Edema Quincke
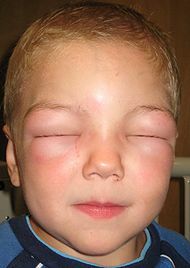
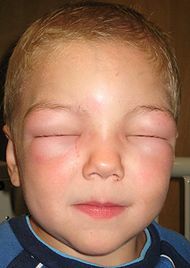 Quincke edema( angio-edema, giant urticaria, trophoneurotic edema, angioedema) - a sudden, sudden acute allergic reaction of the body, characterized by massive swelling of the mucous membranes, skin and subcutaneous fat. Quincke's edema usually develops on the neck, upper body, face, back of the feet and / or brushes. Quite often, Quincke's edema affects the internal organs, joints and membranes of the brain. This pathological manifestation can develop absolutely in any person, but most often occurs in young women and in children.
Quincke edema( angio-edema, giant urticaria, trophoneurotic edema, angioedema) - a sudden, sudden acute allergic reaction of the body, characterized by massive swelling of the mucous membranes, skin and subcutaneous fat. Quincke's edema usually develops on the neck, upper body, face, back of the feet and / or brushes. Quite often, Quincke's edema affects the internal organs, joints and membranes of the brain. This pathological manifestation can develop absolutely in any person, but most often occurs in young women and in children.
Edema Quincke - causes of
There are two types of Quincke edema: pseudo-allergic and allergic.
The development of pseudoallergic edema of Quincke is due to the congenital pathology of the compliment system. For reference: compliment system is blood proteins involved in the development of primary allergic and immune reactions. These proteins in the human blood are in an inactive state, being activated exclusively in case of penetration of a foreign antigen in the place of the penetration itself. With pseudoallergic Quinck's swelling, the compliment system can be activated both spontaneously and in response to chemical or thermal stimuli, leading to the development of an extensive allergic reaction.
Quinck allergic edema, as in other and allergic reactions, arises from the immune response of the body to the penetration of a specific allergen. Quincke allergic edema often accompanies such diseases as hay fever, hives, bronchial asthma and food allergies.
Quincke edema in infants and young children is extremely rare. Predisposing factors in the development of this pathological condition can be diseases of the thyroid gland, liver, stomach, parasitic and autoimmune diseases and blood diseases. Quite often, angioedema develops a recurrent chronic course. Quite often the exact cause of the edema of Quincke can not be established
Quincke Edema - symptoms
The disease always begins suddenly. In a few minutes( less often hours) in different parts of the face and mucous membranes there is a development of pronounced edema. Typical symptoms of Quincke edema are local edema of the oral mucosa( tonsils, soft palate, tongue), eyelids, lips, scrotum, urogenital area, gastrointestinal tract, respiratory tract. Rarely, edema is accompanied by painful sensations, manifested by a feeling of tension in the tissues. The skin in the area of the edema is pale, itching is usually absent. In the region of the edema, the tension of the tissues is palpable when palpation, the pits do not remain with pressure, the swelling itself is painless.
The main places for the localization of edema Quincke - larynx, cheeks, eyelids, lower lip. The most dangerous form for the life of Quincke edema is edema of the trachea, larynx and pharynx, which is observed in 25% of all patients with this pathology. In such patients, aphonia develops, cyanosis of the tongue is observed, difficulty breathing occurs, anxiety arises, and loss of consciousness is possible. When examining the mucous throat, there is swelling of the palatine arch and soft palate, the lumen of the pharynx is narrowed. If the swelling spreads to the trachea or larynx, a fatal outcome is possible due to suffocation.
If Quincke's swelling affects the internal organs, the symptomatology is manifested by vomiting, diarrhea, severe abdominal pain. With damage to the meninges and the brain, neurologic disorders develop( hemiplegia, aphasia, epileptiform seizures).
Quincke edema in children manifests itself as delimited edematous foci on the mucous membranes and skin integuments.
Quincke's edema disappears without leaving a trace in a few hours or days, but often recurs periodically
Possible complications with swelling Acquisition
Perhaps the most threatening complication is laryngeal edema with the increasing symptoms of acute respiratory failure, which include progressive breathing difficulty, barking cough and hoarseness.
In case of defeat of the edema of the urogenital system, the symptomatology of acute cystitis appears. In addition, edema can lead to acute urinary retention.
With edema of the gastrointestinal mucosa, it is possible to simulate acute abdominal pathology, dyspeptic disorders may occur, and intestinal peristalsis may increase. Symptoms of peritonitis and acute pain in the abdomen can often be observed.
This localizationedema of the face, in the process may be involved with the advent meninges meningeal signs and symptoms of Meniere's syndrome( vomiting, nausea, dizziness).In the absence of timely qualified emergency care? Quincke's swelling of this localization often entails a fatal outcome.
Quincke's edema is diagnosed on the basis of the presence of characteristic visual manifestations and the reaction of edema to the injected adrenaline. It is very important in the diagnostic process to determine the root cause, which has become a catalyst for the development of edema, for which skin allergological tests and laboratory blood tests are usually used. Also, it is imperative to make a differential diagnosis with syndrome Melkersson-Rosenthal, erysipelas, collateral edema at periostitis and lymphostasis
Angioedema - first aid
• When edema of airway mucosa( asphyxia) - injection
epinephrine • By reducing blood pressure shown subcutaneous administration of0.1 to 0.5 adrenaline r
• Desensitizing treatment. It involves taking antihistamines: intramuscular injection of 2 ml of 2% suprastina orally Telfast, Erius, Zyrtec, Claritin
• Hormonal therapy: corticosteroids( intravenous from 8 to 12 mg deksazona, intramuscularly from 60 to 90 mg prednisolone)
• inhibitors Formulations proteases
• Diuretics
• detoxification therapy( enterosorption, hemosorption)
• mandatory hospitalization in department of allergy
Phased treatment angioedema
• The immediate therapeutic stage is necessarilyYelnia eliminating direct contact with provoking allergen
• In order to improve the tone of the sympathetic nervous system prescribed calcium preparations efidrin, ascorbic acid
• To reduce histamine levels prescribed Tavegil, Suprastin, diphenhydramine. Parasympathetic activity is reduced using atropine
• To reduce vascular permeability is carried vitamin( Ascorutin etc.)
• Displaying a course of treatment of gamma globulin and B vitamins as well as desensitization therapy prednisolone, cortisone and ATKG
• For the treatment of hereditary angioedema usedDrugs that enhance the body's production of the missing C-1 inhibitor
Prevention of edema Quincke implies strict adherence to a diet in which there is nofoods that can cause allergic reaction. In the case of forced contact with allergens, it is necessary to take antihistamines prescribed by the doctor in a timely manner.