Cancer of the anal canal
Cancer of the anal canal is a very dangerous, but very rare form of malignant formation. Of the total number of such diseases, it is only 6%.In industrialized countries, this disease occurs in only one of 10,000 cases. For example, in the US with a population of 309 469 203 people( data for 2010) is only 3.5 thousand cases a year. The highest incidence of anal cancers in HIV-infected men. Although in Europe, on the contrary, the prevalence of this disease among women in the proportion of 1 to 3. In the Middle East and Asia in the anal canal cancer is detected very rarely. Most often, this disease is detected in people older than 50 years, and in Europe the average age of the sick is 63 years.
Causes of development of anal cancers.
The causes of this malignant formation are very difficult to explain. Doctors suppose that the launched cancers of the anal canal are haemorrhoids, polyps, anal fissures and proctitis. The incidence rate of male homosexuals is almost 50 times higher than that of persons of heterosexual orientation. Recently, the prevailing opinion is that one of the key factors in the development of this disease is HIV.
How does anal cancers appear?
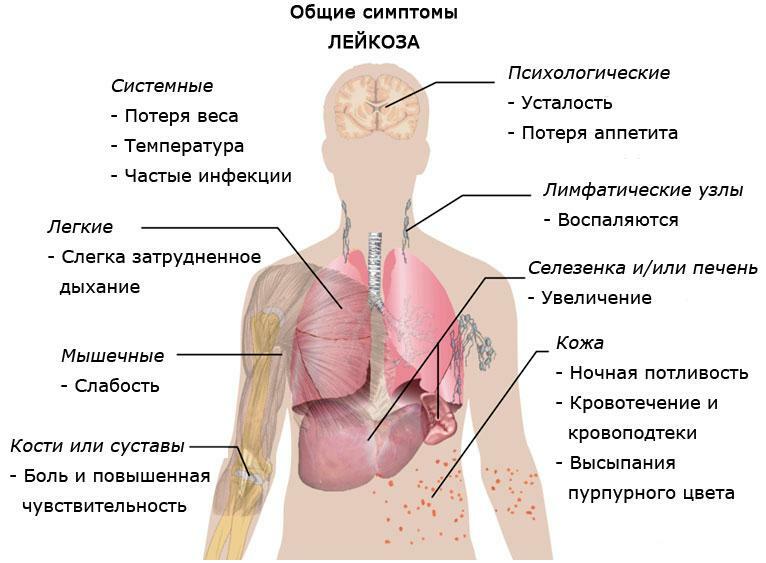
Cancer of the anal canal is marked by pronounced clinical symptoms. There is virtually no case of manifestation of cancers of the anal canal without symptoms. The most common and common symptom is the presence of scarlet blood in a person's stool. However, in case of hemorrhoids, people have exactly the same symptoms, which confuses patients and doctors and does not allow you to correctly, and the main thing is to establish a diagnosis in time. Basically, the amount of the admixture of blood is not significant, but with the damage of large vessels there is very strong bleeding. The admixture of mucus in feces is more rare. However, the presence of mucus and blood makes the clinic a disease similar to dysentery, which also often confuses doctors.
Pain in the anus is also a symptom of anal cancer. At the very beginning of the development of the disease, such pains arise only when a person goes to the toilet. Then they begin to acquire a permanent character and can flow to the genitals, the lower abdomen and thighs. Severe pain is not a fact of neglect or inoperability of anal cancer. All this is due to the high sensitivity of the anal zone. In certain patients, pain can only occur if you try to sit on a chair or any other hard surface. It is not uncommon to see such an unpleasant thing among the symptoms as constipation. They are not so much a violation of the rectum as a man's fear of going to the toilet because of those same pains in the anus. Many patients, when they turn to doctors with complaints about the presence of a tumor in the anus, complain about the sensation of "foreign body".Often you can hear complaints about such a symptom as anal itching, which is caused by irritation of the prianal area and all sorts of pathological discharge from the very anus. In 1/3 of patients there is a decrease in appetite, malaise, weight loss, weakness.
Diagnosis of anal cancer.
Due to the absence of pathognomonic symptoms and the multifaceted clinical manifestations, timely diagnosis of anal cancer is difficult. This is due to several reasons. First, the rapid increase in local symptoms, due to local spread of the tumor. Secondly, with the development of common disorders.
Finger study, prinal area examination and sigmoidoscopy are the main methods of diagnosis of anal canal cancer. In the fair sex, finger examination is supplemented with a bidigital method, which involves entering the index finger into the vagina, and the middle in the rectum. This allows you to clearly understand not only the size and boundaries of the tumor, but also to determine its relationship to the back wall of the vagina and the uterus. These data will be decisive in the choice of surgical intervention.
Recto-manoscopy provides information on the anatomical type of tumor, its location, size, displacement, and in the end, opens the possibility to conduct a targeted biopsy. All other types of research are no longer aimed at establishing a diagnosis, but rather to determine the extent of the incidence of the tumor.
All patients without exception need to perform fibroconoscopy and irrigoscopy to exclude the possibility of primary multiple tumors in the colon. Ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs and inguinal lymph nodes. To exclude the possibility of metastatic lung injury, a radiographic examination of the internal organs of the abdominal cavity is well suited. Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography can also be recommended, but only as additional research methods.
Treatment of anal cancer.
Until the end of the 80s of the last century, the most effective, or rather the only way to treat anal cancer was extirpation, supplemented with the urgent need for Duke's operation. Subsequently, a combination of low dose remote radiation therapy( 30 Gy) and chemotherapy during the preoperative period have already begun to be used. This strategy has shown very good efficiency.
The method of surgical intervention still remains the main component of cancer treatment for the anal canal. But, as a rule, all surgeons' interventions are limited to forming a colostomy and performing biopsies of inguinal lymph nodes. When the disease recurs, abdominal-perineal extirpation of the rectum is performed. Also, such an operation is performed when there is purulent-necrotic complications during the development of the tumor.
This concludes our brief review. We wish you health, both physical and spiritual. Good luck!