Ankylosing spondylitis in women: symptoms and treatment, prognosis for life
Ankylosing spondylitis is an unpleasant disease that, without timely therapy, affects the patient's quality of life and is fraught with rather serious complications.
In this article, we want to tell you what ankylosing spondylitis is and how to treat it, how to recognize the disease in the early stages of development and distinguish it from others. pathologies, and what are the prognosis for the life of patients.
Content
- What is ankylosing spondylitis
- Causes of ankylosing spondylitis in women
- Development mechanism: in simple terms
- Forms of ankylosing spondylitis
- Symptoms and signs of ankylosing spondylitis
- How to distinguish disease from others
- Possible complications
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of ankylosing spondylitis
- Prevention and recommendations
- Patient Predictions
- To summarize
What is ankylosing spondylitis
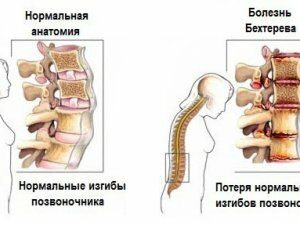
Ankylosing spondylitis (ankylosing spondylitis) is a pathology of the musculoskeletal system, in which the intervertebral joints and joints become inflamed.
Most often disease diagnosed in women aged 15-35.
This disease was first described at the end of the 19th century by the Russian physician V.M. Bekhterev. Of course, people suffered from ankylosing spondyloarthritis long before the disease was described.
For example, characteristic structural changes were found in the skeletons of ancient Egyptian pharaohs, North American Indians, and even some animals that became extinct long before our era.
According to statistics, ankylosing spondylitis suffer about 1.5% population of the globe. At the same time, there are about 10 male patients per sick woman.
Causes of ankylosing spondylitis in women
Unfortunately, there are no definite reasons that could cause ankylosing spondylitis in a woman. It is only known for certain that a genetic predisposition is necessary for the development of pathology: patients who are diagnosed with the disease are carriers of a pathological gene called HLA-B27.
Since the HLA-B27 antigen is found with equal probability in both sexes, the incidence should be expected to be independent of gender. Patients with ankylosing spondylitis almost always have a copy of the HLA-B gene. This gene can be transmitted intrafamily, so that ankylosing spondylitis is a hereditary pathology.
The factors that provoke ankylosing spondylitis are as follows:
- susceptibility to colds;
- systematic hypothermia;
- hormonal disruptions and diseases of the endocrine system;
- chronic inflammatory pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract (for example, Crohn's disease) and urinary system;
- viral infections. There is evidence that in many patients a certain strain of enterobacteria is isolated from the body;
- history of musculoskeletal injuries.
The exact etiology of ankylosing spondylitis or ankylosing spondylitis is unknown, but the pathogenesis of this disease is clearly associated with the presence of a gene HLA-B27. The main clinical picture is enthesitis (inflammation of the site of attachment of tendons to the bones), which is characteristic of ankylosing spondylitis.

Inflammatory factors, interleukin-1 beta, and tumor necrosis factor alpha are also associated with ankylosing spondylitis.
An interaction between the HLA-B27 gene and CD8 + T cells can be hypothesized, which allows the immune system to fight cartilage cells (chondrocytes).
In the case of ankylosing spondylitis, the test for rheumatoid factor is negative, and typical histological findings show inflammation of enthesis, a complex connective tissue complex around the tendon insertion.
In ankylosing spondylitis, the enthesia of the vertebral bodies is affected, which indicates that the cartilage of the connective tissue of the enthesis is a target for the immune system. At an early stage, there is often injury to the sacroiliac joints, including subchondral granulation, which destroys joints and is slowly replaced by connective tissue cartilage, which ultimately leads to ossification.
Read also:Antiphospholipid syndrome
In the spine, ankylosing spondylitis is found on the border of the vertebral bodies and on fibrosis of the intervertebral disc. They ossify in ankylosing spondylitis and form syndesmophytes (vertical vertebral osteophytes). The spine changes its appearance and resembles a bamboo tube with accrete vertebrae.
In addition, mild synovial inflammation may occur, buffering the joints.
With the further course, the periarticular tissue is also affected, ultimately, the fusion of the joints and their immobilization occurs.
Development mechanism: in simple terms
The vertebral column consists of vertebrae, which are separated from each other by plastic intervertebral discs. Thanks to the soft cartilage, the spine is able to change its position in space. On the lateral surfaces of the vertebrae there are ligaments that make the spinal column sufficiently stable and capable of bending in different planes.
With ankylosing spondylitis, chronic inflammation develops in the soft tissues of the joints and in the discs separating individual vertebrae. Because of this, the cartilaginous and connective tissues are gradually replaced by solid bone, which becomes the reason for the limitation of mobility. Gradually, the vertebrae grow together, and the spine becomes completely motionless.
Usually, initially with pathology, the lower part of the spinal column suffers, after which the pathological process spreads upward.
In severe cases of ankylosing spondylitis, the inflammatory process can appear not only in the articular joints, but also in various internal organs, for example, in the heart muscle, liver tissues, etc.
Forms of ankylosing spondylitis
Depending on which joints and organs are affected in ankylosing spondylitis, 4 main forms of pathology are distinguished:
- central - the pathology affects only the intervertebral discs. In the medical literature, two varieties of this form are described: kyphosis, accompanied by kyphosis the thoracic region, and rigid, in which all the bends of the spine almost completely disappear, as a result of which it literally straightens;
- rhizomelic - the pathological process affects not only the spinal column, but also the joints of the shoulder and pelvic girdle;
- peripheral - with this form, it is not the spinal column that is affected, but the joints of the limbs;
- scandinavian - this form of ankylosing spondylitis is characterized by the fact that mainly small numerous articular joints of the hands are inflamed.
Some sources highlight visceral form, in which inflammation develops in the internal organs.
Symptoms and signs of ankylosing spondylitis

Ankylosing spondylitis develops in several stages. Symptoms depend on the stage of the disease:
- Prodromal stage. The disease begins to develop, the symptoms are quite invisible. Patients have back pains at night, "lumbago" become more frequent, which are called "lumbago" in the medical literature. At the same time, in the second half of the day, in most patients, the discomfort in the back gradually fades away, as a result of which they may believe that they are suffering from osteochondrosis. Also the pain gets worse when the weather changes, almost completely disappearing after the simplest exercise or any other physical activity;
- Early stage of development of ankylosing spondylitis: Symptoms in women are manifested by severe back pain, which is exacerbated after a long stay in a stationary position. The pain is especially annoying when patients wake up after a night's sleep. Stiffness of muscles and joints in the lower back and thighs;
- The final stage. At this stage, the patient begins to strongly slouched, he is losing weight, complains of loss of appetite. Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract often join the clinical picture.
Read also:Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis in children: causes, symptoms, methods of diagnosis and treatment, prognosis for the future
Patients have a rather characteristic appearance at a late stage of development of ankylosing spondylitis, the normal curvature of the spine in the lumbar region is smoothed out, and the deflection in the chest area, on the contrary, increases. As a result, the head is pulled forward, and the back becomes rounded: the so-called "supplicant pose" is formed.
Due to ossification of the spine and its loss of flexibility, patients begin to move as if instead of a spinal column they have a fixed stick. For example, turn or bend over sick, suffering from ankylosing spondylitis, can only with the whole body. While walking, the patient cannot fully straighten his legs, as a result of which his gait changes greatly.
Due to the deformation of the spinal column in patients impaired chest mobility, as a result, congestion develops in the lungs. This is fraught with complications such as: bronchitis, pneumonia.
About a third of women suffer from various pathological processes on the part of internal organs, develops myocarditis, inflammation, etc.
How to distinguish disease from others

Often ankylosing spondylitis mistaken for osteochondrosis. The following signs help to distinguish one disease from another:
- with ankylosing spondylitis, the pain is cyclical, which is especially noticeable at an early stage of the development of pathology. Painful sensations intensify in the morning;
- therapy that shows high efficiency in treatment of osteochondrosis, with ankylosing spondylitis does not work;
- at the initial stages of ankylosing spondylitis, a pronounced analgesic effect is given non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. If the patient has osteochondrosis, medicines of this group do not bring relief to patients;
- with osteochondrosis, a person can make bends to the left and right without lifting the feet from the floor. With ankylosing spondyloarthritis, the lumbar region is already affected in the initial stages, as a result, bending is almost impossible;
- osteochondrosis, according to statistics, is more often diagnosed in patients aged 40-50 years. Ankylosing spondylitis in most patients begins at the age of 15-35;
- ankylosing spondylitis is accompanied by weight loss, loss of appetite and fever.
The Scandinavian form of the disease, which mainly affects small joints, is often confused with rheumatoid arthritis.
The main thing to understand is that with ankylosing spondylitis, there are no characteristic seals, or nodules, which are felt on the fingers of people suffering from rheumatoid arthritis. Finally, with ankylosing spondyloarthritis, the joints do not undergo such destructive changes as with rheumatoid arthritis.
Possible complications
The most dangerous complications of ankylosing spondylitis are considered lesions of the heart muscle. In the early stages of the development of pathology, patients may notice pain in the sternum and severe shortness of breath. Such manifestations indicate the presence of myocarditis, that is, an inflammatory process in the heart muscle.
A third of patients have amyloidosis, kidney pathology, which as a result flows into renal failure.
Due to the fact that the volume of the chest decreases, the prerequisites are created for the development pulmonary tuberculosis.
To avoid such complications, at the initial manifestations of the disease, it is necessary to consult a specialist.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, an initial examination is carried out. Further, to diagnose the disease, they are sent to x-ray examination spine. Thanks to x-rays, it becomes possible to identify pathology at a fairly early stage of development: on average, from 4 months after the onset of the disease.
To clarify the form of pathology, they are prescribed Magnetic resonance imaging and CT scan (CT) of the spinal column.
Read also:Fibromyalgia: what it is, causes, symptoms and treatment
Additionally assigned blood test: with spondyloarthritis, due to the presence of a source of inflammation in the joints, an increased level of ESR.
If the diagnosis is in doubt, it is safe to prescribe an analysis to identify the pathological gene HLA-B27.
HLA-B27 it is the only gene that plays a role in the differential diagnosis of autoimmune diseases. Gene found in 90% of fair-skinned people patients with ankylosing spondylitis.
Treatment of ankylosing spondylitis

Ankylosing spondylitis requires a comprehensive long-term treatment.
For therapy are successfully used non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Naproxen, etc., the course of taking pills can be from 2-3 weeks to 5 years or more.
At the same time, during the period of exacerbation of the disease, the dosage of drugs increases, and during remission, you can switch to a maintenance regimen, that is, take about 25% of the maximum dose of the drug.
Thanks to anti-inflammatory drugs, it is possible to quickly restore the mobility of the patient's spine, improve the general condition and quality of life.
Most patients are excellently helped by a drug such as Sulfasalazine. True, the effect of its use has to be expected for several months. Nevertheless, after a course of taking Sulfasalazine, a positive trend is observed in about 65% of patients.
As a local remedy, administration is prescribed corticosteroid hormones directly to the affected area. Injections are made both into the intervertebral discs and into the articular bags.
An excellent result can be achieved cryotherapy. According to statistics, in 90% of cases, patients have a rapid disappearance of pain and stiffness of movements, which arose due to pathological ossification of the ligaments and inter-articular discs.
It will also be useful for patients regular back massage, stay in a sanatorium and a special protein diet.
Prevention and recommendations
You cannot prevent a hereditary disease. The goal of prevention is to avoid more serious complications and reduce the patient's pain. Physiotherapy, massage, and exercise help keep your spine moving.
In the long term, it is also recommended to refrain from smoking.
Patient Predictions
The prognosis for a patient's life depends on many factors, age, stage and form of the disease.
Most patients with ankylosing spondylitis can live a normal life, since this disease, if treated promptly, does not lead to life-threatening secondary diseases. With professionally supervised physical therapy, patients can continue to live despite limited spinal mobility.
In women, ankylosing spondylitis is weaker than in men, they basically have no deformities, only limited mobility. With age, the patient's condition improves, but the disease does not disappear completely.
To summarize
Ankylosing spondylitis, ankylosing spondylitis, is a form of arthritis that causes chronic inflammation of the spine, peripheral joints and extra-articular structures. The pathology mainly affects the spine, sacroiliac joints and hip joints. Ankylosing spondylitis is a form of inflammatory arthritis.
Enthesitis is an important feature of this disease and contributes to pain and stiffness. May lead to a decrease in a person's flexibility and mobility over time. Ankylosing spondylitis can affect various organ systems such as the eyes, heart, lungs, skin, and gastrointestinal tract.
The disease is a leading cause of inflammatory low back pain in both young people and adults.