Enterococcus faecalis: what it is, the presence of a smear symptoms
In the intestine, mouth, and the urogenital tract of men and women present enterococci (lat. enterococcus). So called gram-positive bacteria (release 17 species), belonging to the family of enterococcal (Enterococcaceae).
Most often (about 90%) in the human body reveal Enterococcus faecalis (Enterococcus faecalis).
living beings temperature (35-37 C) is considered an ideal medium for their habitat. What is it Enterococcus faecalis?
Methods of infection and multiplication of causes
Bacteria have a round or elongated shape. Size microorganisms 0.6-2.0 microns to 0.6-2.5. They are facultative anaerobes - can develop in the absence of oxygen, and that, if any. Growth and proliferation of bacteria is carried out at a temperature of 10 ° -45 ° C.
safe concentration enterococcus faecalis assays (feces, urine or a smear) adult does not exceed 10 to 3 degrees, in small children - 10 to 7 degrees.
The increase in performance requires further examination and treatment.
Enterococcus faecalis can survive for 30 minutes while heating to 60 ° C. They can not destroy handle most disinfectants. Live microorganisms mainly in the intestine, but remain viable outside the body and is rapidly rebuilding its metabolism under the changed conditions.
Enterococcus fekalis considered opportunistic. In the body, they mostly perform a protective function: inhibit proliferation of other pathogenic bacteria. Additional properties is their ability to carry out the enzymatic metabolism, and lowering the acidity in the digestive organs.
In the event of friendly microorganisms, they show their quality pathogenic conditions.
Most often, health problems provokes prolonged antibiotic therapy.
Others, provoking bacterial multiplication factors, are:
- the use of infected products;
- chronic diseases (diabetes, tuberculosis);
- hypothermia;
- unbalanced diet;
- hormonal imbalance;
- stress;
- AIDS;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- alcohol abuse;
- instrumental examinations.
The occurrence of diseases in adulthood always points to decreased immunity.
Urinary tract infection
Inflammatory processes triggered by Enterococcus fekalis a child up to a year, are shown:
- flatulence;
- appetite loss;
- increased nervousness and tearfulness;
- diarrhea.
The examination bacteria detected mainly in the feces or urine.
Infection with the fairer sex Entrococcus faecalis provokes:
- pyelonephritis;
- vaginitis;
- urethritis;
- cystitis;
- vulvitis;
- adnexitis.
The main manifestation of infection becomes lower abdominal pain and discoloration of urine. Other symptoms include:
- frequent and painful urination;
- decreased libido;
- fast fatiguability;
- temperature increase.
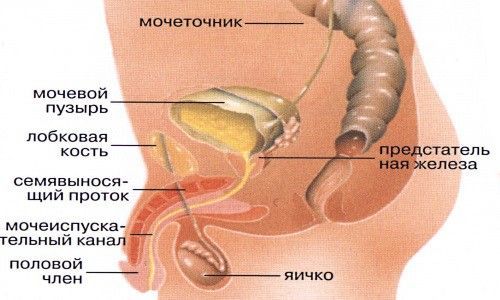
May suffer from headaches.
During pregnancy Enterokokkus fekalis often found in urinalysis. Woman's uterus grows in size, and the pressure in the kidneys increases. There comes the stagnation of urine, which can provoke inflammation in the kidneys or urinary tract. Signs of disease are:
- discoloration of urine;
- pain with urination;
- temperature increase;
- discomfort in the abdomen.
Infection can cause premature birth and intrauterine infection of the child.
Detection of enterococcus faecalis in blood smears in men also leads to inflammatory changes in their genitourinary system. acute period is characterized by certain features:
- pain in the urethra area;
- erectile dysfunction;
- discomfort during urination or defecation;
- discharge with an admixture of pus from the urethra;
- raising the temperature;
- unpleasant odor of urine;
- general weakness.
For a long time the disease is asymptomatic.

Defeat Enterococcus faecalis other organs
Enterococcus faecalis can cause infectious diseases, not only of the genitourinary system, but also other vital organs (heart, intestine, brain). The effects of intense reproduction of microorganisms are:
- diverticulitis - an inflammation of the colon wall protrusions. Accompanied by uncomfortable sensations in the stomach, changing the character of stool, fever, nausea, vomiting;
- peritonitis - inflammation of the covering of the abdominal cavity. Complication manifested by abdominal pain, pyrexia, violation of stool, nausea, vomiting;
- pyelonephritis - an infectious disease of the kidneys. Proceeds with excessive sweating, general weakness, nausea, vomiting, poor appetite;
- dysbiosis - a violation of the balance of normal microflora. Symptoms: change in stool, abdominal discomfort, bloating;
- meningitis - an infection of the meninges. Tags: change of temperature, nausea, vomiting, cephalalgia, stiff neck muscles, emotional instability;
- pleurisy - inflammation of the serous membranes of the lungs. Manifested by shortness of breath, cough, change in temperature, discomfort in the chest;
- endocarditis - inflammation of the inner lining of the heart. For pathology is characterized by: an increase in temperature, change in color of the skin, impaired thermoregulation;
- gastritis - inflammation of the gastric mucosa. Symptoms: abdominal discomfort, appetite loss, heartburn, nausea, vomiting, belching, bloating;
- enteritis - infection of the small intestine. Tags: change in stool, bloating, pain around the navel;
- sepsis - blood poisoning. Infective process is accompanied by breach of the central nervous system (reaction rate change), headaches, tachycardia, increased pressure. Skin acquire a light gray color.
When the consumption of contaminated food enterococcus faecalis possible food poisoning. Microorganisms also periodically cause nosocomial infections.
Diagnosis and treatment of enterokokkusa fekalisa
Diagnosis of pathological growth of microorganisms includes the capture and research in the laboratory Biomaterials (urine, feces, blood, swabs taken from the vagina or the urethra) by plating on nutrient environment.
If the analysis found significantly higher than normal amount of enterococcus faecalis - to prevent complications of the treatment should be carried out. It is the appointment of antibiotic therapy, immunostimulant, the application of local effects of drugs.
Antibacterial agents are selected on the basis of the diagnosis of the susceptibility of microorganisms to drugs. Effective drugs to eliminate enterococci fekalisa are:
- ceftriaxone;
- gentamicin;
- rifaximin;
- ampicillin;
- linezolid;
- Roxithromycin.
For drugs of local impacts include some gels, suppositories, ointments. They contribute to the regeneration of injured tissue and reduce the risk of complications.
- To improve blood flow to the organs of the urogenital system of the stronger sex is recommended prostate massage.
- To normalize the microflora used probiotics - Bifidumbacterin, Atsipol, Linex.
- In order to enhance immunity appointed immunnostimulyatory - Immunal, Lizobakt, Imudon, ICR-19.
- When pain syndrome may be recommended antispasmodics - No-Spa, papaverine.
- Nausea and vomiting effectively eliminate metoclopramide Domidon, pipolfen.
- For relief of discomforts pelvic prescribed alpha-adrenergic blockers (Bazetu, Adenorm) and muscle relaxants (Baklosan, Mydocalm).
- The use of vitamin and mineral supplements (Aerovit, Vitalux, Pregnavit) helps to normalize the functioning of the main systems of the body.
Treatment of children and pregnant women begins with the appointment of bacteriophage (phage-Intest). This is due to the fact that the number of side effects from their use is minimal in comparison with antibiotic therapy.
Treatment of folk remedies
The use of traditional medicine recipes inhibits the development of Enterococcus faecalis and other pathogens microorganisms (staphylococci, streptococci, E. coli), as well as improves the protective resources body.
Treatment should continue for at least 28 days. Effective popular recipes:
- Parsley - has a pronounced bactericidal and diuretic effect. To get rid of enterococcus fekalisa used leaves of the plant. For the preparation you will need to take 1 tbsp. chopped raw material and combine with 0.5 L of cold water. Insist need within 10 hours. Drink medicine necessary for every 40 ml of 2 chasa;
- the fruits of juniper, birch leaves, parsley seed - 2 tbsp. spoons ingredients (in a ratio of 5: 5: 2) to pour 0.5 l of boiling water for 10 hours. Consumed 50 ml 5 times a day;
- cornflower - 1 tbsp. Plants need spoon filled into 200 ml of boiling water and infuse about an hour. Recommended to drink the infusion of 2 tbsp. spoon 3 times a day for half an hour before meals;
- blackcurrant - 100 g of crushed leaves must connect with 400 ml of boiling water for 2 h. Drink recommended infusion 200 ml, 2 times a day;
- horsetail, plantain leaves, erect cinquefoil - 2 tbsp. spoon mixture mixed with 0.5 l of boiling water for about 10 hours. Drink 50 ml before each meal;
- chamomile and black chokeberry - 1-2 hours. raw spoons need to pour 200 ml boiling water for half an hour. Drink before meals twice a day;
- gryzhnik naked - 1 hr. plant spoon to pour 200 ml boiling water, leave for half an hour. Drink 100 ml, 2 times a day;
- honey and propolis - Mix the components in equal proportions, to withstand 3 days and take 1 hour. l. 3 times a day;
- licorice root - 20 grams of ground roots of plants need to fill in 1 l of boiling water for 24 hours. Take 100 ml, 2 times a day;
- collection of leaves, cranberries, Viola tricolor flowers, calendula, flax seed - 2 tbsp. spoons plants connected to mixture of 0.5 l of boiling water for 12 hours. Drink 50 ml before eating;
- Zelenchuk yellow - 3 tbsp. spoons grass must be connected with 0.5 l of boiling water for about 30 minutes. Recommended drink 200 ml three times a day before meals.
See also:Age norms bilirubin in the blood of men
For the healing of the mucous genitals used ointment of hemp seed sowing. They mulled and mixed with a small amount of water.

Reduce the multiplication of microorganisms use barberry, dried apricots, fresh or frozen berries blackcurrant, raspberry, strawberry, bilberry.
Prevention of enterococcus faecalis
For the prevention of the growth and reproduction of bacteria it is important to have good immunity. recommended:
- lead an active lifestyle, engage in sports, physical training, and maximum move;
- adhere to the rules of personal hygiene;
- time to treat co-morbidities;
- avoid stress and hypothermia;
- enough time to sleep;
- eliminate bad habits;
- not be used without a doctor's prescription of antibacterial agents.
It is necessary to adjust the diet. The daily menu should be present vegetables, fruits, various berries, and dairy products. Should be excluded from canned food, pickles, fatty and fried foods. There is a need to frequently (5-6 times a day) and in small portions.
Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) is a natural immunostimulant. Her many in parsley, lemon, kiwi, berries, wild rose, viburnum, buckthorn.
Enterococcus fekalis - integral components of the environment and living organism. Bacterium becomes dangerous only when propagated under conditions of immunosuppression. Therefore, strengthening the body's defenses - the best method for preventing inflammation.
The main causes of the inflammatory process caused by enterococci
Enterococcus faecalis can affect both sexual organs and the urinary system, with serious flow - the kidneys and bladder. Since the active growth of microorganisms in the female begin to appear alarming symptoms.
Pain symptom - an essential attribute, indicating activation of pathogenic flora. Pain may vary in intensity and character of the development of the disease, they become severe.
In lesions of the genital tract and vagina copious, differ in color - from grayish to light brown, unpleasant smell. Isolation accompanied by a burning sensation and discomfort in the vagina.
The changing nature of urination - it becomes rapid, meager. sudden sharp impulses may occur Urine process becomes painful.
Signs of inflammation in the genitourinary system of men caused by enterococci
Increasing the amount of Enterococci fekalis leads to inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system. Fekalis enterococcus can cause inflammation, not only in the urogenital system, but also on mucosa of the small intestine and colon, it all depends on the location of the largest number of seats bacteria.
In most cases, men suffer from inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system caused by enterococci fekalis. They are hidden for a long time, but the adverse conditions to the body's inflammatory process becomes more pronounced. There are a number of the most characteristic symptoms of obvious lesions of the genitourinary system man fecal enterococci:
- Sharp pains in the urethra or the whole groin.
- Pain accompanying defecation process.
- Frequent urination.
- Obvious problems with ejaculation and erection.
- Changing the appearance of urine.
- The appearance of white-green discharge.
- Difficulty urinating.
- Stale orgasm.
- Decreased libido and potency.
- Common symptoms, including excessive fatigue, depression and weakness.
Many men do not notice any visible symptoms of the early stages of the disease. With this embodiment, detection of the disease increased titer conditionally pathogenic occurs during the routine inspection and sampling of urine for analysis and smear. As a rule, in this case does not require special treatment, but appointed physiotherapy measures aimed at improving the overall health and immunity.
The sharp increase in the population of enterococcus faecalis causes inflammation:
- in the urogenital system;
- in the mucous of the small intestine;
- on the colonic mucosa.

Unfortunately, the negative impact of the bacteria becomes noticeably not once, even though it is the cause of most problems in the functioning of the male urogenital system.
Manifested its effect only when the weakening of the body.
There are some typical signs that inflammation male urogenital system caused by enterococci:
- Pain syndrome in the groin area and in the urethra;
- Pain at the time of defecation;
- Frequent urination;
- Problematic erection and ejaculation;
- The color and smell of urine differ from the usual;
- Allocating white-green color (like pus);
- Difficulty urinating;
- Erased an orgasm;
- Decreased libido and potency;
- Symptomatology peculiar general weakening of the organism (fatigue, weakness, depression).
Since the initial development stage of the disease is difficult to fix independently, the detection excess opportunistic bacteria occurs at a planned trip and taking urine samples and smears on analysis. In most cases, special treatment is not appointed, but the prescribed physical therapy action that strengthens the immune system and improves the general condition.
The inflammatory process in the female genitourinary system, if it is caused by enterococci, may have the following symptoms:
- Frequent urination, thus the process becomes painful enough;
- The presence of discharge from the urinary ducts;
- Increased body temperature;
- When urinalysis revealed excessive increase in the level of white blood cells;
- Pain in the abdomen;
- The presence of bloody or purulent discharge from the vagina;
- Tissue swelling;
- Burning and itching;
- Plaque and ulcers.
Prevention of enterococcus faecalis
To avoid contamination by fecal enterococci, to prevent its propagation in the intestinal and vaginal flora, it should stick to simple measures of preventive orientation.
A woman should closely monitor the state of health, in any atypical secretions alarming color, texture, volume, refer to the gynecologist, hand over a smear
Detection assays in women fecal enterococcus - uncomfortable and quite dangerous. Symptoms of the disease are undermining the general condition, prevent a full life. But do not panic - when detected early and reasonable treatment of opportunistic pathogenic flora can be defeated completely. And in the future prevention avoids the problem of returning.
Prevent the negative impact of enterococcal infections is quite simple.
It is only necessary to comply with the rules mentioned below list:
- Not to engage in anal sex without a condom;
- Strictly observe personal hygiene;
- Anyone receiving antibiotics should be combined with the reception of immunomodulators;
- When in a public place to apply antibacterial wipes;
- Try not to contact directly with the plumbing in the public toilets.
https://brutoman.ru/proyavlenie-u-zabolevshego-bakteriey-enterococc/
Types of enterococci. Causes of infection
Enterococci have more than 17 species, some of them can cause infections of the genitourinary system, endocarditis and so on. The most common are Enterococcus faecalis (faecalis enetrokokk) and Enterococcus faecium.
Although the normal habitat of enterococci is the intestine, up to 25% of healthy men Enterococcus faecalis is present in front of the urethra. That's why enterococci referred to as opportunistic (transient) microflora of the urogenital organs. In turn, Enterococcus faecium is responsible for the majority of vancomycin-resistant infections enetrokokkovyh. The insensitivity of bacteria to antibiotics is a serious problem of modern medicine.
Enterococci have both their own, thanks to the special structure and acquired antibiotic resistance. This provides a significant contribution to the development of these bacteria of nosocomial infections, and limits the ability of physicians in relation to such an important aspect as the treatment of Enterococcus.
Enterococcus men (often - Enterococcus faecalis) can cause diseases of the urogenital tract, especially in those that took place the appropriate tool inspection and / or receive antibiotics:
- prostatitis;
- balanoposthitis;
- urethritis;
- epididymitis / orchiepididymitis;
- cystitis and others.
Ways of infection:
- sexual contact (especially the alternation of genital-genital and anal-genital);
- improper hygiene after using the toilet;
- transmission from mother to newborn baby;
- rarely - in organ transplantation.
When injected into the genito-urinary organs enterococci may be in them from a few hours to a few weeks, with the time being destroyed defense mechanisms. This condition is called temporary or transit carriage. In this case, the carrier can transmit the pathogen of sexual partners. Finding the temporary Enterococcus carriers of precision possible methods (e.g., PCR).
See also:Methods of treatment of hemorrhoids in men
Also in small quantities enterococci may reside in the urogenital organs (persistent carrier). They prevent the growth of the same defense mechanisms and normal microflora. By reducing the number of normal microorganisms and / or security breach enterococci begin to multiply rapidly, evolving inflammatory process. Resistant usually asymptomatic carrier state, except the period of exacerbation, detection of enterococcus possible PCR, cell culture study. In this case also there is a possibility of the partner becoming infected.
When the body stops to restrain development enterococci, there is the manifestation of the disease. Factors predisposing to the development of enterococcal infections:
- the presence of severe disease;
- previously transferred gonococcal / chlamydial infection;
- violation of protection mechanisms genitals (such arrangements are neutral / slightly alkaline medium in the urethra, prostate antimicrobial factor, mechanical, local immunological protection);
- chronic prostatitis (assuming that this disease affects due to lower zinc content and, as a consequence, disruption of prostate antimicrobial factors - the complex of zinc-peptide);
- prolonged antibiotic therapy;
- abuse of local anesthetics, leading to urethral burns;
- urinary catheterization or other inspection tool, which can cause trauma to mucous membranes;
- older age, and so forth.
Symptoms of enterococcal infections
Specific signs of lesions of the genitourinary system enterococcus not. With the development of pathologic process, patients complain that are typical for the particular type of disease (depending on the localization of inflammation).
Urethritis accompanied by:
- quickening, painful manifestations during urination;
- urethral secretions;
- redness, irritation, discomfort in the urethra.
For prostatitis is characterized by:
- syndrome of pain and discomfort in the perineal pain in the testicles, rezey / urethral pain, burning after intercourse \ urination;
- urinary disorders syndrome (increased frequency, sensation of incomplete emptying, weak / intermittent stream);
- disorders of orgasm, ejaculation (pain, effacement orgasm, premature ejaculation or tighten sexual intercourse);
- when combined with chronic urethritis - allocation muco-purulent character.
When balanitis / balanoposthitis patients complain of pain and redness in the area of the glans penis, redness (erosions, ulcers, fissures), coating, swelling, discharge.
Orchiepididymitis is a combination of testicular inflammation (orchitis) and an appendage of the latter (epididymitis). In acute illness marked blunt severe pain in the scrotum, the increase / sealing of one or both testis, scrotal skin hyperemia, increased / sealing appendage with the sharp soreness. Pain is reduced in the scrotum during its lifting. Chronic disease is characterized by symptoms of blurred, sometimes the appearance of blood in the semen.
methods of diagnosis
Diagnosis of enterococcus in the organs of the male urogenital tract includes holding:
- inspection technician;
- general urine and blood;
- Polymerase chain reaction (reveals the microorganism even in asymptomatic carrier);
- culture studies (otherwise bacteriological seeding) with determination of antibiotic susceptibility;
- other laboratory such as RIF, ELISA, etc. smear microscopy.
And instrumental (ultrasound, ureteroscopy, MRI, CT) studies to exclude other causes of disease (neenterokokkovyh genital infections, tumor processes, etc.).
Laboratory investigated urine samples, semen, prostatic secretion, urethral discharge.
In the presence of negative phenomena from the urogenital tract it is important to understand what is causing enterococcus infrequently such problems. If the tests did not show the presence of other pathogens may need to re-diagnosis (sometimes even in another laboratory). Only after eliminating other possible pathogens (Trichomonas vaginalis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, chlamydia, etc.) assigned individual therapeutic course for eliminating enterococci.
Therapies Enterococcus
If you accidentally identifying enterococcus during a routine inspection treatment is recommended only in the presence of specific complaints, planning surgery of the urinary tract organs (in some situations, your doctor may recommend an appropriate treatment planning pregnancy). This is due to the fact that such a microorganism can be detected normally have absolutely healthy men.
Diagnostically significant (in the absence of clinical manifestations) Enterococcus considered titers of about 1 x 10 6 th degree. Thus asymptomatic bacteriuria (detection of enterococcus in urine) may require medical supervision and only when necessary for periodic analysis: repeated crops. Boys without urinary tract infection symptoms, routine laboratory detection of enterococcus is not recommended.
If enterococcus is suspected as the only cause of problems in men from the urogenital tract (urethritis, prostatitis pyelonephritis, cystitis, etc.), necessary to conduct adequate antibiotic therapy. Given the enhanced stability of such microorganisms to antibacterial drugs is highly desirable to carry out pre-treatment determination of an appropriate sensitivity (unfortunately, this time-consuming exercise and is not always possible to postpone the start of treatment).
In most cases of inflammatory diseases of the urogenital system of male cause of infection is Enterococcus faecalis (Enterococcus faecalis). This type of enterococcus is usually:
- sensitive to rifaximin, levofloxacin, nifuratel, some strains - to doxycycline;
- moderately sensitive to ciprofloxacin;
- slightly sensitive (for most strains) tetracycline;
- virtually insensitive to lincomycin.
Penicillins, some cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones early inactive or weakly active against fecal enterococcus.
For treatment, usually only one drug at its inefficiency may be assigned a different or a combination of several. After completing the course, a refresher diagnostics enterococcus. Treatment of sexual partners is carried out on the advice of a doctor (often in the case of pregnancy planning). In case of mixed infections are selected drugs active for each pathogen.
Course of antibiotics is usually sufficient to complete cure. However, in some cases, your doctor may prescribe extra:
- various physical therapy treatments;
- massage course (often used in inflammatory pathologies of the prostate gland);
- enzyme preparations;
- vitamins;
- immunomodulatory agents;
- homeopathic treatment;
- traditional medicines (bath decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs, cranberry juice drink, etc.);
- local treatment (injections, so called instillation into the urethra solutions of various drugs, e.g., preservatives).
Ignoring the doctor's recommendations, overreliance on self-medicate and folk remedies may not only lead to recovery, but also significantly worsen the patient's condition. For example, misuse of the infusion into the urethra antiseptic solutions often results burns of mucous, which in itself is a precipitating factor for the development of bacterial infection.
complications
In the absence of adequate therapy of enterococcal infections are possible:
- the spread of inflammation to other organs and tissues;
- the transition of the disease into a chronic form;
- sperm quality deterioration and, accordingly, the development of male infertility;
- erectile dysfunction, etc.
prevention
Prevention of infection is enetrokokkovoy:
- compliance with the rules of safe sex (use of barrier methods of protection, a regular partner);
- timely detection and elimination / control of chronic diseases;
- competent therapy identified genital infections (especially gonococcal, trichomonas);
- healthy lifestyle (normalization of work and rest, complete quality nutrition, moderate exercise, minimizing stress and so forth.) and others.
https://hron-prostatit.ru/enterococcus.htm



Which means the detection of enterococci in prostatic secretions or smears from the urethra?
Modern means of self-defense - it's an impressive list of objects of different principles of action.
The most popular are those that do not need a license or permit to purchase and use. In Internet Tesakov.com store, you can buy to protect themselves without a license.
 In most cases, enterococci can be detected in a smear from the urethra: it is a normal physiological phenomenon. Much depends on the number of pathogenic microorganisms. The more, the higher the probability that the immune system fails.
In most cases, enterococci can be detected in a smear from the urethra: it is a normal physiological phenomenon. Much depends on the number of pathogenic microorganisms. The more, the higher the probability that the immune system fails.
Pattern becomes apparent upon detection of said body in prostatic secretions. This means that the microflora multiplied to such an extent that has already penetrated above the ascending path. At any time, may develop prostate or whether it has already begun. more research is needed to clarify the nature and the type of process.
Clinical manifestations
Clinical signs of enterococci are numerous. In most cases, it makes itself felt the acute period following characteristic phenomena:
- Pain syndrome in the penis. Pain differ intense character, give (irradiate) in the groin, testicles, waist, crotch. Patients describe pain as a sharp, burning, or aching drawing. It comes to the fact that the patient can not walk properly. Enhanced uncomfortable during movement, micturition (cramps, most typical for sexually transmitted diseases).

- Discomfort, manifested during defecation. Pain increases during defecation straining, due to the acute process in the urethra or prostate.
- Pollakiuria. Frequent false urge to urinate. There are compelling urge to urinate when they can not keep.
- Problems with erection. Erectile dysfunction is evidence in favor of the possible onset of prostatitis.
- Problems with ejaculation. The reverse effect when ejaculation does not occur at all.
- The changing nature of urine. It becomes dark or muddy protein flakes.
- Discharge from the urethral channel. Have a greenish tint and a sharp, unpleasant smell putrid nature.
- Signs of general intoxication - weakness, drowsiness.
- Fever subfebrile (37-37,5 ° C).
- A stream of urine becomes too weak.
Can meet all of these manifestations. It can only be a part of.
Is it possible to asymptomatic carriage?
Since enterococci relates to conditionally pathogenic flora, asymptomatic carriage is not just possible, it's probably because the bacterium is found in all people without exception. Another thing that may reduce the effectiveness of the immune system, in which case the carrier will result in unpleasant consequences for the patient. 
Risk of enterococcus fekalis
The microorganism has a considerable danger for several reasons. Because no treatment is fraught with adverse consequences for the patient's body:
- Enterococcus has considerable vitality. He is not afraid of the critical temperature changes.
- The second significant factor - resistance of microorganisms to many antibiotics.
- Enterococci are not afraid of the lack of oxygen.
- They are easily propagated by fermentation with dyspepsia.
Therefore it requires a careful approach to diagnosis and treatment.
complications
In the absence of a competent treatment failure described microorganism is fraught with the following consequences: 
- prostatitis;
- urethritis;
- pyo-inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs;
- sepsis.
The possibility of severe consequences for life and health.
Diagnostics
Diagnostics enterococcal infections engaged infectious disease physicians. In addition to routine tests, questioning and examination, used bacteriological seeding of biomaterial on nutrient media. It makes it possible to sow the pathogen as well as to determine its sensitivity to antibiotics.
Treatment
Fecal enterococci - a bacteria that help maintain optimal inside our intestines acid-base balance, is involved in the production of vitamin and 1/3 along with other microbes, they make a lot of our feces. Therefore indiscriminately kill enterococcus illogical, since normally it is still useful to us. You need to use only those means that may lead to the destruction of urogenital localization of the pathogen, and does not affect with its intestinal form.
 Of course, completely impossible to do it: because antibiotics kill bacteria anywhere in the body. And what if you do not use antibiotics? Can we do without them? Yes, you can. To do this, apply a specific enterococcal bacteriophage. Bacteriophages - are viruses that feed on a certain type of microorganisms. In particular, enterococcal bacteriophage active, except for these cocci, more and E. coli, Salmonella, Shigella, as well as to Proteus, and many other micro-organisms.
Of course, completely impossible to do it: because antibiotics kill bacteria anywhere in the body. And what if you do not use antibiotics? Can we do without them? Yes, you can. To do this, apply a specific enterococcal bacteriophage. Bacteriophages - are viruses that feed on a certain type of microorganisms. In particular, enterococcal bacteriophage active, except for these cocci, more and E. coli, Salmonella, Shigella, as well as to Proteus, and many other micro-organisms.
Men with urogenital enterokokkoze should do the installation of the bacteriophage solution into the urethra, wash them glans penis and the inner layer of the foreskin. This will allow local populations to destroy viruses bacteriophages, tunes from the intestine.
Since most of the microorganisms are brought out of the rectum, the bacteriophage is also applied rectally for the prevention of "self-infection." The treatment bacteriophage 7-10 days, one dose for rectal administration of 50 ml of the drug in the form of enema which should be placed after a bowel movement. Available "Intest - bacteriophage" in vials of 100 ml.
In addition, the recommended topical application of creams and ointments containing antibiotics, and allowing disinfect mucosa of the genital tract. Thus, advantageously can be used: chlorhexidine, and furatsilina miramistina, according to the instruction.
The use of bacteriophage instead of antibiotics ensures that the population of healthy and necessary microorganisms in the gut remain healthy and not develop intestinal dysbiosis, which often accompanies any treatment with antibiotics.
http://menquestions.ru/venerologiya/enterococcus-faecalis-u-muzhchin.html
Features bacteria
What is striking:
- Reproductive system.
- Bladder.
- Kidney and pelvic organs.
- Prostate.
- Urethra.
Enterococcus faecalis with an increase in its rules causes inflammation. Treated only with antibiotics in infectious diseases hospital under the supervision of doctors.
Enterococcus faecalis is sowed in the stool, swabs from the urethra or urine. This bacterium is quite hardy and can survive in any environment. Resistant to many drugs.
Therefore, when a man is ill ordinary colds and infectious illnesses, where necessary the use of antibiotics, the bacteria Enterococcus faecalis, even in the destruction of the intestinal microflora multiply.
Enterococci survive anywhere and under any impact on them. A large number of their appearance was observed after conservative treatment with antibiotics or surgery.
Upon failure of the immune system are activated enterococci in large quantities in the body and can hurt him.
Enterococcus faecalis, and are positive factors. It is used in the fermentation of dairy products, it is made from whey, kefir, yogurt.

evidence
The bacterium enters the male genitourinary tract through the urethra. In the initial stages of development of enterococcus no clinical picture does not exist. A large gathering of Enterococcus faecalis such symptoms may appear in the urethra:
- Pain when urinating.
- Impurities in the urine, blurred.
- Purulent mucus from the urinary canal.
- Violation of libido.
- Frequent urging "in a little."
- Fatigue, weakness.
- Aching pain in the groin, the urethra.
Watching at one of these symptoms, a man should consult a urologist to pass necessary tests and medical treatment with antibiotics directed against this microbe.
As he enters the reproductive system
Pathogenic bacteria enterococcus faecalis is present in every healthy man, but its rapid reproduction begins to feed the cells of those organs in which their growing congestion. This may be the urethra, prostate, kidney, gastrointestinal tract (GI tract).
As the bacteria multiply enterococci:
- Improper hygiene, neglect. Often, unscrupulous representatives of the stronger sex can affect the microbe.
- Those who do not like to wash and do it every 3 days or even less, the pathogenic microbe is activated in large quantities in the urethra and prostate. Wash hands after using the toilet is very important that the bacteria had not been able to develop.
- Infections of viral etiology. Infection of the urethra and ureter enterococci, there is the period of venereal disease. Men who suffer from chronic pathologies, diabetes, sexually transmitted diseases and HIV, especially prone to infection with enterococci prostate.
- Violation of the intestinal microflora. If a man goes antibiotic therapy, then under the influence of beneficial micro-organisms are killed and the place occupied by enterococci.
Enterococcus bacteria multiply rapidly and develop on the background of weak immunity.
Analysis and diagnosis
Primarily engaged in the disease infectious disease, but you must start with a urologist, venereology. Research to identify enterococcus men:
- Swab from the urethra and intestines.
- Analysis of blood and urine.
- Semen. In the absence of libido.
- Bakposev prostate secretion.
For effective Aftercrops bacteria need to properly prepare. It is not necessary to wash antiseptics, soap, do not take any drugs, including antimicrobials. For high-quality planting semen is necessary to abstain from sex for 4 days prior to analysis.
Treatment
some antibiotics treatment does not work, because this bacterium is quite hardy. Therefore, in the treatment of a microbe enters the complex therapy scheme:
- Antibiotics. Levofloxacin (Tavanic) Rifaximin Doxycycline. These drugs are not toxic to the body and transferred quite easily. Used for the genitourinary system. Treatment calculated for 1 week to 1 tablet (0.5 g), 2 times a day.
- Antimicrobials. Metronidazole Russian production of a wide range of actions destroys pathogenic microbes in the digestive tract.
- Immunomodulator. To strengthen the immune system in conjunction with a common therapy prescribed Viruter, Panavir etc. They oppose the development of further enterococci male.
- Physiotherapy, exercise therapy.
prevention
Any disease can be prevented by taking appropriate measures.
- Personal hygiene.
- Condom use with any type of sex.
- Wash hands after using the toilet.
- Change clothes every day.
- Receiving antibiotics should be combined with laktatsidami and immunomodulators.
Do not neglect personal hygiene, take care of your health. Subscribe to our website. Share useful information with your friends. Be healthy!
https://flintman.ru/enterococcus-faecalis-u-muzhchin/