Fetal alcohol syndrome: what is it, causes, symptoms, prognosis
Content
- What is Fetal Alcohol Syndrome?
- Signs and symptoms
- Causes and risk factors
- Affected populations
- Symptomatic disorders
- Diagnostics
- Standard treatments
- Forecast
What is Fetal Alcohol Syndrome?
Fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS) or fetal alcohol syndromebut (ASP) is a characteristic pattern of mental and physical birth defects resulting from the use of alcohol by mothers during pregnancy. The range and severity of the associated deviations can vary greatly from case to case. However, characteristic features may include growth retardation before and after birth (prenatal and postnatal growth retardation); malformations of the skull and facial (craniofacial) area; brain abnormalities; and / or additional physical attributes. Fetal alcohol syndrome can also be associated with varying degrees of mental retardation, learning disabilities and / or behavioral problems, which in some cases may occur in the absence of obvious physical violations.
Signs and symptoms
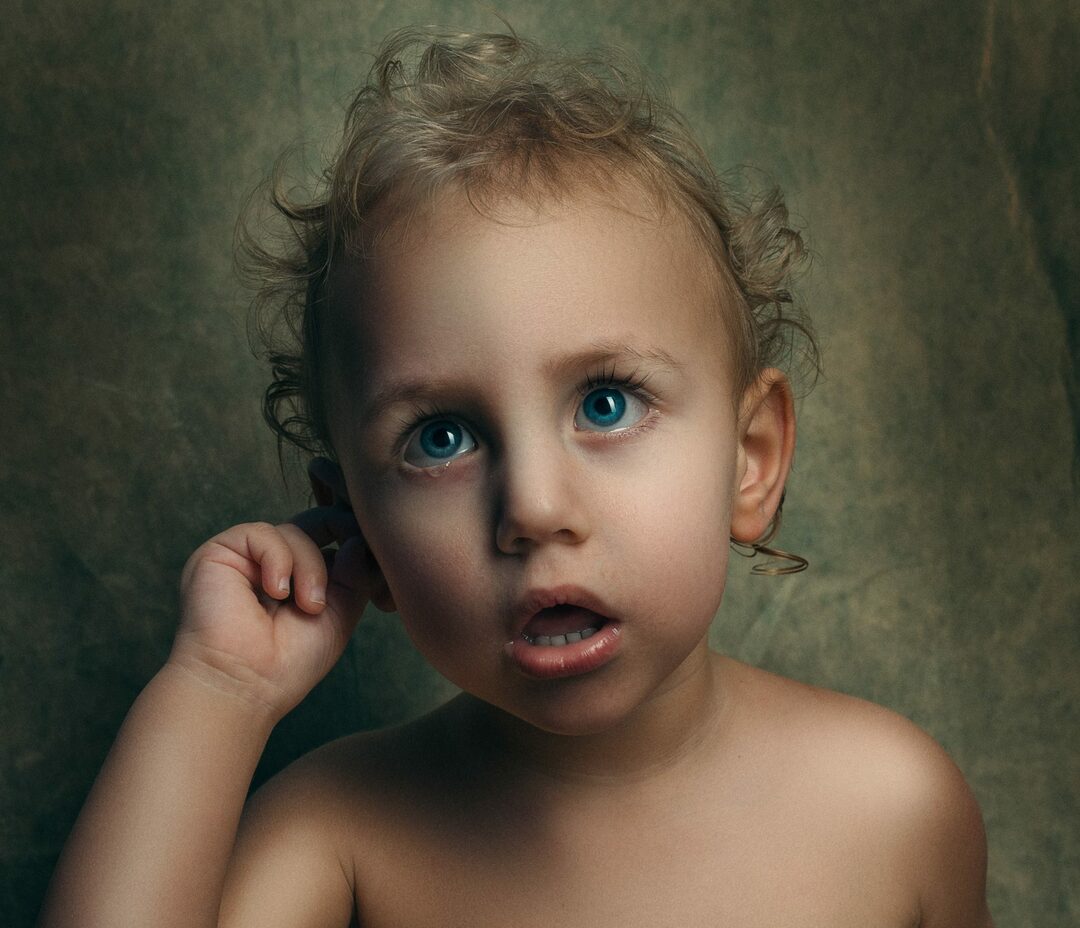

Prenatal alcohol exposure can have several effects, including miscarriage, growth deficiency, mental a disorder or specific pathology of malformations at the severe end of the spectrum known as fetal alcoholic syndrome (FAS). Fetal alcoholic effects (FAE) can be said to be manifested in infants and children with weaker lesions.
The symptoms and signs associated with FAS can vary from case to case. However, characteristic signs often include prenatal and / or postnatal growth retardation, resulting in weight and height loss. Many affected newborns may also have increased irritability, increased sensitivity to sounds (hyperacusis), poor muscle tone and subtle motor dysfunction, including tremors, poor grip and poor hand coordination, and eye.
Evidence suggests that fetal alcohol syndrome is the leading cause of mental retardation. The degree of intellectual impairment can range from mild to severe. The term "microcephaly" indicates that the head circumference is smaller than one would expect for age and gender. Microcephaly is a common feature of FAS that is thought to be due to a general decrease in brain growth. In addition, specific brain abnormalities have been reported in association with FAS, including the absence of a band of nerve fibers that connects cerebral hemispheres (corpus callosum), and underdevelopment of the brain area involved in the coordination of voluntary movements (hypoplasia cerebellum).
Children with FAS typically have learning disabilities, difficulty solving problems and memory, and / or speech impairments. In addition, many have certain behavioral abnormalities, including hyperactivity, impaired judgment, mild distraction, impulsivity, and impaired social and adaptive behavior. In some cases, such anomalies may be present in the clear absence of physical anomalies.
FAS can also be associated with certain facial anomalies, for example, there are short folds of the eyelids (eye slits); vertical folds of skin that may cover the inner corners of the eyes (epicantal folds); and / or a short inverted nose with a wide nose bridge. Additional salient features may include:
- thin upper lip;
- an abnormally long, smooth vertical groove (groove) in the center of the upper lip
- small jaw (micrognathia);
- flattened mid-facial areas (midface hypoplasia).
Eye abnormalities may also be present, for example, unusually small eyes (microphthalmia), drooping of the upper eyelids (ptosis) and / or abnormal deviation of one eye in relation to the other (strabismus). Reports indicate that disease-related facial features can sometimes be relatively thin; In addition, they may become less noticeable as the baby reaches puberty.
In some cases, various heart defectsin particular, an abnormal opening in the septum between the lower or upper chambers of the heart (ventricular or interatrial septal defects). Affected children may also have joint abnormalitiesincluding improper positioning and / or reduced range of motion. Additional physical abnormalities have also been reported in some people with the syndrome.
Causes and risk factors
Alcohol consumption by a mother during pregnancy can lead to multiple consequences for the developing embryo and fetus, including fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS). The exact amount of alcohol consumption that can cause fetal alcohol syndrome has not been determined. However, evidence suggests that moderate to high alcohol consumption during pregnancy can disrupt normal fetal growth and development. Some researchers point out that drinking alcohol throughout pregnancy can lead to more serious, widespread abnormalities associated with FAS, while accidental drinking at high levels can lead to certain characteristics of FAS, with specific defects depending on the time alcohol is exposed to fetus.
It is not known if the adverse effects of alcohol on fetal development can be caused by alcohol itself or one of its byproducts. In addition, the potential contributing role of other factors remains unclear, such as genetic factors, affecting alcohol metabolism or additional environmental factors (such as tobacco use mothers). Some researchers suggest that alcohol consumption may interfere with the transmission of some important nutrients through the placenta, playing a role in the prenatal growth retardation characteristic of syndrome.
Since the amount of alcohol required to cause FAS is unknown, it is recommended that pregnant women abstain from alcohol consumption.
Affected populations
Researchers estimate that fetal alcohol syndrome (FAD) occurs in about 1-2 cases per 1000 live births. According to reports in the medical literature, ASP is considered the leading cause of mental retardation in Western countries.
Symptomatic disorders
Symptoms of the following disorders may be similar to those of fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS). Comparisons can be useful for differential diagnosis:
The use of certain medications during pregnancy (such as the anticonvulsant drug hydantoin) may result in certain characteristics similar to those associated with FAS. In addition, some chromosomal abnormalities and genetic syndromes may also show similar symptoms and signs in some cases.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing FAS is difficult because there is no single or simple test that can capture the wide range of signs and symptoms of FAS. Certain physical signs, developmental problems, behavioral problems, or school failure should prompt the parent, or a pediatrician, or other child development practitioner, consider FAS as a potential diagnosis, especially in the context of prenatal exposure to alcohol. A known history of alcohol use during pregnancy is helpful in the diagnosis but is not required for the diagnosis of FAS.
Standard treatments
Treatment for FAS is usually symptomatic and supportive. Early intervention is important to enable affected children to reach their potential. Specialty services that may be helpful include special education, speech therapy, physical therapy, and / or other medical, social, and / or professional services.
Prevention of FAS is achieved by avoiding alcohol consumption during pregnancy.
Forecast
The prognosis for people with fetal alcohol syndrome is extensive. Some evidence suggests that having a confirmed diagnosis of fetal alcohol syndrome improves prognosis, possibly because it improves access to health care. Other FAS studies suggest that early diagnosis improves prognosis because early intervention programs are implemented at a younger age.
In one study, researchers looked at the natural history of a group of people with fetal alcohol syndrome between the ages of 12 and 51. Although no comparison group was included, rates of various mental, social and legal problems were documented as follows:
- mental health problems (95%);
- incarceration in a prison, drug or alcohol treatment center, or psychiatric hospital (55%);
- problems with the law (60%);
- inappropriate sexual behavior (52%);
- inability to live independently (82%);
- employment problems (70%);
- alcohol and drug problems (> 50% males, 70% females).
In a more recent study, Swedish researchers evaluating the psychosocial characteristics of 79 adults with fetal alcohol syndrome, also found higher rates of special education, unemployment, disability, prescription of psychotropic drugs and hospitalizations for alcohol abuse and mental health problems compared to their age, gender and place of birth - matching cohorts. However, both groups had similar levels of felony.