Bowel cancer: treatment
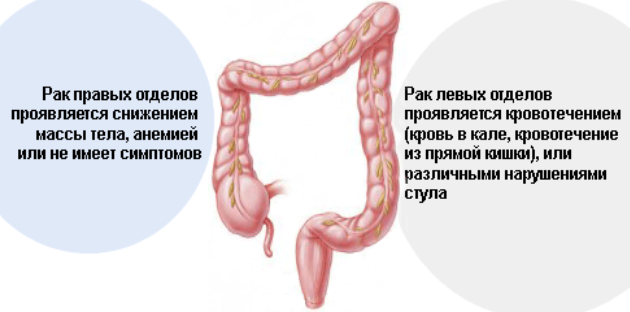
Bowel cancer is a tumor of the malignant type of the intestinal mucosa. This disease can affect any part of the intestine, but in many cases, cancer occurs in the large intestine. Unfortunately, this disease is not uncommon, the most affected people are in countries with the most developed economies. For today among oncological diseases, intestinal cancer ranks second in the frequency of occurrence in older people.
Men and women are at greater risk of becoming infected after 45 years, and the incidence rate increases by 10 percent every ten years. In 96% of cases, intestinal cancer develops from intestinal epithelial cells.
In the initial stages, cancer is treated surgically. Quite often, all cancer cells are removed from the body, and the patient can be considered completely free of treacherous cancer. After surgery, the patient undergoes a course of chemotherapy to reduce the chances of a relapse.
In the case of a colon tumor, before and after surgery, radiotherapy, sometimes in combination with chemotherapy, will be necessary. This is necessary in order to reduce the number of cancer cells, and thereby simplify the operation.
If the disease is started, the tumor has already spread to different parts of the body, in medical language this is called local spread. If the tumor has captured other organs, for example, the liver or lungs, it is metastatic or secondary cancer. At this stage, the cancer does not respond to treatment. But you can still prolong life and improve your health. It also happens that the treatment is not at all effective and, in addition, it can cause various side effects.
Treatment of a colon tumor depends on:
- a variety of oncology;
- area of tumor spread;
- course of treatment.
In advanced cases, chemotherapy is used, radiotherapy is used to reduce the tumor and relieve pain. The operation is also possible. The operation is carried out in order to restore the patency of the colon and the removal of secondary cancer from the liver and lungs. For the temporary suspension of tumor development, monoclonal antibodies( bevacizumab and cetuximab) are used.
Pros and cons of treating intestinal cancer
Some patients are afraid to treat due to possible side effects. There are also people who want to know what will happen if there is no treatment at all.
To decide on treatment at an early stage of the disease is not difficult, there is a high probability that the cancer will heal completely. In the late stages of cancer, some patients generally refuse treatment. But doctors still prescribe to them medicines that will contain the symptoms.
Chemotherapy
In the early stages of the disease, such types of chemotherapy are used:
- adjuvant treatment, which is performed to reduce relapse after surgery;
- is a neo-adjuvant treatment that is performed before surgery to reduce the number of cancer cells and to simplify resection;
- Neo-adjuvant chemoradiotherapy, which is performed before surgery, chemotherapy along with radiotherapy.
In the early stages, such drugs are used to treat colon cancer: 5-fluorouracil with folinic acid, or oxaliplatin.
Secondary tumor is also treated with chemotherapy. This type of cancer is almost incurable, but therapy helps slow the progression of the disease and alleviate the suffering of the patient.
There are both advantages and disadvantages in the treatment of chemotherapy for advanced cancer of the small and large intestine. It is very difficult to predict how chemotherapy will affect the body of a patient. But if the patient has a normal condition, then most likely, chemotherapy will have a positive effect.
If the disease reaches the last stages, the patient may refuse chemotherapy, and doctors will prescribe other medications that can help stop the disease.
Treatment can be continued only by analyzing the general condition of the patient, the effect of previous therapy, and the degree of cancer development.
For the treatment of colon tumors use:
- oxaliplatin;
- capecitabine;
- irinotecan;
- tegafur with uracil together with folinic acid;
- 5-fluorouracil together with folinic acid.