Types of disorders of cerebral circulation

Under the cerebral circulation is understood the blood circulation in the vessels feeding the central nervous system - the brain and spinal cord.
Nowadays various types of pathologies of cerebral circulation are diagnosed more and more, which is connected with a number of reasons.This is a bad ecology, and bad habits, and poor nutrition, and a sedentary lifestyle and genetically determined diseases.
Table of contents:Why are cerebral circulation disorders developing?
Among the immediate causes that result in impaired blood flow to the central nervous system include:
- Vessel inflections;
- significant narrowing of the lumen of the arteries;
- thrombosis( occlusion of clot lumen);
- embolism;
- aneurysms.
One of the leading causes leading to hemorrhage into the brain tissue and the formation of a hematoma is a significant increase in blood pressure.With a sudden jump in blood pressure, a rupture of the blood vessel is possible.
 A rupture of arterial aneurysm - protrusion on the vascular wall, devoid of a powerful elastic and muscular base, is less common in clinical practice.Even a relatively small increase in BP against a background of low physical exertion or psychoemotional stress may well cause a rupture of the pathologically altered portion of the vessel wall.
A rupture of arterial aneurysm - protrusion on the vascular wall, devoid of a powerful elastic and muscular base, is less common in clinical practice.Even a relatively small increase in BP against a background of low physical exertion or psychoemotional stress may well cause a rupture of the pathologically altered portion of the vessel wall.
Note: if the aneurysm is localized in the vessel of the brain envelope, then an intracerebral and subarachnoid hemorrhage develops.
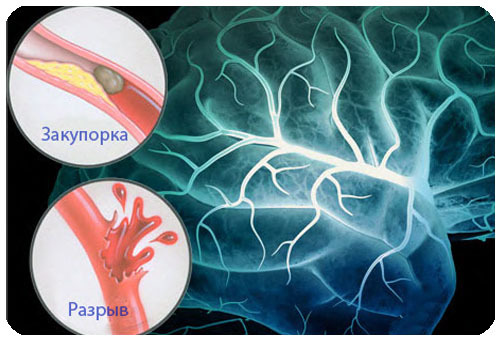
Clogging of the main vessels usually leads to the detachment of a thrombus or infiltrate formed on the heart valves during inflammation.Emboli with blood flow migrate to the cerebral vessels and clog the one whose diameter of the lumen is less than the diameter of the thrombus.Embolus may be a fragment of an atherosclerotic plaque.The occlusion of the vessel leads to the fact that the feeding of the brain region stops.In such cases it is customary to talk about the embolic mechanism of the development of ischemic stroke.
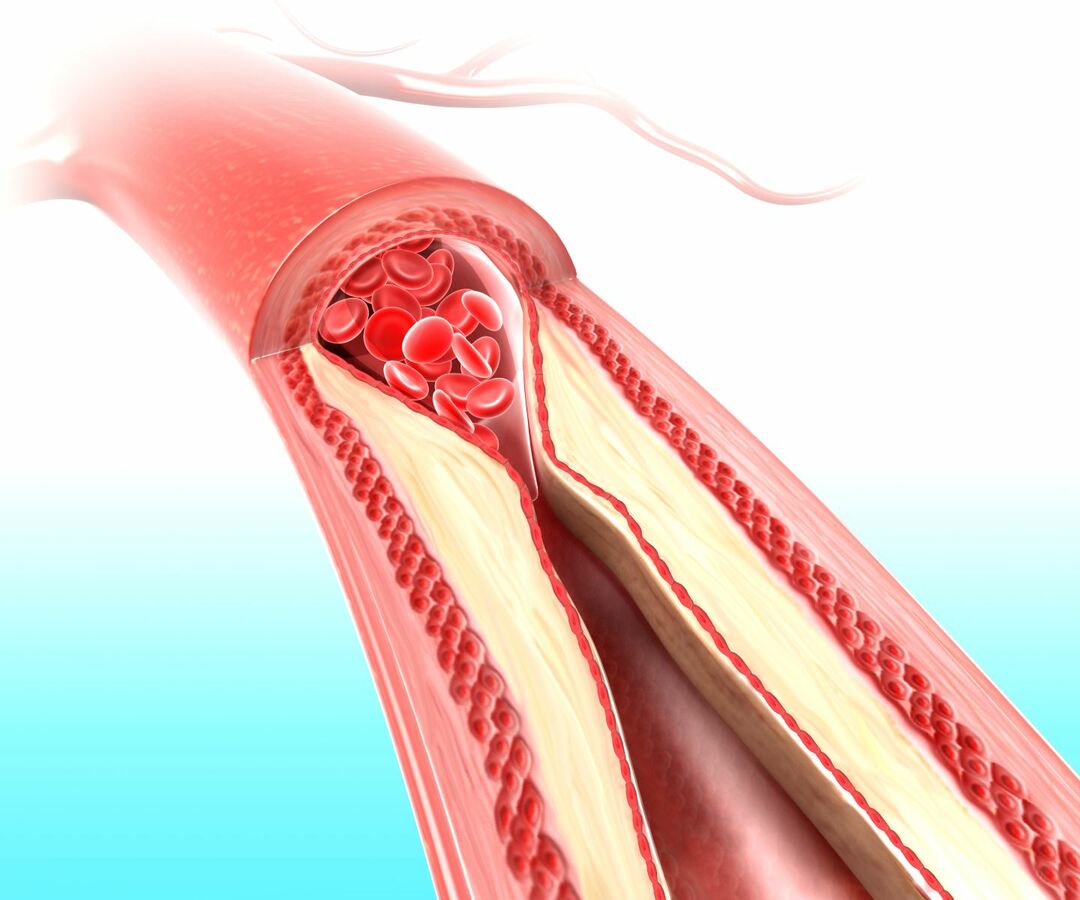
A thrombus can gradually form directly in a cerebral vessel in the immediate vicinity of an atherosclerotic plaque.Gradually, the plaque fills the lumen, which causes a slowdown in blood flow.The wall of the vessel in the zone of atherosclerotic lesion has an uneven surface, which additionally promotes the aggregation of platelets.The combination of local factors with the slowing of blood flow and causes a thrombosis of the vessel with the subsequent development of cerebral circulation disorders in the form of ischemic stroke.
Blood supply to the brain is often violated against the backdrop of spasm of musculature of the vascular walls.
Complete occlusion of the main vessel is not a prerequisite for the development of a cerebral infarction.In a number of cases, for an insufficient supply of blood to a certain area, it is enough to bend the vessel.
The mechanism of development of cerebral circulation disorders in the form of transient ischemic attacks( "micro strokes") resembles the mechanism of ischemic stroke, but in the first case compensatory mechanisms work adequately for several hours.
Symptoms of cerebral circulation disorder
We recommend to read:Depending on the individual characteristics of the patient, his age, the area that is fed by the affected vessel, and the mechanism and severity of the process, pathological changes in the tissues also differ.Accordingly, the clinical symptomatology can also vary.
According to the accepted classification, all morphological changes are divided into diffuse and focal.
Focal disorders of the cerebral circulation:
- ischemic stroke;
- hemorrhagic stroke:
- subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Important: ischemic stroke is often called "cerebral infarction" by doctors.
Diffuse disorders of cerebral circulation:
- small necrotic foci;
- fine-particle material changes;
- hemorrhages of small size( single and multiple);
- small cystic lesions;
- gliomesodermal scar changes.
With pathology of the cerebral circulation, the patient often has only subjective symptoms, which include:
- headaches of varying intensity;
- dizziness;
- sensitivity disorders of different locations.
 Objective neurological symptoms may not be detected.
Objective neurological symptoms may not be detected.
Local sensory dysfunctions, development of organic symptoms with preservation of CNS functions, motor disorders( eg, hyperkinesis or paralysis), epileptiform seizures, memory or cognitive impairment are also possible.
By the nature of development, all pathologies of this category are divided into:
- slow progressing( dyscirculatory encephalo- or myelopathy);
- initial( transient ischemic attacks and hypertensive crises);
- acute( strokes and subarachnoid hemorrhages).
Note: transient ischemic attacks as people far from medicine, and practicing doctors are often called "micro-insults".
Signs of chronic slow progressing disorders
Circulatory encephalopathy is a pathology characterized by gradual progression.It is caused by impaired cerebral vessels.In this disease, focal structural changes in subcortical areas are formed.
General clinical features of dyscirculatory encephalopathy:
- severe headaches;
- increased irritability;
- occasionally occurs dizziness;
- reduced memory capacity;
- coordination disorders;
- diffuse;
- insomnia;
- depression.
Dyscirculatory encephalopathy develops gradually;There are 3 consecutive stages.
-
 The first stage is characterized by a syndrome, in many ways reminiscent of the asthenic form of neurasthenia.There is no decrease in intellectual abilities.
The first stage is characterized by a syndrome, in many ways reminiscent of the asthenic form of neurasthenia.There is no decrease in intellectual abilities. - In the second stage, the symptomatology progresses.There is a slight decrease in intelligence, and organic symptoms are manifested - trembling of limbs, coordination disorders, paresthesia, as well as mild dysarthria.The patient with the second stage determines pathological reflexes.
- At the third stage of the progression of mental disorders( up to the development of dementia).The patient is diagnosed with neurologic syndromes - cerebellar ataxia, parkinsonism, etc., which indicates a focal brain lesion.There is a possible sharp deterioration in the condition, in which there are signs similar to the manifestations of a stroke.
Discirculatory myelopathy, caused by circulatory disorders in the spinal cord, also progresses gradually.
Symptoms of discirculatory myelopathy
Discirculatory myelopathy is a lesion of the spinal cord of vascular genesis, manifested as pelvic disorders, sensitivity disorders, various paresis.It also progresses gradually.
Disorders of the spinal cord blood circulation usually take the form:
- of the Persona-Turner Syndrome, in which discirculation occurs in the zone of the shoulder-shoulder arteries, which leads to paresis of the muscles of the hands and pains in the cervico-brachial region.
- of the Preobrazhensky Syndrome characterized by dyscirculatory disorders in the region of the anterior cerebral artery
The development of this type of cerebral circulation disorder includes 3 stages of the :
- compensated;
- is subcompensated;
- decompensated.
At the initial stage, the patient is determined by increased fatigue or weakness of the muscles of the arms and legs.In the second stage, pathological changes become more noticeable, reflexes and paresthesia are added.Decompensated stage is characterized by the appearance of disorders from the pelvic organs( stool and urine retention), as well as the development of paresis of various localization and paralysis.
Symptoms of initial cerebral circulatory insufficiency
Initial signs of cerebral circulatory insufficiency usually develop on the background of mental or physical stress or exposure to unfavorable conditions( with lack of oxygen or high temperature in the room).
The main signs of initial failure are:
-
 sensation of noise in the head;
sensation of noise in the head; - significant reduction in efficiency;
- intermittent or persistent headaches;
- sleep disorders;
- daytime sleepiness.
The emergence of such clinical signs of cerebral circulation disorders is the basis for a comprehensive medical examination to identify possible atherosclerotic vessel changes, hypertension( high blood pressure), and vegetative-vascular dystonia.

Transient disorders of the cerebral blood supply are characterized by cerebral or focal signs, which persist for no more than 24 hours.
Transient ischemic attacks are transient disorders of cerebral circulation caused by insufficient blood flow to certain parts of the central nervous system.
Symptoms of transient ischemic attacks:
- speech disorders;
- problems with coordination of movements and statics;
- double vision;
- flashing "flies" before the eyes;
- paresthesia( impaired sensitivity of the limbs);
- feeling of weakness.
Important: If you notice that your friend or colleague answers inappropriately, drops objects or moves insecurely, he probably needs urgent medical attention.Many signs of "micro-strokes" are similar to those in alcoholic intoxication.
Hypertensive crises, leading to circulatory disorders in the brain, are caused by a spasmodic increase in blood pressure.
Symptoms of hypertensive cerebral crises:
- intense headache;
- feeling of nausea;
- vomiting( not always);
- dizziness.
If a typical neurological symptomatology is diagnosed in a patient for more than 24 hours, a "stroke" is diagnosed, ie, it is already an acute impairment of cerebral circulation.
Signs of acute disorders
Symptomatic of ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes, thrombosis of venous sinuses, as well as venous hemorrhages is similar to the clinic of transient cerebral circulatory disorders, but neurological symptoms are diagnosed within a day or more.
Important: in most cases, strokes develop early in the morning or late at night.A patient with suspicion of this acute circulatory disorder often needs hospitalization with placement in a neuroreanimation unit.
Ischemic strokes are caused by the cessation of blood flow to the areas of the brain due to blockage or a sharp spasm of blood vessels.
Hemorrhagic hemorrhages are caused by a hemorrhage into the brain tissue when the integrity of the vascular wall is violated.
Ischemic changes increase gradually over a period of several hours( in some cases, up to a day).Hemorrhagic stroke develops almost instantaneously.With him, the patient has an intense headache and loss of consciousness.
Important: for any stroke is characterized by severe impairment of sensitivity and paralysis, often unilateral.When the lesion is localized in the right hemisphere, the left side of the body suffers and vice versa. The patient usually develop visual impairment and articulation.
Subarachnoid hemorrhage develops against the background of rupture of the aneurysm of the vessels of the arachnoid membrane.It is usually not accompanied by the appearance of neurological symptoms.A characteristic feature is the intense headache of the "dagger" character and loss of consciousness.
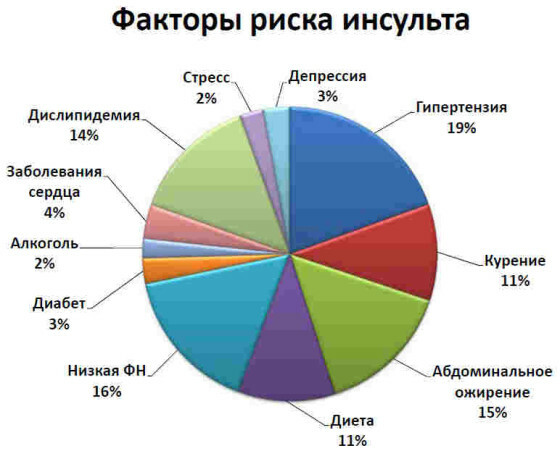
Factors that increase the risk of development of ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes:
- elevated blood pressure;
- smoking;
- alcohol abuse;
- use of oral contraceptive pills;
- myocardial ischemia;
- blood disorders( coagulation disorders);
- atherosclerotic vascular lesions;
- overweight and obesity( especially - in combination with atherosclerosis);
- disorders of microcirculation in peripheral arteries;
- disorders of lipid metabolism( fat metabolism);
- physical inactivity;
- regular stress;
- presence of strokes in the anamnesis.
For more information on the forms, symptoms and methods of treatment of cerebral circulation disorders, you will receive a video review:
Plisov Vladimir, medical reviewer