Laparoscopy in gynecology: indications and benefits
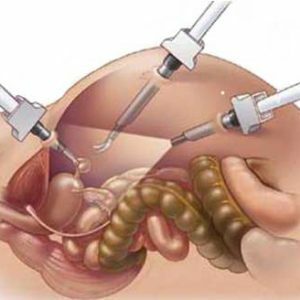 The laparoscopic method is the ability to carry out medical manipulations within the human body with the help of a laparoscope - a modern device with an optical system that allows physicians to look even to remote corners without requiring large cuts for this.
The laparoscopic method is the ability to carry out medical manipulations within the human body with the help of a laparoscope - a modern device with an optical system that allows physicians to look even to remote corners without requiring large cuts for this.
Gynecology is one of the fields of medicine where laparoscopy took an honorable place and helped to solve not one problem of female health - in diagnostics, if, despite the high professionalism and experience of the doctor, it is difficult to diagnose the diagnosis, and in treatment, significantly reducing the operational traumatization of tissues.
Table of contents:Essence of gynecological laparoscopy
Both diagnostic and therapeutic laparoscopy relate to operative methods of gynecology - in order for the laparoscope to be inserted into the small pelvis, cuts must be made in the anterior abdominal wall.This is also a traumatization of tissues, but not comparable with traumatism in the open surgical procedure - , the diameter of laparoscopic access is about 0.5 cm, unlike laparotomy incisions of 8-10 cm and more.
In order for the laparoscope to be inserted into the small pelvis, 2 incisions are usually done in the anterior abdominal wall:
- , one of them introduces a laparoscope - a thin tube that has a lens( lens system) at one end,, And on the other - an eyepiece for observation by a doctor.Or on the other end of the device, which is immersed in the patient's cavity, fix the video camera, which transmits the picture to the monitor or screen;
- through another incision is introduced the functional part of the laparoscopic system - the one that will be used for proper manipulation( clamps, devices for electrocoagulation and so on).
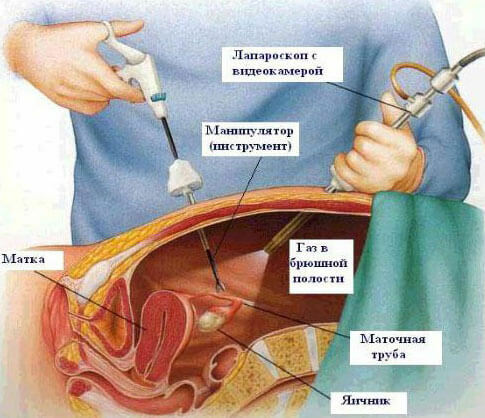
All laparoscope elements that are inserted into the pelvic cavity of the patient during the application of this method are made with strong hypoallergenic materials.
In order for the internal organs not to interfere with the operating gynecologist to work aiming with this or that organ, a lump of gas is injected into the small pelvis during laparoscopy, because of which the organs do not touch each other and with the abdominal wall.Due to such a technical solution with the help of an optical system it is possible to inspect internal structures from all sides - the field of view of the operating physician is increased.
Diagnosis of gynecological diseases with laparoscopy
The main indications for the use of diagnostic laparoscopy in gynecology are:
- infertility;
- acute gynecological pathology;
- chronic diseases of female reproductive organs;
- signs of acute surgical pathology, with which it is necessary to carry out differential diagnosis of female diseases.
Laparoscopy makes it possible to identify the following causes of infertility:
- obstruction of the fallopian tubes, which causes infertility in approximately 30% of cases;Benign neoplasm of the uterus;
- ;
- Incorrectly performed artificial abortion( abortion or artificial delivery)
and others.
Acute gynecological pathology, for the diagnosis of which the laparoscopic method is used, is:
- torsion of cysts on the foot;
- ruptured cyst;
- internal bleeding
and so on.
The most frequent chronic gynecological diseases, for the diagnosis of which laparoscopy is successfully used, are:
-
 cysts of one or both ovaries;
cysts of one or both ovaries; - uterine fibroids of various locations;
- endometriosis is a disease in which the cells of the inner layer of the uterus( endometrium) grow outside this layer, and during menstruation they begin to cover and flake;
- dysmenorrhea - violation of the ovario-menstrual cycle in the form of pathological soreness.
In some cases, due to the characteristics of the female body, signs of acute gynecological pathology may be indistinct or absent in their classical manifestation.Earlier, in such complex diagnostic cases, a diagnostic laparotomy was used - access to the small pelvis by an open method.The "minus" of the open method consisted in unjustified traumatization of tissues - the diagnosis could not be confirmed, which meant that the anterior abdominal wall had been traumatized in vain. The laparoscopic method avoids non-targeted insertion into the small pelvis.
Very often under acute gynecological pathology, acute surgical diseases are masked.For example, because of the pelvic location of the inflamed appendix, the clinical picture will be perverted, and this will affect the correctness of the treatment - in particular, incorrect operative access will be selected.In the clinic, cases are also observed, with the exact opposite - when on the basis of the symptomatology an incorrect diagnosis of an acute disease of the abdominal cavity is put, although in fact the gynecological sphere suffers.With the help of laparoscopy, you can avoid such errors in both cases.
Treatment of gynecological diseases with laparoscopy
If a diagnosis of a gynecological disease is confirmed, very often surgeons immediately go on to eliminate the causes of the disease: diagnostic laparoscopy becomes therapeutic manipulation - in particular, it concerns acute gynecological diseases, Requiring emergency surgery( internal bleeding, rupture of the cyst, and so on).
In some cases, operative laparoscopic intervention requires preparation of the patient, as well as a more thorough examination - for example, studying a biopsy specimen( piece of tissue) in order to find out whether the diagnosed tumor is good or malignant.After a certain period of time, surgeons-gynecologists perform a repeat laparoscopy, but with a therapeutic purpose.
Not all chronic pathologies require preparation for the operation - so if the inopportunity of the fallopian tubes has been established as a cause of infertility, the operating team can immediately proceed with its elimination.
With the help of a laparoscopic method, almost all diseases of the gynecological sphere can be treated, as discussed above in the diagnostic view. So, excellent results are obtained with laparoscopic treatment of virtually all known and common ovarian cysts:
- follicular;
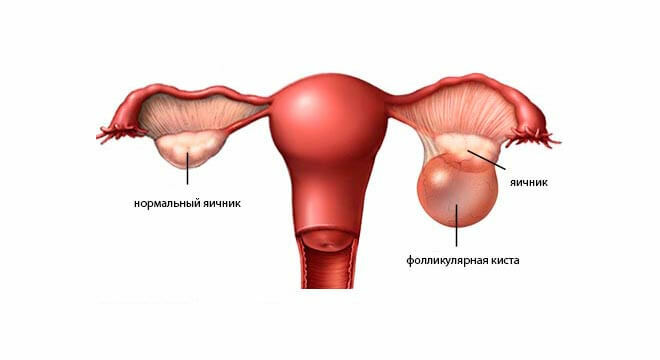
- of the yellow body;
- dermoid
and so on.
 In endometriosis, the treatment method we are considering is more than justified by the . Due to the mobility of the laparoscope, it is possible to detect and remove endometrial cells with an atypical location in almost any localization of the process in the small pelvis, while sparing the tissue.During an open surgery with a classic incision of the anterior abdominal wall, the operating doctor discovers an accurate localization of the endometrium only during surgery and is often forced to expand the operative access - in other words, to make the incision of the abdomen longer.In this case, the degree of tissue trauma increases, and in the future the aesthetics of the anterior abdominal wall will suffer because of the postoperative scar( even if a so-called atraumatic suture has been applied).
In endometriosis, the treatment method we are considering is more than justified by the . Due to the mobility of the laparoscope, it is possible to detect and remove endometrial cells with an atypical location in almost any localization of the process in the small pelvis, while sparing the tissue.During an open surgery with a classic incision of the anterior abdominal wall, the operating doctor discovers an accurate localization of the endometrium only during surgery and is often forced to expand the operative access - in other words, to make the incision of the abdomen longer.In this case, the degree of tissue trauma increases, and in the future the aesthetics of the anterior abdominal wall will suffer because of the postoperative scar( even if a so-called atraumatic suture has been applied).
Laparoscopic treatment of dysmenorrhea is a finding for gynecologists: the method proved effective in severe forms of this disease that can not be treated conservatively.It was noted that after laparoscopic treatment improved in 80% of women who were unsuccessfully treated for secondary dysmenorrhea by other methods.
Preparing for laparoscopy
Laparoscopy in gynecology is a surgical procedure, therefore it should be performed after the standard preoperative preparation of the patient , which includes the methods of research and the direct preparation of the female body for laparoscopy.
Before gynecological laparoscopy, research methods such as:
- general blood test;
- blood coagulation test;
- determination of blood type and Rh factor;
- chest fluorography;
- ultrasound of pelvic organs;
- consultation of the therapist - he should give the conclusion that the patient has no contraindications to the laparoscopy.
Preparation before the operation consists in the following actions:
- if necessary - adjusting blood counts, circulating blood volume;
- abstinence from eating at least 8 hours before laparoscopy, liquid for 3 hours;
- staging of a cleansing enema( preoperative cleaning of the intestine should be performed by medical personnel, not by the patient herself);
- half an hour before the transportation of the patient to the operating room - premedication.It consists in the introduction of drugs that will enhance the subsequent anesthesia.
How does lasparroscopy work?
 Laparoscopy is performed in a specially equipped operating ( in particular, the presence of monitors is necessary). It is performed under anesthesia - intravenous, masked or, if it is necessary to "switch off" the anterior abdominal wall from the act of breathing, endotracheal( in this case, the ventilator breathes).
Laparoscopy is performed in a specially equipped operating ( in particular, the presence of monitors is necessary). It is performed under anesthesia - intravenous, masked or, if it is necessary to "switch off" the anterior abdominal wall from the act of breathing, endotracheal( in this case, the ventilator breathes).
During the introduction of the patient into a state of drug sleep( which is also a narcotic sleep, it is anesthesia), antiseptics treat the anterior abdominal wall.The treatment is performed widely - in the expectation that after diagnosis of the disease, the operating team can proceed to its elimination.
Puncture the anterior abdominal wall.To elevate it and better access to internal organs, carbon dioxide is injected into the abdominal cavity.It is injected until the gas pressure in the abdominal cavity reaches a certain point, after which the operating doctor inserts a laparoscope into the abdomen and begins the examination. Duration of diagnostic manipulation varies - from 30 minutes or more. The time of diagnostic laparoscopy may increase, as it may be necessary:
- to overcome technical difficulties( for example, removal of splices in a pronounced adhesive process, which does not allow to examine internal organs);
- a consultation of doctors( including related specialties);
- waiting for the result of a biopsy study( a piece of seized tissue)
and so on.
The duration of treatment laparoscopy depends on the amount of necessary manipulation.
Regimen after laparoscopy of ovaries, fallopian tubes and uterus
 If a laparoscopy was performed for diagnostic purposes, the patient is recommended to remain in the clinic for a day to monitor the postoperative condition. The length of stay in the hospital after the patient has been operated by a laparoscopic method is determined by the operating physician - in any case, it is substantially less than the length of stay in the hospital after an open procedure. At the request of the patient and in consultation with the doctor, the period of inpatient stay can last 3-4 days, but such a need for medical reasons does not practically arise due to the small size of postoperative wounds - because:
If a laparoscopy was performed for diagnostic purposes, the patient is recommended to remain in the clinic for a day to monitor the postoperative condition. The length of stay in the hospital after the patient has been operated by a laparoscopic method is determined by the operating physician - in any case, it is substantially less than the length of stay in the hospital after an open procedure. At the request of the patient and in consultation with the doctor, the period of inpatient stay can last 3-4 days, but such a need for medical reasons does not practically arise due to the small size of postoperative wounds - because:
- the patient practically does not experience any painful sensations, noThe need to prescribe potent painkillers of the narcotic series that require monitoring;
- the possibility of complications from the postoperative wounds is minimized, so there is no need for daily long bandages and the doctor's control.
The attending physician will appoint a follow-up date after laparoscopy, as well as give recommendations regarding the resumption of sexual activity - they are individual.If there were no complications, after a diagnostic laparotomy, you can have sexual intercourse in 2 weeks. The doctor will also choose contraceptives, and if necessary, orient, whether the time should be waiting for the conception of the child.
In general, after laparoscopic intervention( both diagnostic and therapeutic), there is no special regimen that must be adhered to.
Advantages of gynecological laparoscopy
They are:
-
 Laparoscopy allows simultaneous diagnosis and treatment of the disease;
Laparoscopy allows simultaneous diagnosis and treatment of the disease; - tissue trauma and blood loss during surgery - insignificant;
- any contact with tissues is reduced to a minimum - only in a certain location, sighting;
- with tissues does not contact the surgeon's gloves and napkins - due to this the possibility of adhesions in the small pelvis and abdominal cavity is sharply reduced;
- postoperative wounds heal quickly;
- there is no discomfort in the field of postoperative wounds and non-esthetic post-operative scars;
- there is no need for prolonged hospitalization;
- there is no need to follow a strict postoperative regimen and diet, as with an open surgical procedure;
- recovery is rapid, the patient can return to the usual rhythm of life and work as early as a week after laparoscopy.
Disadvantages of the
method Laparoscopy has practically no drawbacks. The only drawback is the need for anesthesia with its possible consequences , but this is a minus of non-gynecological laparoscopy, and surgical interventions in general.
Contraindications
Laparoscopy is a progressive, verified method. But in some cases its performance is contraindicated in such cases as:
-
 terminal status of the patient( in other words, states on the verge of life and biological death) - pre-agony, agony, clinical death;
terminal status of the patient( in other words, states on the verge of life and biological death) - pre-agony, agony, clinical death; - various types of com;
- chronic recurrent diseases of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, which are accompanied by cardiovascular and respiratory insufficiency;
- Purulent complications( purulent peritonitis and sepsis).
There are so-called relative contraindications to for performing gynecological laparoscopy - those during which there is a risk of an unsuccessful outcome, but it is not 100% . These are diseases and conditions, such as:
- open cavity operations that have been carried over the last 4-6 months;
- marked obesity( extreme degree);
- pregnancy at a later date;
- complicated chronic diseases;
- general infectious pathology;
- disorders from the coagulation system of the blood.
Sometimes it is possible to switch from a laparoscopic technique to an open surgical procedure. This clinical situation can be observed with severe technical difficulties during laparoscopy or individual anatomical and physiological characteristics of the patient, revealed only during laparoscopy.
Kovtonyuk Oksana Vladimirovna, medical reviewer, surgeon, consulting physician



