Multiple myeloma: what is it, why or what provokes the disease
What it is?
Multiple myeloma (other names: multiple myeloma, generalized plasmacytoma, or Rustitsky-Kalera disease) Is a type of cancer that affects plasma cells.
Plasma cells are a type of white blood cell found in the bone marrow, which is the soft tissue inside most of your bones and produces blood cells.
In the bone marrow, plasma cells form antibodies, which are proteins that help the body fight disease and infection.
Plasmacytoma occurs when an abnormal plasma cell develops and reproduces very rapidly in the bone marrow. The proliferation of malignant myeloma cells ultimately outweighs the production of healthy cells in the bone marrow.
As a result, cancer cells begin to accumulate in the bone marrow, displacing healthy white blood cells and red blood cells.
Like healthy blood cells, cancer cells try to make antibodies. However, they can only produce abnormal antibodies called monoclonal proteins or M proteins.
When these harmful antibodies build up in the body, they can cause kidney damage and other serious problems.
Content
- The causes of myeloma
- Disease provoking factors
- Multiple myeloma symptoms
- Types of multiple myeloma
- Stages of the disease
- Diagnostics
- Multiple myeloma treatment
- Drug treatment
- Treatment of complications of multiple myeloma.
- Surgery
- Nutrition for myeloma
- How not to get sick with Rustitsky-Kalera disease
- Forecast
The causes of myeloma
The exact reason why the disease occurs is unknown. However, the disease begins with a single abnormal plasma cell that multiplies rapidly in the bone marrow.
The resulting myeloma cancer cells do not have a normal life cycle. Instead of multiplying and dying, they continue to share endlessly. This destroys the body and impairs the production of healthy cells. Basically, patients have a genetic predisposition to the disease.
Disease provoking factors
But what triggers the development of multiple myeloma:
- genetic predisposition;
- chemical and radiation radiation;
- constant antigenic stimulation;
- obesity, as metabolism is disturbed;
- male sex, the development of the disease occurs with a decrease in the amount of male sex hormones;
- bacterial and viral infections;
- surgical interventions.
Multiple myeloma symptoms


Multiple myeloma has a long course. It takes 10-20 years from the first symptoms of the disease to clear clinical signs.
- Bone-marrow syndrome is manifested by bone lysis. The spine, flat bones, and proximal tubular bones are mainly affected. The distal regions are rarely affected. Patients complain of bone pain, frequent fractures. On percussion, pain in the limbs.
- Kalera Triad (osteoporosis with spontaneous fractures, pain, tumors) is pathognomonic for these patients.
- Disturbance in the work of the central nervous system is characteristic up to the development of paraplegia (complete immobility in the limbs), weakness, fatigue. Due to the deposition of amyloid in the bones of the skull, disturbances in the functioning of the cranial nerves are possible. Typical is the defeat of the peripheral nerves of the extremities and impaired sensitivity of the "gloves and socks" type. Lack of sensitivity in the distal extremities.
- Renal failure may be caused by high levels of M protein in the body.
- Immunoglobulinopathy Syndrome. Amyloid protein begins to be synthesized. In the process of urination, it is actively reabsorbed by the kidneys, damaging them. In the urine, proteinuria (Bens-Jones protein) increases. The concentration and filtration function of the kidneys gradually decreases, edema appears, a positive symptom of tapping (pain in the lower back when tapping with a fist in this area).
- Immunodeficiency Syndrome. Normal protein begins to be replaced by pathological one. The synthesis of antibodies and immunity components is impaired. As a result, the humoral immunity defect gradually increases. Patients become unprotected from bacterial and viral infections. The appearance of opportunistic infections is characteristic. Any contact with an infectious agent leads to the development of the disease
- High viscosity syndrome: increased bleeding Raynaud's syndrome (violation of microcirculation in the distal segments of the extremities), hemorrhages in the retina, decreased blood supply in the brain, possibly the development of DIC - syndrome.
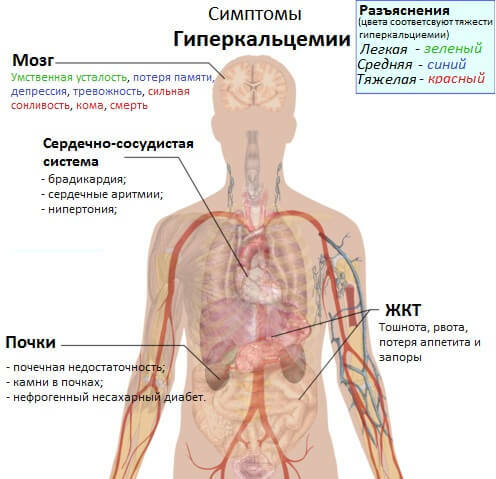
- Hypercalcemia. As a result of the increased activity of osteoclasts (cells that destroy bones), large amounts of calcium are released into the blood. Symptoms of hypercalcemia - nausea, vomiting, convulsions. Characterized by a violation of cardiac conduction: the QRS and T interval increases, a decrease in AV conduction, up to an AV block. Kidney stones. This is due to the deposition of calcium, filtration and reabsorption are reduced. The kidney shrinks.
- Internal organ damage: splenomegaly, hepatomegaly, gastric ulcer. Amyloid is deposited in various organs and tissues, which leads to disruption of their work. The characters of pain in the heart, expansion of the boundaries of cardiac dullness, deafness of tones. Muscle pain can be permanent.
- Anemic syndrome. Tumor cells eventually displace the normal hematopoietic germ. The amount of hemoglobin decreases, erythrocytes. The skin becomes covered with bloody spots and turns pale (see. 2 photo above), there is a constant feeling of weakness. Hair and nails become brittle.
Read also:Autoimmune hemolytic anemia
Types of multiple myeloma
There are two main types of multiple myeloma, which are classified according to their effect on the body.
Lazy myeloma does not cause any noticeable symptoms. Usually develops slowly and does not cause bone tumors. There is only a slight increase in M-proteins and M-plasma cells.
Single plasmacytoma causes swelling with a mass, usually in the bones. He usually responds well to treatment, but needs close monitoring.
Stages of the disease

- Stage I. The amount of hemoglobin is more than a hundred, the level of calcium in the blood is within normal limits, and there is no bone destruction. Immunoglobulin J is less than 50 g / l, immunoglobulin A is less than 30 g / l. Bens Jones protein in urine is less than 4 grams per day.
- Stage II. The amount of hemoglobin is from 85 g / l to 120 g / l. Moderate bone destruction. Immunoglobulin J 50 - 70 g / l, immunoglobulin A 30 - 50 g / l. Bens-Jones protein 4 - 12 grams per day.
- Stage III. The amount of hemoglobin is less than 85 g / l. Blood calcium levels exceed normal levels. Marked bone destruction. Immunoglobulin G is above 70 g / l, immunoglobulin A is more than 50 g / l. Bens-Jones protein in urine is more than 12 grams per day.
By the degree of progression:
- smoldering - the disease does not progress for many months and years;
- slowly progressive;
- rapidly progressing;
- aggressive.
Diagnostics
Doctors often detect multiple myeloma before any symptoms appear. If there is a suspicion of illness, doctors will take the following:
- collection of anamnesis of the disease (the doctor finds out what, in the patient's opinion, the disease is connected with, when the complaints appeared);
- general examination (on examination, it is possible to reveal hemorrhages on the skin, pallor, with percussion of pain in the bones);
- general blood test (for all forms, normocytic anemia, in more than half of the cases, an increase ESR, there may not be any changes in white blood, but neutrophilia with a shift to the left is often observed);
- bone marrow puncture (megakaryocytes are secreted in the bone marrow);
- general urine analysis (use the morning urine sample for analysis. Within a few hours, it must be delivered to the laboratory. In urine - an increased level of relative density due to the presence of protein molecules, proteinuria. Pathognomic sign of multiple myeloma (Bens-Jones protein);
- biochemical blood test (total protein, ALT, AST, bilirubin, level creatinine, uric acid);
- X-ray of all bones of the skeleton except for the distal regions (pictures are taken from the middle of the shoulder to the hand and from the middle of the thigh to the foot);
- computed tomography can detect foci of bone tissue destruction, compression of the spinal cord;
- sternal puncture is the main diagnostic method (a puncture is made with a special needle in the sternum or ilium. The cells are removed and a smear is made. In a smear, a bone marrow tumor, a large number of plasma cells, immature blood cells are found);
- urine analysis according to Zimnitsky (allows you to assess the concentration ability of the kidneys. To perform this analysis, during the day, a person collects urine every three hours, a total of eight portions are obtained. Evaluate the total amount of urine, density, night and day urine output).
Read also:Angioma
Multiple myeloma treatment

Treatment methods include:
- local irradiation of a bone marrow tumor;
- inpatient chemotherapy;
- high-dose chemotherapy with bone marrow transplant.
The initial tactics of patient management is determined by his age, the presence or absence of severe concomitant diseases.
High-dose chemotherapy with bone marrow transplantation is used for patients under 65 years of age and no severe pathology. Local irradiation of myeloma is mainly used as a palliative method of treatment, especially for severe tenderness in the skeletal region.
Drug treatment
Chemotherapy is the most popular treatment for multiple myeloma. Drugs can only be prescribed by a chemotherapist.
During therapy, it is necessary to constantly monitor the patient's condition and the blood picture.
There are the following approaches to chemotherapy:
- monochemotherapy - treatment with one drug;
- polychemotherapy - the use of more than two drugs.
Drugs used for treatment:
Alkeran (Melphalan) - antineoplastic, cytostatic agent
Side effects:
- dyspeptic symptoms: nausea, vomiting;
- itchy skin;
- allergic reactions;
- pneumofibrosis;
- decreased ovarian function.
Prednisolone - hormonal agent. It has an immunosuppressive effect. Reduces protein synthesis in blood plasma, enhances protein catabolism in muscles. It is prescribed to prevent the side effects of chemotherapy.
Cyclophosphamide - antineoplastic agent.
Side effects:
- allergic reactions;
- cystitis;
- at high doses, cardiotoxic;
- hives.
Vincristine - an antitumor agent of plant origin. It blocks substances required for the synthesis of plasma cells. Vincristine is administered continuously intravenously throughout the day.
Side effects:
- convulsions;
- nausea, vomiting;
- hives;
- dysuria, urinary retention.
Adriablastine - an antibiotic that has antitumor activity. Reduces the growth and activity of neoplastic cells. Under the influence of adriablastin, free radicals are formed, which affect the cell membrane.
Side effects:
- phlebitis;
- dermatitis;
- violation of cardiac conduction;
- allergic reactions
- pain in the region of the heart.
After a course of chemotherapy, patients are prescribed Interferon to maintain immunity. If anemia occurs, red blood cell transfusion is necessary.
Bortezomib (Bortezomibum) - is a new drug in the treatment of the disease. Its mechanism of action is to stimulate apoptosis. Administered intravenously in a hospital setting.
Combination schemes of the drug:
- VAD scheme. It includes three drugs: vincristine, dexamethasone, doxorubicin;
- VBMCP scheme. It includes 5 drugs: prednisolone, melphalan, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, carmustine.
Signs of the effectiveness of therapy:
- fracture healing;
- an increase in red blood cells and hemoglobin in the blood;
- reduction in the size of the tumor;
- a decrease in the number of plasma cells in the blood.
Local radiation therapy is indicated for patients at high risk of fracture. Especially in the supporting parts of the skeleton: spine, pelvic bones.
Unfortunately, even after effective therapy and complete remission is achieved, the risk of relapse is high. This is due to the fact that the tumor contains a variety of cells, which, after stopping chemotherapy, begin to divide again.
Treatment of complications of multiple myeloma.
Anesthetic therapy is carried out in several stages. To eliminate mild pain, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used:
- Spazmalgon;
- Ibuprofen;
- Indomethacin.
For severe pain and ineffectiveness of NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), opioid analgesics are prescribed:
- Codeine;
- Tramadol;
- Prosidol.
With prolonged use, they can cause drug addiction, so they must be used with caution. For unbearable pain, strong opioids are prescribed:
- Morphine;
- Naloxone;
- Buprenorphine.
A magnetoturbotron is an effect of a low frequency magnetic field. It reduces the side effects of chemotherapy, reduces pain, and disrupts plasma cell division. The course is held 2 times a year.
Read also:Malaria
Electrosleep is the effect of low-frequency currents on the structures of the brain. Currents reduce pain, have a calming effect.
Antibacterial and antiviral therapy is used to treat infectious complications. Since immunity in all patients is reduced, the development of infection is a frequent occurrence. For treatment, they mainly use cephalosporins of the III and IV generation, protected penicillins (ampicillin).
The use of antibiotics with nephrotoxicity (gentamicin) should be avoided.
Fracture treatment should not differ from that in healthy people. Surgical treatment and immobilizing dressings are used. In the postoperative time, bed rest is shown, wearing orthopedic structures.
Osteoporosis is treated with bisphosphonates (zoledronate). They inhibit osteoclast activity.
In multiple myeloma, paraproteins (pathogenic proteins of the immunoglobulin class) are deposited in the kidneys, which leads to impairment of their function. To avoid this, it is important to stop the progression of plasmacytoma growth.
Special medications are used to maintain kidney function.
- Chophytol promotes blood purification, removes urea.
- Retabolil is an anabolic drug that promotes muscle growth. Under its influence, nitrogen is used for protein synthesis.
- Sodium citrate is used in violation of acid-base metabolism, reduces the amount of calcium in the blood
- Prazosin dilates peripheral vessels, lowers blood pressure. Increases renal blood flow.
- Captopril is an ACE inhibitor. Expands peripheral vessels, reduces resistance in them, promotes the excretion of calcium. Improves renal filtration
- With a serious violation of the filtration function of the kidneys - plasmapheresis.
For hypercalcemia, use glucocorticosteroids and chemotherapy
Surgery
For multiple myeloma, bone marrow transplantation is used as a surgical treatment. This can be either autologous transplantation (transplantation of one's own bone marrow) or allotransplantation (bone marrow transplantation from a donor).
Autotransplantation (or autologous transplantation) allows you to increase the doses of cytostatics (a group of anticancer drugs), improve the result of treatment, and increase the period of remission.
Allotransplantation has good results, but is only used in young patients. Since it has a large percentage of deaths.
Nutrition for myeloma
For any cancer, it is important to follow a diet. Smoked meats, fried foods, flour, canned foods should be excluded from the menu.
Food should be varied, contain as many vegetables and fruits as possible. Limit protein intake in order to reduce paraproteinemia and the toxic effect of nitrogen, which is formed during protein breakdown, on the kidneys.
The drinking regime is three liters. About two and a half liters per day should be excreted with urine. If there is edema, then you need to limit the consumption of table salt.
How not to get sick Rustitsky-Kalera disease
You can prevent Rustitsky-Kalera disease in yourself by following the following tips:
- avoid contact with infectious patients;
- lead a healthy lifestyle, give up bad habits (alcohol, smoking);
- include more fresh vegetables and fruits in the diet;
- maintaining immunity: hardening, sports, try not to overcool;
- carefully study the composition of food.
Forecast
The prognosis depends on the sensitivity to chemotherapy and the stage of the disease. The best results in people with stages I and II of the disease and those under 60 years of age.
Before treatment, risk factors are assessed and a prognosis is based on this. Blood myeloma is incurable, but with the right tactics, long-term remission and a high standard of living can be achieved.
Poor prognosis criteria:
- a large number of plasma cells;
- rapid tumor growth, which is determined clinically and radiographically, on radiographs - an increase in the area of defects;
- an increase in paraproteins (an abnormal protein of the immunoglobulin class);
- the presence of metastases;