treatment is used.
The main goals of drug therapy are anesthesia and lowering blood pressure to low digits.
For narcosis analgesics are used.The pressure should be reduced as quickly as possible.For this, preparations of the group of beta-blockers are used which, when unsuccessful( lack of stabilization of arterial pressure at the level of 110 mm Hg and below) is replaced by sodium nitroprusside.
In the presence of vomiting, metoclopramide is used, with increased anxiety - diazepam.
Drug treatment is not used in every case of stratification.Abstinence from surgical treatment is possible with a lesion of the descending aorta and a stable condition of the aneurysm.If its ascending part is affected or the disease progresses - the operation should be carried out in the shortest possible time.Most often, surgeons just close the defect in the intima of the aorta, through which the blood that exfoliates it walls enters.Sometimes stenting operations are performed( artificial expansion of the lumen of the vessel using a special tube) or prosthetics of the affected area.
Prophylaxis
Based on the reasons, one can understand who is at risk for aortic dissection:
- smokers;
- hypertension;
- people suffering from dyslipidemia.
Prevention measures, respectively, are in the
- quitting;
- carefully monitor blood pressure with all possible means;
- normalization of the lipid profile.
Forecast for life
The timeliness and completeness of the medical care depends on the patient's chances of recovery.However, even with the immediate initiation of therapeutic measures, the death rate with the dissection of the aorta remains incredibly high: 25% of patients die in the first day and 50% in the first week.Alas, but more than a year after the first attack, 9 people die out of 10. Therefore, it is so important to follow preventive measures, because it is better to prevent than to cure, especially with such poor chances of recovery.
Bozbey Gennady, ambulance doctor