Gigantism
 Gigantism is a disease characterized by a clinical syndrome that occurs as a result of increased production of growth hormone in childhood or adolescence, and is also manifested by a sufficient increase in the body, especially in length. There is also partial or partial gigantism, which develops due to increased sensitivity in individual locations of tissue receptors to somatotropin. But genetic gigantism or constitutional, anomaly is not considered.
Gigantism is a disease characterized by a clinical syndrome that occurs as a result of increased production of growth hormone in childhood or adolescence, and is also manifested by a sufficient increase in the body, especially in length. There is also partial or partial gigantism, which develops due to increased sensitivity in individual locations of tissue receptors to somatotropin. But genetic gigantism or constitutional, anomaly is not considered.
Generally, gigantism appears as a result of pituitary adenomas, which produce growth hormone;Hypogonadism;Syndrome Klinefeltera( with delayed puberty with preservation in the bones of growth zones).
Gigantism is diagnosed on the basis of external data of patients;Radiological, neurological, ophthalmological studies;Determination of pituitary hormones in the blood, as well as family history.
With adequate treatment methods, the prediction of gigantism is relatively favorable, but at the same time, their ability to work is reduced in patients. In most cases, patients with gigantism are infertile.
Gigantism of the causes of
In 99% of cases, as K. Benda first described in 1900, the etiology of gigantism has a connection with the tumor, somatotropinoma, which develops from the eosinophils forming the somatotropic hormone( STH).Somatotropinomas, as a rule, refer to benign pathologies, however, sometimes they can be invaded. Basically, they are localized in the adenohypophysis, but can be located in the gastrointestinal tract, pancreas, parapharyngeal areas, bronchi and sinuses of the main bones.
Almost one percent of gigantism occurs as a result of hyperproduction of somatocrine of the hypothalamus and hyperplasia of growth hormones.
Among the risk factors that can cause eosinophilic cells to hyperplasia, even pregnancy is considered. Macro-adenoma is the cause of the disease in 90% of cases, and 9% falls on the adenohypophysis microadenoma. The rare cause is the "empty Turkish saddle" syndrome. Also, the appearance of gigantism can be affected by the increased sensitivity of the tissue receptors of the epiphyseal cartilage to the growth hormone.
There is a model of genetic pituitary gigantism. At the heart of this species are somatic mutations in somatotrophs, which cause a neoplastic reaction.
Excessive amount of STH leads to the growth of not only tissues and organs, but also hypertrophies of the kidneys, myocardium, develops erythropoiesis and promotes the healing of wounds.
Giantism Symptoms
Gigantism is classified into infantile and acromegaly forms. And also two stages of the disease, such as stable and progressive, are distinguished.
The clinical picture of gigantism consists of complaints of adolescents in the form of weakness, dizziness, almost permanent headaches, poor memory, pain in the extremities and increased heart rate. In girls, there is an excessive increase in the growth and size of the foot, mammary glands develop poorly, and hyposexuality is noted in young men. Very much attracts the surrounding growth in girls over 190 cm, and boys - over 200 cm
Sometimes in the symptomatology of gigantism in the foreground is a rough appearance with the general infantilism of man. In addition, young men sometimes have macrogens. Patients with gigantism have a body mass that corresponds to growth, and the limbs are somewhat elongated.
The psychic of many patients is characterized by a certain underdevelopment in the form of average abilities, childishness, propensity to depressed state and persecution mania.
People with gigantism always outpace others physically. Somatic organs are large, but this is usually imperceptible with high growth. But the size of the heart does not have time to grow behind the growth of the body, so there are dizziness and fainting.
Depending on hypertrophy and hyperplasia of soft tissues, macroglossia, diastema and laryngeal enlargement are noted. All this leads to changes in the timbre of the voice, i.e. It sounds from the depths, very low. Also, the ears, lips and nose increase, and the lower jaw is advanced forward( prognathism).As a result of sinusitis, the mouth is often in a semi-open position, resulting in the appearance of characteristic folds on the face. The skin becomes warm, moist, oily, hyperpigmented, and sometimes there are polyps, sebaceous cysts, acanthosis and hypertrichosis. The size of the head and foot increases. Sometimes diagnose kyphoscoliosis.
The functions of the organs are mostly preserved, but gigantism still leads not only to cosmetic problems, but also to metabolic problems. Such patients occasionally develop euthyroid goiter, as well as autoimmune thyroiditis. Diffuse toxic goiter is less common.
Gigantism lowers the perception of glucose by the type of latent and overt diabetes, with resistance to conventional methods of therapy, and also to insulin therapy. But the secretion of growth hormone hyperglycemia does not suppress.
Almost 30% of young people have reduced potency and libido, and girls are broken monthly. In addition, all patients have hyperprolactinaemia.
In case of poorly treatable cases, hypogonadism of the secondary plan develops.
Gigantism can cause complications that are manifested by panhypopituitarism, the development of acromegaly, diabetes, sexual dysfunction, myocardial dystrophy, and increased blood pressure. In more severe forms, patients lose sight. Somatotropinoma can pass into the malignant adenocarcinoma of the pituitary gland.
Partial Gigantism
This is a disease that affects individual parts or half of the body as a result of embryogenesis or neuropathic disorders.
Partial gigantism is extremely rare, therefore the reasons for its development have not been studied enough. But there are certain theories that try to allegedly explain the emergence of partial gigantism. These include: mechanical, embryonic and neuro-trophic theories.
In the first case( mechanical theory) partial gigantism can be formed as a result of squeezing certain parts of the fetus during pregnancy, as well as the incorrect position of the baby in the uterus, can contribute to stagnant phenomena in any part of the body, and from here to provoke their increase.
The embryonic theory explains the increased growth of the organ or part of the body due to disturbances during the laying of the organism at the genetic level.
The neuro-trophic theory asserts that partial gigantism develops under the influence of special influences of a neuro-trophic character on a specific department of the organism. In this case, the main factor can be the defeat of sympathetic fibers.
Partial gigantism is sometimes diagnosed with changes that occur in the endocrine system, but this can not be the basis for finding its pathogenesis in the endocrine sphere.
For the treatment of partial gigantism, surgical treatment is applied to the enlarged parts of the body or organs.
Giantism in children
This is a disease that occurs when chronically overgrowth with growth hormone growth hormones - STH or somatotropin. With the early onset of the disease, when bone growth areas remain uncovered, gigantism is formed in children, i. E.Very high growth. If the disease begins to develop after the closure of these zones, then it is characterized by signs of acromegaly. The combination of gigantism and acromegaly is observed mainly among adolescents. At this age, the disease is more common among young men than girls.
Children's gigantism, which occurs with excessive amounts of growth hormone as a result of pituitary production, can be found extremely rarely. The cause of its formation is a pituitary tumor of benign etiology. There are suggestions that sometimes gigantism can develop due to the growth of the tumor process in some parts of the hypothalamus, which are responsible for the constant state of the internal environment of the body, its needs, etc. It has been proved that tumors provoke an increased production of somatotropin.
As a rule, a rapid increase in the child's growth becomes evident from eight to fourteen years, and sometimes such changes occur even at the age of five. The final length of the body can reach 250 cm and the limbs have relatively long dimensions in relation to the body.
After cessation of growth in children, the signs of acromegaly join the pathology( increase of all organs), which is manifested by an increase in the limbs and face. The size of the skull becomes significantly larger, the nose widens, the chin sinks down, and the tongue increases. As a result of the increase in the lower jaw, the teeth are very rare, and the face looks rather rough. The fingers on the upper and lower limbs grow in width, and the legs and arms become thick and resemble a shovel. There is also a curvature of the spine in the form of kyphosis.
Very quickly, these children get tired, they have signs of delayed puberty. In addition, there are severe pain in the head, weakness, which later goes into violation of consciousness. And for ophthalmological examinations, the absence of side vision is diagnosed.
When carrying out laboratory tests, an increased content of somatotropin in the blood is almost 400 ng / ml. And also recorded its increase during sleep.
A tumor that continues to grow can disrupt gonadotropin production processes that are involved in sexual functions;Hormone, stimulating the work of the follicle;Prolactin and LH.
On the roentgenogram, you can see how the bones inside the skull and paranasal sinuses expand, which are located in the face area. Very often there are mesh drawings of the bones of the fingers on the limbs and thickening of the bone on the heel. The tumor continues to develop slowly enough, so the disease can last for many years.
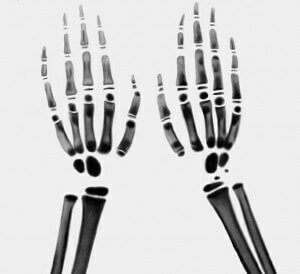
But children can also observe macrodactyly, i.e. A congenital form of gigantism. This pathological disease is caused by the processes of violation of volumetric and linear parameters of the extremities. They can acquire sufficiently large sizes.
There are three forms of gigantism in children in this form. The first form includes congenital pathology, in which soft tissue predominantly increases. In this case, it has distinctive characteristics, such as the increased length and volume of all segments on the affected limb with a sharp increase in the surface of either the hand or the foot( the limb acquires an ugliness).In addition, the degree of soft tissues increases with respect to the bones of the skeleton in length and width, which does not coincide with the age norm. Clinodactyly is also observed in the area of the interphalangeal joint and metacarpophalangeal affected finger or fingers, as well as hyperextension in them.
The second form of the disease is characterized by congenital gigantism, in which there is an increase in bone content. This type of pathology is manifested by an increase in the size of the length of the altered segments of the limb( the appearance of the soft tissues is not changed).And the bones of the skeleton in their enlargement, especially in length, exceed the increased degree of soft tissues, which also distinguishes them from the age norms. Clinodactyly is observed in the metacarpophalangeal and interphalangeal joints on the affected fingers, but hyperextension is completely absent.
With the third form of true innate gigantism, short muscles are mostly affected. Gigantism in this case is manifested by an increase in the length of the limb segment, which has suffered lesions due to the metacarpal bones. The volume of soft tissues increases, the feet and palms expand considerably as a result of the formation of gaps between the metacarpal bones. Also, if you compare the increase in the age grid, then they do not meet the standards. Clinodactyly and flexural contracture are found in the metacarpal and phalangeal joints, and sometimes there is an openness in the joints of the first finger.
Children under ordinary gigantism are assigned surgical treatment after confirmation of the tumor process. As a rule, gigantism in children with varying degrees begin to be treated from six or seven months. Basically, they can reduce the length of the finger to normal size, using a shorter resection for metacarpal bones and phalanges. Clinodactyly of deformed fingers is eliminated with simultaneous shortening. Syndactyly is treated after a complete restorative course of the altered fingers to their normal length.
When the finger is increased by almost 300% or more from the norm, the only effective manipulation is performed - this is an amputation. Sometimes they offer a microsurgical operation in the form of a finger transplant, for example, from a healthy foot to an affected hand.
In the first form of the disease, surgical intervention is performed using lateral resection of phalanges. At the second - the central resection of the phalanx. At the third - the metacarpal bones are brought together in different fixation. This will depend on the pronounced strain and age of the child.
During the operation, the accompanying deformities are corrected: the excess of soft tissues is excised, the hyperextension of the deformed fingers is eliminated and the looseness is present.
All these orthopedic and surgical techniques allow to bring the injured hands and feet of children closer to the physiological norm, and also to preserve their anatomical proportion.
Treatment of gigantism
To treat this disease, complex therapy should be applied taking into account the stage, shape and phase of gigantism. As a rule, the treatment of gigantism is aimed at the processes of reducing the level of growth hormone( somatotropin) in the blood by suppression, destruction or removal of the activity of the STH-secreting tumor, which can be achieved by modern and traditional methods of treatment. Correctly chosen method of treatment prevents the development of various complications. And in their presence, the main method of therapy involves the means that correct violations in the neurological and endocrine system.
Gigantism begins to be treated with the appointment of a diet, where the proteins are limited and calories are counted. In addition, the basis of treatment can include: drug therapy, radiation and surgical intervention.
The blockade of production of somatotropin is achieved with the help of Dopamine antagonists( Lergotril, Lizurgida, Parlodela, Bromocriptin, Metergoline, Dostinex and L-dopa) or analogues of STG( Sandostin), which are used for many years or for life. At the time of cancellation of these drugs, the level of somatotropin increases, and gigantism again turns into progression.
In adenocarcinoma, and if there is a threat of blindness or a wedge-shaped tumor is destroyed, a radical transsphenoidal hypophysectomy or cryo-hypophysectomy is performed using liquid nitrogen.
For beam irradiation use proton beams, heavy L-particles, teletemmatherapy and, last but not least, use pituitary X-ray therapy.
Good results can be achieved by implantation into the pituitary gland of radioactive needles made of gold, iridium and yttrium.
The form of gigantism without a tumor is treated with Testosterone, which makes it possible to close the areas of bone growth.
In the formation of pathology in the thyroid gland or the appearance of diabetes mellitus, appropriate therapy is prescribed.
With the preventive purpose it is necessary for patients with gigantism to avoid infections, various cranial traumas, not to use anabolic steroids and questionable in composition nutritional supplements for sports and muscle building. The younger generation should preferably limit their use of mobile phones. In addition, constantly undergo anthropometric control, especially from 13 to 16 years.
At the moment of the adorable development of gigantism, to stop excessive growth, Testosterone is used with X-ray control of bone growth zones.
People suffering from gigantism are in the dispensary group and under the supervision of an endocrinologist, neurologist and oculist. Such patients with endocrinology are never removed.
Pregnant women with gigantism are not recommended for abortions. If during the first pregnancy the child develops gigantism, then the subsequent ones are very undesirable. It is important to remember that somatotropinoma refers to a neoplasm in the brain. It can provoke compression inside the skull. Therefore, patients with gigantism should be treated as an oncological patient.