Granulating periodontitis
 Granulating periodontitis is a chronic ailment, prone to relapse. It manifests with sore pains, progressing with biting. In the mouth, a deep cavern in the tooth is marked, filled with a substance with an unpleasant odor. Mobility of the tooth, swelling and redness of the gum may be noted. An important aspect of granulating periodontitis is a fistula on the gum, with and without separable. X-ray transformation of the bone in the version of the "tongues of flame".The treatment of granulating periodontitis is aimed at cleansing the root system and the apical area, restoring the bone, closing the void of the canal and recreating the tooth, with normalization of its commensurate purpose. In addition, pharmacological and physiotherapy is carried out.
Granulating periodontitis is a chronic ailment, prone to relapse. It manifests with sore pains, progressing with biting. In the mouth, a deep cavern in the tooth is marked, filled with a substance with an unpleasant odor. Mobility of the tooth, swelling and redness of the gum may be noted. An important aspect of granulating periodontitis is a fistula on the gum, with and without separable. X-ray transformation of the bone in the version of the "tongues of flame".The treatment of granulating periodontitis is aimed at cleansing the root system and the apical area, restoring the bone, closing the void of the canal and recreating the tooth, with normalization of its commensurate purpose. In addition, pharmacological and physiotherapy is carried out.
Causes of granulating periodontitis
Etiological factors of granulating periodontitis are heterogeneous in pressure and contact point. It is necessary to consider them in the ratio from entering the root canal. The main agents provoking granulating periodontitis: trauma, infection, medicines. A review from the position of the action of the trauma will allow one to speak of two of its currents. Acute trauma( stroke, bruise, fall) will lead to a sharp tension of the vascular-neural weave and its death, which will cause the emergence of acute traumatic periodontitis. If treatment is unavailable, the infection will be reorganized into a chronic stage. The chronic fibrous periodontitis will develop. With a decrease in immunity, attachment of infection, the body will try to delimit the process by developing a granule around the tip. The aggressive action of microbial agents( toxins) breaks gradually the capsule, spreading with a different degree of severity. Granulating periodontitis on the x-ray is noted in the version of the "tongues of flame" against the background of this spread.
Chronic traumatism of the tooth can manifest itself in the pathology of the occlusion( overestimation).Occlusion transformations are likely after therapeutic( surplus fillings) and orthopedic intervention( the designs are not fit for bite).The congestion of the surviving teeth and in the absence of a number of standing is possible. Long-term action of the overload will cause gradual dying of blood vessels and nerves, will cause the emergence of chronic fibrous periodontitis, gradually passed into a granulomatous stage. Granulating periodontitis will develop with a combination of attachment of infection and a decrease in immunity.
The microflora plays a key role in the formation of granulating periodontitis. Primary action has a conditionally pathogenic microbial environment present in the mouth. The medium represents: streptococci, staphylococci, Veylonella, Klebsiella and others. Infectious agents are activated when the immune abilities of the body fall off. Isolating exo - and endotoxins, primary alterative transformations occur. This microflora penetrates through the crown( caries, pulpitis, periodontitis of other forms) or through the periodontal depression( with the diseases of the periodontal tissues).Another source of microbial flora penetration into the root canal through blood and lymph( pathologies of heterogeneous systems).
Iatrogenic cause of granulating periodontitis origin occupies a special concentration of the study. Errors are possible during the healing of the tooth. In the stage of processing the granulating periodontitis with burs and channel files, when breaking the apex, it is possible to push the working area of the endodontic instrumentation( it is used by manual or machine variant).When irrigation of granulating periodontitis with antiseptics( 3-5% Hypochlorite of sodium), penetration into apex can burn periodontal tissues. At the stage of closing the cavity of the tooth canal with the granulating periodontitis seal, the release of the filling substance is possible, with the use of an antidote for arsenic periodontitis( Iodine 3-5%), can cause inflammatory changes and an allergic response afterwards. Mediated effect on the genesis of granulating periodontitis: avitaminosis, metabolic defect, stress and other factors.
Symptoms of granulating periodontitis
Variations in the symptomatology of granulating periodontitis are due to the pronounced transformations locally and at the height of a single organism. General manifestations marked by the patient in the stage of protracted flow of granulating periodontitis: minor ailments, indicated by a headache, strengthening when the head tilts to the side, low rise in temperature, loss of appetite.
Local manifestations of granulating periodontitis are based on defects in the face or mouth. The patient does not notice changes in the control of his reflection;Small heat in relation to the tooth can be identified, determined by the application of the hand, a bad exhalation from the mouth. Most of the symptoms of granulating periodontitis, which are clearly hinted at the source of pain, are based in the mouth. There is a change in the color of the tooth, the presence of a deep cavity with dark contents, with the food fragment present in it. With granulating periodontitis, there may be swelling of the gums, redness. The patient gives pain at an occlusion tension, a clearly calculated pain of a grinding nature. There is also an extension in the tooth, extension of it from the arch, the tooth is mobile. When lifting the upper or lowering of the lower lip, a slight swelling in the root apex region is noted. When you press discomfort appears.
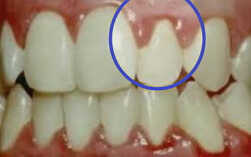
Exacerbation of granulating periodontitis provoke is capable of decreasing the immune abilities of the organism in viruses, bacterial infection, overstrain. The aggravation of granulating periodontitis along with the marked symptomatology is indicated by markedly marked feelings and phenomena. In the patient's condition: hyperthermia, more pronounced sleep and appetite defects, headaches. When visualizing the face, asymmetry and heat from the causal area. Lymph nodes are painful, enlarged. In the mouth, the symptomatology is stronger. Pain is stronger, mobility is higher in degree. With granulating periodontitis within the radius of the apex from the mucosal edge, a fistula is visualized. If there is a hole, then the presence of the separated contents is noted, without the presence of blood or with it. If the inlet to the formation is closed, then small detachments of the tissue can stand out. In the variant of pressing the tooth and opening the outlet in the formation, a small amount of exudate leaves. Also, the feeling of education will give the release of content. If the input is blocked, then the pain on the tooth will increase. With granulating periodontitis, the fistula can be noted on the face and neck. When the fistula is in the opening stage, patients note a relief of well-being, since the pus release goes from the area of the lesion. After the escalation, there is a remission with a long-term transformation.
Chronic granulating periodontitis
Granulating periodontitis is indicated by a prolonged course, with intervals of escalation and subsequent remission. Provoke an aggravation of granulating periodontitis may decrease immunity in other diseases, nervous overexertion, etc. The causes of the formation of granulating periodontitis are similar to other variants of chronic periodontitis. If we consider from the perspective of the pathogenesis of granulating periodontitis, then we can note certain features. The chronic form can be marked by an acute outcome, or independently develop under not strong influence of factors.
Regarding options for the development of granulating periodontitis. Initially there is a development of the fibrous stage, with uniform action of the damage agents. Then passes in 2 directions. The first: the organism tries to distinguish the inflammatory transformations of the apical region - a granuloma is formed. With the continuation of the time, the granuloma grows, the body continues to try to contain growth. And it lasts a number of months or years. Gradually formed swelling in the radius of the apex and breakthrough capsule. The infection spreads, penetrating the bone and beyond. Granulating periodontitis on the x-ray is manifested in the variant of "flame tongues" on the x-ray. Another option: there were events that contributed to the malfunction of immune abilities. And the body does not arrive in time to distinguish the inflammation in the capsule, using the appropriate cells. As a result, inflammatory phenomena dislocate unevenly in the radius of the apex, developing a granulating form.
With regard to the symptoms of the granulating form: grinding pain, a feeling of expansion, a change in tooth color, a cavity in the tooth with contents, swelling of the gums and redness, the presence of a fistula with exudate or without in the mouth, or on the face or neck. General transformations with granulating periodontitis: defect of health( pain in the head, sleep and appetite are disturbed), hyperthermia, increase and soreness in the lymph nodes. Visually: asymmetry of the face. The severity of symptoms increases with escalation. The granulating periodontitis on the x-ray is indicated in the dimming variant in the radius of the tip of the radix, with fuzzy uneven contours. Darkening is represented by emptiness and therefore non-radiocontrast. This object is made with pus. It is also possible to trace the course of pus as a blackout separating from the top. This will designate the direction of the fistula.
Diagnosis of granulating periodontitis
The diagnosis of the granulating form on the collection of a series of data and the conduct of various manipulations is based. Initially, they perform oral information collection: the term for the designation of manifestations, with which it dock, how the state and the maxillofacial department are transformed, the ailments transferred and the existing illnesses of relatives. An important aspect of correlating the appearance of the granulating form will be the presence of trauma, discomfort after medical work in the mouth( restorations, orthopedic constructions, endodontic work), unsatisfactory structure of dense tissues of the tooth and mucous membrane. Later, they begin the examination of the maxillofacial fragment and mouth. The facial skull and neck are examined for asymmetry, the growth and soreness of the lymph nodes, the presence of transformations of the skin( fistula with exudate and without), the degree of opening of the mouth( usually normal).
In the mouth: a tooth with a deep cavern filled with necrotic contents, a crown-root message, sounding of the canal mouths is painless, percussion is positive. Color of the tooth is changed, mobility is noted. The gums in the radius of the causative fragment are edematic, red in color, the tooth-gingival attachment is broken. The palpation of the transitional fold in the radius of the apex of the root is sensitive, the fistula is visualized with a substance of serous purulent or bloody-purulent character. Either the entrance to the fistula is closed by the outgrowths of the granulation tissue. Either a tooth with a sealed seal, however, the apical transformations in the idea of a fistula will be revealed and the corresponding manifestations too( it is necessary to designate the introduction of microbial agents through the blood and lymph).
Additional methods of examination of granulating periodontitis: electrodontometry, x-ray( contact photography, fistulography, test with a gutta-peristal pin), histological examination, general blood test. EOM: with periodontitis in the granulating stage it will show a value of more than 100 μA, which indicates necrosis. The basic method of diagnosing X-rays.
The granulating periodontitis on the roentgenogram is indicated in a variant of darkening with fuzzy boundaries, with uneven dislocation from the apex. A sample with a gutta-peristal pin as a subspecies of contact radiography is defined in the attachment to the causative tooth of a gutta percha pin, smaller in diameter of the channel lumen, careful advance to the stop, X-ray examination. This method will show the direction of the stroke for the fistula to be separated.
Fistulography: the method of X-ray diagnosis of granulating periodontitis under the influence of contrast preparations of various substances to determine the movement of fistulous moves. Produce an introduction of a slow drug through the entrance to the fistula, to the obstruction. Then the radiography in the facial and profile is performed. Histological examination of exudate for differentiation with actinomycosis and other ailments. Taking the material: scraping, smear-imprint, smear-reprint. Separately about exudate: serous-purulent. This means that the initial inflammation, within the radius of the periodontal top, marked in the phase of exudation by the development of a serous response, began to be reconstructed into a purulent topic. And, accordingly, this restructuring structure moves to the release from the cavity of the tooth. Bloody-purulent exudate: the contents of a purulent nature, the inflammatory process is supplemented by the destruction of small capillaries along the course of the movement of destructive phenomena. A general blood test will mark the relative leukocytosis and an increase in ESR slightly. According to the need of the patient sent to the reception to another specialist( suspicion of the source of pathological changes in another organ).
Treatment of granulating periodontitis
Therapeutic measures of granulating periodontitis are aimed at securing the release of a purulent substance, disinfection of the canal, restoration of the broken bone in the radius of the apex, closing of the radix seal space, restoration of the crown( restoration, orthopedic construction).Release of a purulent secretion is performed by cutting the entrance to the fistula. Additional palpation of the regional gum leads to a greater secret. There is relief of discomfort. If necessary, put anesthesia. In the cavity of the tooth, an autopsy is performed, an opening( if there is a seal), an expansion of the cavity, with detritus removal, mechanical cleaning of canals with manual and machine endodontic files. Simultaneously with the physical action, the means for removing the lubricated dentine layer are applied( the action of the chemical components: Verifix, Canal-glide).Perform antiseptic irrigation of the root system alternately with the effects of files( Belodez 3-5%, Chlorhexidine bigluconate 2%).
Antiseptic substances( Cresofen) are introduced for better disinfection of the channels for several days. In the future, a secondary purification is performed and a preparation is selected for repositioning the bone and closing the void in the apical part. To restore bone, osteotropic materials( Metapex, Calceppt) are used, which also have an antiseptic effect. Substances containing calcium are administered from 2 weeks to several months. Use more often X-ray contrast preparations. After a while, secondary treatment is performed in the root system. Select the substances for permanent fixation in the radix( gutta-percha, paste), sealed by the chosen method. X-ray monitoring is carried out. An important aspect after the introduction of drugs shortly in the root, close the mouth temporary seal. After a permanent root filling after a couple of days, the functional integrity of the crown is restored. With respect to the destroyed crown, restoration is carried out, with preliminary bleaching, or the orthopedic stage is started( installation of KShV and crowns, and other structures).In case of exacerbation of granulating periodontitis in the first visit, in addition to anesthesia, after opening the canals, a tooth in the form of an opening is left for 2 days and salt rinses are prescribed.
Drugs, for blocking the inflammatory manifestations of granulating periodontitis: antibiotics of a wide range of effects( tsiprolet), nonsteroidal agents for inflammation( Diazolin), analgesics( Ketanov) and antipyretic drugs( Panodol), if necessary. All drugs are taken strictly according to the instructions given the condition. Add physiotherapy is not in the escalation period: UHF, magnet, laser. If it is impossible to conduct only a therapeutic intervention, I add surgery. Perform a resection of the tip of the radix( then close the channel with a filling of ¾ length) or tooth-preserving measures( amputation of the radix, hemisection).If it is not possible to conduct all types of intervention, extraction is indicated.