Congenital heart diseases and their causes
 Congenital heart defects occur during the intrauterine period of the child's development.Anatomically, they are anomalies of the formation and growth of the heart and its structural elements - muscle partitions between chambers, valve flaps between the cavities of the ventricles and atria, the aorta and the pulmonary artery.
Congenital heart defects occur during the intrauterine period of the child's development.Anatomically, they are anomalies of the formation and growth of the heart and its structural elements - muscle partitions between chambers, valve flaps between the cavities of the ventricles and atria, the aorta and the pulmonary artery.
The data obtained from different sources relative to the incidence of this type of pathology differ from each other.Some authors claim about 5-10 cases of malformations per 100 newborns, others - about 1 out of 300.
Note: disease prognosis depends on the type of blemish and the timing of the onset of radical treatment.Some types of diseases are recognized accidentally during medical examination.Without treatment, such patients live to their old age.
Table of contents: Predisposing conditions and causes of congenital heart disease Combined systematization of vices How many patients live with congenital heart disease How to identify congenital heart disease?Complaints and Symptoms of Congenital Heart Defects Types of Treatment for Congenital Heart Defects What complications are congenital heart defects Prevention Information on the most common types of congenital heart diseaseVideo "Congenital heart defects in a child":
Predisposing conditions and causes of congenital malformationsHearts
Pathologies arise as a result of hereditary predisposition and exposure to harmful environmental conditions, infectious diseases, bad habits berA woman, with the use of certain medicines.The result of damaging effects of these causes in the first trimester of pregnancy often become congenital heart disease in children.
The risk of a child developing one of the variants of congenital malformation increases with the age of the pregnant woman under 17 and in the category over 40. The disease also develops in cases of weighed heredity.If there were cases of defects in the family, the probability of their appearance in the heirs is quite high.
Endocrine diseases of the mother are considered to be a contributing factor in the formation of malformation in the fetus:
- diabetes mellitus;
- thyrotoxicosis and other diseases of the thyroid gland;
- adrenal pathology;
- pituitary neoplasms.
Infectious diseases can become the cause of malformations:
- measles rubella;
- some types of herpetic infection;
- systemic connective tissue diseases( lupus);
- household and industrial poisons, different types of radiation;
- pathological habits( alcohol consumption, smoking, uncontrolled intake of drugs, drugs, etc.)
Combined systematization of defects
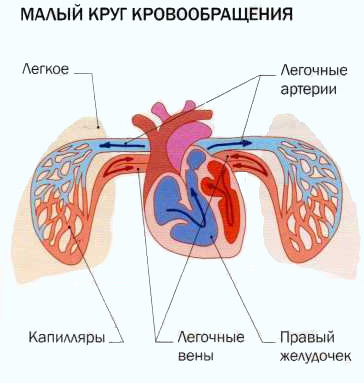
The most important criterion by which congenital malformation should be assessed is the state of circulation( hemodynamics), Especially its influence on the blood flow of the small circle of blood circulation.
This property divides the defects into 4 main groups:
- defects that do not involve changes in blood flow in the small circle of the circulation( ICC);
- defects that increase pressure in the ICC;
- pathologies that reduce blood flow in the ICC;
- combined violations.
Malformations that do not cause changes in blood flow to the ICD:
- abnormal heart location;
- atypical position of aortic arch;
- coarctation of the aorta;
- different degree of aortic narrowing;
- atresia( specific narrowing of the tricuspid aortic valve itself);
- failure of the pulmonary artery valve;
- mitral stenosis( narrowing of the so-called mitral valve, ensuring the passage of blood from the left atrium to the left ventricle);
- mitral valve insufficiency with atresia( expressed as incomplete closure of valvular flaps, which provokes a return of blood from the ventricle to the atrium with systole;
- heart with three atria;
- defects of the coronary arteries and conductive system
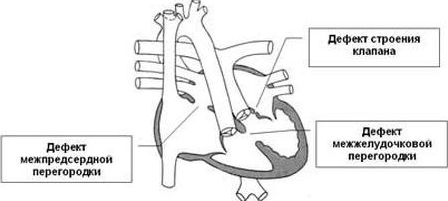
Flaws provoking an increase in pressure and blood flow in the ICD:
- not accompanied by cyanosis( cyanosis) - open( uninfected) arterial( botall) duct, defect of the septum between the atria, defect of the septum between the ventricles, the Lyutembash complex( congenital narrowing of the holeBetween the left atrium and the left ventricle and the defect of the septum between the atria), fistula between the aorta and the pulmonary artery, pediatric coarctation;
- with cyanosis - atresia of the tricuspid valve and narrowing of the opening in the septum between the ventricles, open the ducts of the ducts, ensuring the return of blood to the aorta from the pulmonary artery.
- narrowing( stenosis) of the pulmonary artery( trunk) without blueing( cyanosis);
- with blueing( cyanosis) - triad, tetrad, pallada Fallo, tricuspid atresia with stenosis of the artery of the lung.Anomaly( illness) of Ebstein, accompanied by a "failure" of the valves of the tricuspid valve in the right ventricular cavity, hypoplasia of the right ventricle.
- transposition of the artery of the lung and aorta( the aorta departs from the right ventricle, and the pulmonary trunk - from the left);
- aortic and pulmonary artery trunk from one ventricle( right or left).Can be complete, partial with different options;
- Taussig-Bing syndrome, a combination of a high interventricular septal defect with aortic transposition, a left pulmonary trunk location and right ventricular hypertrophy, a common vascular trunk, a heart consisting of three chambers with one ventricle.
- examination of the patient.At this stage of diagnosis of congenital malformation, the appearance, physique, coloring of the skin is assessed.Based on the results obtained, the presence of the disease can be suspected;
- listening to the operation of the heart valves( auscultation).By the presence of extraneous noise and splitting of tones, one can determine the variant of the existing heart defect in a child and an adult;
- finger tapping of the chest( percussion).This method allows you to determine the boundaries of the heart, its size.
- electrocardiography;
- Doppler echocardiography;
- ultrasound of the heart and blood vessels;
- X-ray methods;
- laboratory diagnostics, allowing to determine the presence of existing complications;Angiography methods.
- .
- cardiac( cardiac) pain, irregularities and palpitations;
- "stagnant" phenomena, in which there is accumulation of blood in separate organs and parts of the body.In connection with the inability of the heart to perform the function of the "pump", pallor or cyanosis of the skin appears, acrocyanosis( cyanotic fingers, nasolabial triangle), the formation of chest protrusion( heart hump).There are attacks of dyspnea, fainting, weakness, dizziness, general physical weakness, even to the impossibility of moving.There is an increase in the liver, puffiness, accumulation of stagnant fluid in the abdominal cavity, between the membranes of the pleura, cough with sputum expectoration, sometimes with an admixture of blood, the phenomenon of dyspnea;
- symptoms of oxygen starvation of tissues, causing physical underdevelopment, metabolic disorders( fingers resembling drumsticks, nails in appearance similar to watch glass).
- Phase I - adaptation of the body.With a slight defect, there are also minor symptoms of the disease.Serious defects lead to a rapid formation of signs of cardiac decompensation.
- II phase - compensatory, which includes all the protective reserves of the body and is invariably accompanied by an improvement in the general condition of the patient.
- Phase III - terminal, caused by the depletion of the internal reserves of the body and the development of incurable pathologies and menacing symptoms of circulatory disorders
- medicated( conservative).Its goal is to reduce the symptoms of chronic heart failure, to prepare the patient for surgery;
- surgical.The only method that enables the patient to live.The operation can be carried out urgently, if there is a momentary threat to the patient's life, or in the planned mode.
- ;
- diuretics, which remove excess fluid from the body;
- vasodilators that dilate the blood vessels;
- prostaglandins( or their inhibitors) that cause an improvement in the flow of blood to the lungs and other organs and systems;
- antiarrhythmic drugs.
- X-ray surgical interventions are low-traumatic operations involving the insertion into the heart cavity of specially folded tubes and a canister through the vessels, which, if necessary, can both increase the lumen of the vessel, apply "patches" to pathologicalHoles or create missing "holes", remove stenosis of the valve.
- Closed operations - operations without opening the cardiac cavity.Revision and loosening of stenoses with this method is performed by the fingers of the surgeon or a special instrument, and the doctor reaches the heart halfway through the auricles.
- Open operations - operations involving temporary disconnection of pulmonary and cardiac activity, transfer of a patient to an artificial circulation device, subsequent opening of the cardiac cavity and elimination of existing defects
- acute and chronic heart failure;
- infectious-toxic endocarditis( inflammatory process in endocardium - internal cardiac membrane);
- pneumonia;
- disorders of cerebral circulation;
- angina pectoris caused by insufficient blood supply to the heart muscle;
- cardiac arrest.
Defects causing a decrease in blood circulation( hypovolemia) in the ICD:
Combined defects due to anatomical atypical location of vessels and cardiac structures:
Note: lists the main types and groups of defects.In fact, there are more than a hundred of them.Each vice is different in its own way.Also specific is the diagnosis, examination and treatment methods, of which we will talk later.
How many patients live with congenital heart disease
The duration and quality of life depends on the type of defect, its severity.With some vices people live to old age, with others death occurs during the first year of life.The main problem is late surgical treatment.Unfortunately, the cost of heart surgery is very high, and in the absence of material opportunities is not available to all patients.The problem is also complemented by the shortage of medical personnel and hospitals working in this area.
How to identify congenital heart disease?
Complex heart defects are defined in newborns in utero.In the older age, mild degrees of congenital heart disease, in a compensated state and not felt by patients, can be detected.The first to determine the existing congenital malformation may be ultrasound examining the pregnant woman.
Heart examination consists of a set of diagnostic methods, including:
In out-patient and hospital settings, the following apply:
Complaints and symptoms of congenital heart disease
 The manifestations of the disease depend on the type of defect and severity.Symptoms can be determined immediately after the birth of the child, and sometimes in different age groups: in adolescents, at a young age and even in elderly patients who were not previously examined and have a compensated, mild form of congenital malformation.
The manifestations of the disease depend on the type of defect and severity.Symptoms can be determined immediately after the birth of the child, and sometimes in different age groups: in adolescents, at a young age and even in elderly patients who were not previously examined and have a compensated, mild form of congenital malformation.
The following complaints are most often present in patients:
As a rule, the development of congenital malformation occurs in three phases:
Types of treatment for congenital heart diseases
With mild vices, a person can live a lifetime.But the heavy are subject to mandatory surgical treatment, otherwise to live with congenital heart disease even before adulthood will be a big problem.
 What kinds of treatment are applicable:
What kinds of treatment are applicable:
The planned interventions are prepared for a certain time, which is necessary to improve the patient's well-being and increase the resistance to infections.
The choice of a method of treatment largely depends on both the variety of the present congenital malformation and the phase of development in which it is located.As a rule, in the first phase of the disease, the operation is prescribed only in the presence of symptoms that threaten the patient's life.The patient is shown the restriction of physical and mental loads, monitoring his condition, proper nutrition, emotional rest.
With the development of stage II, the entire treatment process is aimed at keeping the patient in the compensatory phase.If necessary, prescribe medication, carry out routine operations.
III phase of the disease - a period of severe deterioration, the emergence of severe symptoms of heart failure.The main treatment for this phase of congenital malformation is taking medications to improve the functioning of the heart.
Cardiac glycosides for cardiac enhancement may be prescribed:
Operative intervention at this stage is extremely rare, which is due to the extremely poor overall condition of the patient.
Important : in the presence of severe blemish, surgical treatment should be performed as early as possible, which reduces the risk of complications and avoids major changes in the work of organs caused by the consequences of the defect.
Often in the treatment of congenital heart defects resort to two-stage operations.Especially if it is a patient in a decompensated state.The first stage is the facilitating operation ( palliative), which, with a small amount of injury, allows to improve the patient's well-being and prepare him for the next stage.
The radical operation allows you to completely eliminate the defect and the attendant consequences.
Several types of operations can be used:
In those cases when the operation can not eliminate congenital malformation and the patient's condition is very difficult,Can be applied heart transplant.
Modern technologies sometimes allow you to perform an operation and eliminate congenital malformation even at the stage of intrauterine development.
Video "Operative treatment of congenital malformation":
What complications give congenital heart defects
The consequences of an untreated defect can be the following:
Prevention
Prevention of congenital malformations includes the preparation of a pregnant woman for childbirth, excluding bad habits, nutrition, walks, careful use of medications, avoiding rubella foci, and treatment of co-morbidities.
Data on the most common types of congenital heart disease
 Defect of the interventricular septum - is very common.In severe cases, the septum is absent altogether.In this pathology, oxygen-enriched blood from the left ventricular cavity is supplied portionwise to the right.Accumulation of it leads to an increase in blood pressure in the pulmonary circle.The vice in children gradually increases.Patients appear flaccid, pale, with a load of cyanosis.When listening to the heart, there are specific noises.Without treatment, babies develop a pronounced insufficiency, and they die in early childhood.The operation involves suturing holes, or patching plastic materials.
Defect of the interventricular septum - is very common.In severe cases, the septum is absent altogether.In this pathology, oxygen-enriched blood from the left ventricular cavity is supplied portionwise to the right.Accumulation of it leads to an increase in blood pressure in the pulmonary circle.The vice in children gradually increases.Patients appear flaccid, pale, with a load of cyanosis.When listening to the heart, there are specific noises.Without treatment, babies develop a pronounced insufficiency, and they die in early childhood.The operation involves suturing holes, or patching plastic materials.
Atrial septal defect - is a common type of defect in which the increased pressure created in the right atrium is well compensated.Therefore, unoperated patients can survive to adulthood.The operation eliminates the defect as well as in case of problems in the interventricular septum - with suturing or patches.
Non-invasion of the arterial( botallic) duct - is normal after the birth of the duct, which connects the developing fetus to the aorta and the pulmonary artery falls off.Its non-infection promotes the discharge of blood from the aorta into the lumen of the pulmonary trunk.There is an increase in blood pressure and excess in the pulmonary circle of the circulatory cycle, which causes a sharply increasing load on both ventricles of the heart.Treatment consists in bandaging the duct.
Stepanenko Vladimir, surgeon

