Coronary bypass: indications for conduction and postoperative period
Coronary artery bypass surgery is a fairly widespread procedure these days.Surgical intervention is necessary for patients suffering from ischemic heart disease with ineffective drug treatment and progression of pathology.
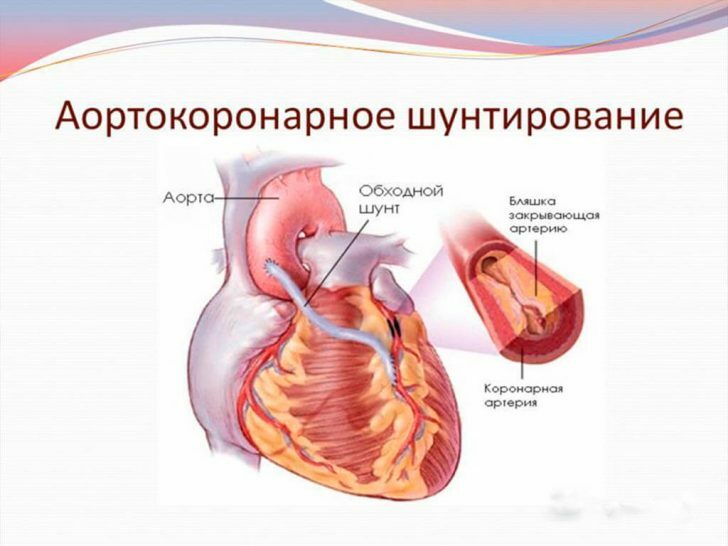
Coronary bypass surgery is an operation on the vessels of the heart, during which the arterial blood flow is restored.In other words, shunting is the creation of an additional path bypassing the narrowed portion of the coronary vessel.The shunt itself is an additional vessel.
Table of contents: What is coronary heart disease?Coronary artery bypass surgery Aortocoronary bypass: Postoperative period Mortality statistics after coronary artery bypass graftWhat is coronary heart disease?
Recommended reading:Ischemic heart disease is an acute or chronic decrease in the functional activity of the myocardium.The cause of the development of pathology is the insufficient supply of arterial blood to the heart muscle, resulting in oxygen starvation of tissues.
In most cases, the development and progression of the disease is due to the narrowing of the coronary arteries, which are responsible for supplying the myocardium with oxygen.Vascular transmission decreases with atherosclerotic changes.Insufficiency of the blood supply is accompanied by pain syndrome, which at the initial stages of pathology appears with a significant physical or psychoemotional load, and as progression - and at rest.The pain in the left side of the chest or behind the breastbone was called stenocardia( "angina pectoris").They, as a rule, irradiate into the neck, the left shoulder or the angle of the lower jaw.During an attack, patients feel a lack of oxygen.Characteristic is also the appearance of a sense of fear.
Important: in clinical practice there are so-called."Painless" forms of pathology.They represent the greatest danger, as they are often diagnosed already in the late stages.
The most dangerous complication of ischemic disease is myocardial infarction.With a sharp restriction of oxygen in the area of the heart muscle, necrotic changes develop.Infarcts are the leading cause of death.
The most accurate method of diagnosing IHD is radiocontrast( coronary angiography), in which a contrast agent is injected into the coronary arteries by means of catheters.
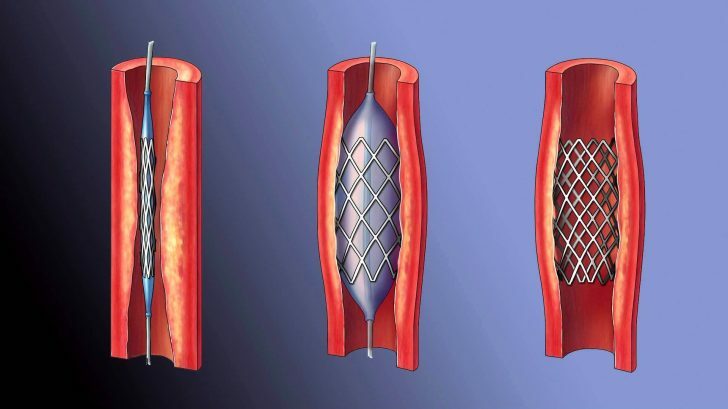
Based on the data obtained during the study, the question of the possibility of stenting, balloon angioplasty, or coronary artery bypass grafting is being addressed.
Coronary bypass operation
This operation is scheduled;The patient is usually placed in a hospital 3-4 days before the intervention.In the preoperative period, the patient undergoes a comprehensive examination and studies methods of deep breathing and coughing.He has the opportunity to get acquainted with the surgical team and get detailed information about the nature and course of the intervention.
On the eve preparatory procedures are carried out, including a cleansing enema.An hour before the start, premedication is performed;The patient is given medications that reduce feelings of anxiety.
A timely operation prevents the development of irreversible changes in the myocardium.Thanks to the intervention, the contractility of the cardiac muscle is significantly increased.Surgical treatment can improve the patient's quality of life and increase its duration.
The average duration of the operation is from 3 to 5 hours.In most cases, the patient needs to be connected to the cardiopulmonary bypass, but in some situations it is possible to interfere with the beating heart.
Surgical treatment without patient connection to the cardiopulmonary bypass device has several advantages, including:
- shorter duration of intervention( up to 1 hour);
- reduced recovery time after coronary artery bypass graft;
- exclusion of possible damage to blood cells;
- no other complications associated with connecting the patient to the IR device.
Access is through a cut made in the middle of the chest.
Additional incisions are made in the area of the body from which the graft is taken.
The course and duration of the operation depends on the following factors:
- type of vascular lesion;
- degree of severity of pathology( number of shunts created);
- the need for parallel aneurysm removal or reconstruction of the heart valves;
- some individual characteristics of the patient's body.
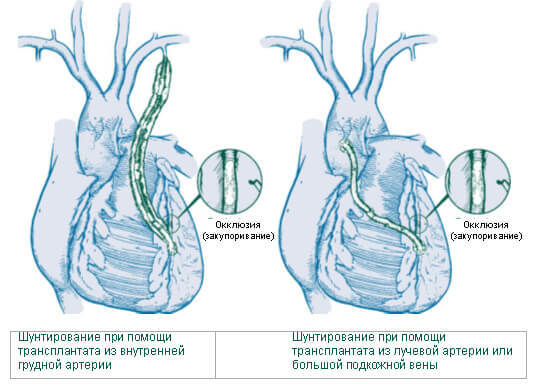
During the operation, the graft is sutured to the aorta, and the other end of the graft is to the branch of the coronary artery, bypassing the narrowed or obturated section.
To create a shunt, the fragments of the following vessels are taken as a transplant:
- large subcutaneous vein( from the lower extremity);
- internal thoracic artery;
- radial artery( from the inner surface of the forearm).
 Note: using a fragment of an artery allows you to create a more fully functional shunt.Preference for fragments of subcutaneous veins of the lower extremities is given for the reason that these vessels are usually not affected by atherosclerosis, that is, they are relatively "clean".In addition, the fence of such a transplant does not subsequently lead to health problems.The remaining veins of the legs take on a load, and the blood circulation in the limb is not disturbed.
Note: using a fragment of an artery allows you to create a more fully functional shunt.Preference for fragments of subcutaneous veins of the lower extremities is given for the reason that these vessels are usually not affected by atherosclerosis, that is, they are relatively "clean".In addition, the fence of such a transplant does not subsequently lead to health problems.The remaining veins of the legs take on a load, and the blood circulation in the limb is not disturbed.
The ultimate goal of creating such a workaround is to improve the blood supply to the myocardium to prevent attacks of angina and heart attacks.After coronary bypass surgery, the life expectancy of patients with coronary artery disease significantly increases.In patients, physical endurance increases, work capacity is restored, and the need for pharmacological drugs is reduced.
Coronary bypass graft: postoperative period
 After completion of the operation, the patient is placed in the intensive care unit, where he is monitored 24 hours a day.Means for anesthesia adversely affect respiratory function, so the operated person is connected to a special device that supplies oxygen-enriched air through a special tube in the mouth.With a quick recovery, the need to use this device usually disappears within the first 24 hours.
After completion of the operation, the patient is placed in the intensive care unit, where he is monitored 24 hours a day.Means for anesthesia adversely affect respiratory function, so the operated person is connected to a special device that supplies oxygen-enriched air through a special tube in the mouth.With a quick recovery, the need to use this device usually disappears within the first 24 hours.
Note: in order to avoid uncontrolled movements that can lead to the development of bleeding and the disconnection of the patient's droppers the patient's hands are fixed until fully conscious.
In vessels on the neck or thigh, catheters are inserted through which drugs are introduced and blood is taken for analysis.From the cavity of the chest cells are drawn to suck up the accumulating fluid.
To the body of the patient who underwent coronary artery bypass grafting, special electrodes are attached in the postoperative period, allowing to monitor cardiac activity.To the lower part of the chest cells are fixed, by means of which, if necessary( in particular - with the development of ventricular fibrillation), electrostimulation of the myocardium is performed.
Note: continues the action of drugs for general anesthesia, the patient may be in a state of euphoria.Disorientation is also characteristic.
As the condition improves, the patient is transferred to a regular ward of a specialized hospital department.During the first days after shunting, there is often an increase in body temperature, which is not a cause for concern.This is a normal reaction of the body to extensive tissue damage during surgery.Immediately after coronary bypass surgery, patients can complain about unpleasant sensations at the site of the incision, but the pain syndrome is successfully cured by the introduction of modern analgesics.
In the early postoperative period, strict control of diuresis is required.The patient is offered to enter in a special diary the data on the amount of liquid drunk and the volume of urine being separated.To prevent the development of such complications, as the patient's postoperative pneumonia is introduced to the complex of respiratory exercises.Lying on the back contributes to stagnation of fluid in the lungs, so the patient is recommended to turn on his side a few days after the operation.
A careful local massage with tapping in the projection of the lungs is indicated to prevent clusters of secretion( improvement of the cough).The patient should be informed that coughing will not lead to divergence of the sutures.
Note: To accelerate the healing process, a thoracic corset is often used.
 The patient can consume liquid a half to two hours after the removal of the respiratory tube.At first, the food should be semi-liquid( wiped).The period of transition to normal diet is determined strictly individually.
The patient can consume liquid a half to two hours after the removal of the respiratory tube.At first, the food should be semi-liquid( wiped).The period of transition to normal diet is determined strictly individually.
Restoration of motor activity should be gradual.Initially, the patient is allowed to sit in a sitting position, a little later - briefly walk around the ward or the corridor.Shortly before discharge, it is allowed and even recommended to increase the time of walks and climb the flight of stairs.
 The first days of the bandage are regularly changed, and the seams are washed with an antiseptic solution.As the wound is tightened, the bandage is removed, as the air contributes to drying out.If tissue regeneration proceeds normally, the seams and the electrode for stimulation are removed on the 8th day.After 10 days after the operation, the area of the incisions can be rinsed with usual warm water and soap.As for general hygiene procedures, you can take a shower only after a week or one and a half after the removal of stitches.
The first days of the bandage are regularly changed, and the seams are washed with an antiseptic solution.As the wound is tightened, the bandage is removed, as the air contributes to drying out.If tissue regeneration proceeds normally, the seams and the electrode for stimulation are removed on the 8th day.After 10 days after the operation, the area of the incisions can be rinsed with usual warm water and soap.As for general hygiene procedures, you can take a shower only after a week or one and a half after the removal of stitches.
The sternum is fully restored only after a few months.While it is growing together, the patient may have painful sensations.In such cases, the reception of non-narcotic analgesics is indicated.
Important: until weightlifting of the sternum is eliminated lifting weights and making sudden movements!
If the transplant was taken from the foot, the patient's first time may be disturbed by burning in the incision and swelling of the limb.After a while these complications pass without a trace.While symptoms persist, it is advisable to use elastic bandages or stockings.
After coronary artery bypass, the patient is in hospital for another 2-2.5 weeks( provided there are no complications).The patient is discharged only after the attending physician is fully confident in stabilizing his condition.

To correct complications and reduce the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, correction of the diet is required.The patient is recommended to reduce consumption of table salt and to minimize the number of foods containing saturated fats.Persons suffering from nicotine dependence should completely stop smoking.
To reduce the risk of recurrence will help complexes LFK.Moderate physical activity( including regular walking) contributes to the speedy rehabilitation of the patient after coronary bypass surgery.
Mortality statistics after coronary artery bypass grafting
According to data from long-term clinical observations, 15 years after the successful operation, the mortality rate among patients is the same as in the population as a whole.Survival largely depends on the extent of surgical intervention.
The average life span after the first bypass is about 18 years.
Note: , at the time of the completion of the large-scale study, whose purpose was to compile mortality statistics after aorto-coronary bypass surgery, some patients who underwent surgery in the 70s of the last century had already celebrated their 90th anniversary!
Vladimir Plisov, medical reviewer