Goldenhar syndrome: what is it, symptoms, photos, treatment, prognosis
Content
- What is Goldenhar syndrome?
- Signs and symptoms
- Causes and risk factors
- Affected populations
- Diagnostics
- Standard treatments
- Forecast
What is Goldenhar syndrome?
Goldenhar syndrome - a rare congenital disease characterized by abnormalities in the development of the eyes, ears and spine.
Also known as oculo-auriculo-vertebral syndrome, Goldenhar syndrome was first documented by Maurice Goldenhar, an ophthalmologist and general practitioner.
The disorder affects one in every 3,000 to 5,000 newborns.
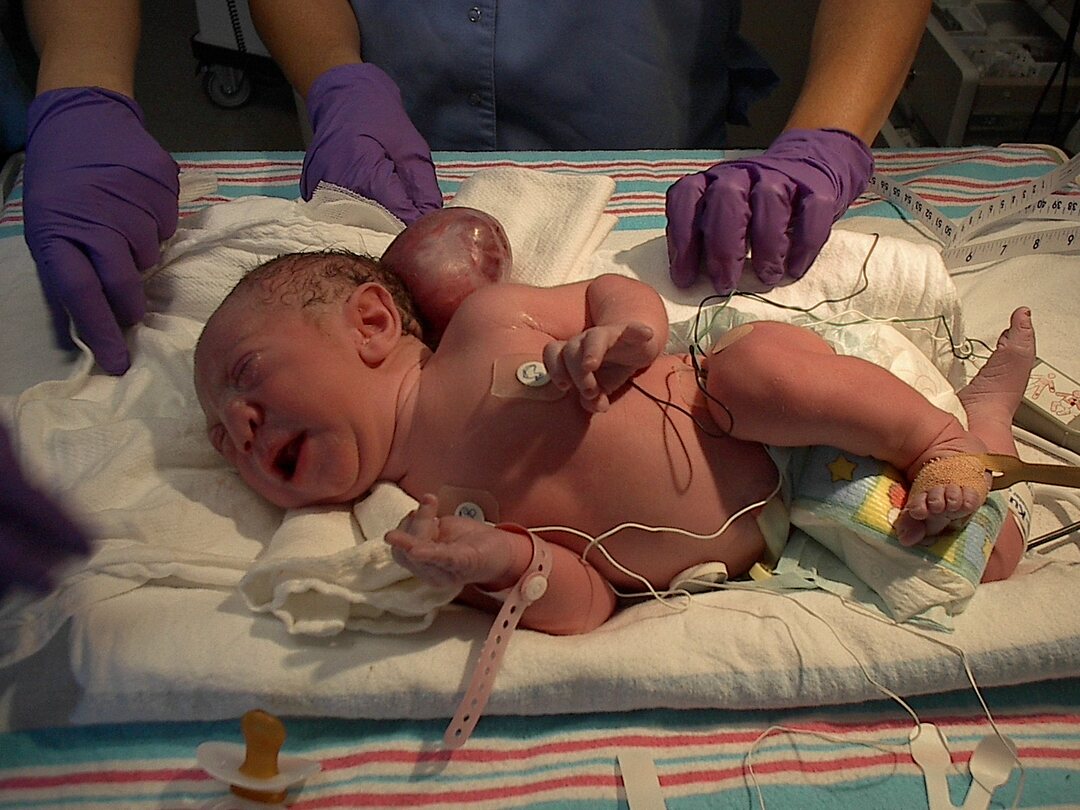
Babies with Goldenhar disease are born with partially formed or completely missing ears, benign eye growths, and spinal deformities such as scoliosis. Oculo-auriculo-vertebral syndrome can also affect structures of the face and other organs of the body, such as the heart, kidneys, lungs, and nervous system. In most cases, deformities affect only one side of the body.
One aspect of Goldenhar syndrome is hemifacial microsomia, in which the jaws and cheekbones are underdeveloped on one side of the face. This underdevelopment, along with eye and ear abnormalities, results in distinctive facial features in children with Goldenhar syndrome.
Spine and chest deformities are also common in Goldenhar syndrome. In some cases, the vertebrae in the spine and / or ribs are not fully formed, missing, or not properly connected. 50% of patients with Goldenhar syndrome have congenital scoliosis. Spine disorders caused by the disease result in incomplete growth and lung diseases.
Signs and symptoms




The symptoms of Goldenhar syndrome can vary, but may include one or more of the following:
- spinal disorders leading to scoliosis, kyphosis or both at once;
- abnormal rib structure, including missing or fused ribs, resulting in poor growth, chest failure, and decreased lung function;
- decreased lung function due to curvature of the spine and pathological growth trends that can lead to respiratory failure;
- many craniofacial anomalies (see. photo above), including:
- hemifacial microsomia, in which the tissues on one or both sides of the face are underdeveloped, especially in the area affecting the ears, mouth, jaw;
- cleft lip and / or palate;
- wider than usual mouth; one side of the mouth may be higher than the other;
- benign cysts and / or growths on the eyes (ocular dermoid cysts);
- a partially formed or completely missing ear (microtia);
- hearing loss, usually in one ear; there may be partial or complete deafness on the affected side;
- congenital heart disease;
- respiratory problems;
- diseases of the kidneys and genitourinary system;
- disorders of the central nervous system.
Causes and risk factors
The origin of Goldenhar syndrome is currently unknown. Most cases of Goldenhar disease occur in families with no history of the disorder.
Rarely, oculo-auriculo-vertebral syndrome can be inherited and follow an autosomal dominant pattern. This means that if one parent has Goldenhar syndrome, each of their children has a 50 percent risk of inheriting the disorder. However, for most people with Goldenhar syndrome, the chance of having a baby with Goldenhar syndrome is extremely low.
Affected populations
Oculo-auriculo-vertebral syndrome affects men more often than women, approximately in a ratio of 3: 2. There is some disagreement in the medical literature regarding the incidence of the disorder. Estimates range from one in 3,000 to 5,000 live births to one in 25,000–40,000 live births. Most of the physical signs associated with the disorder are present at birth (congenital), with possible with the exception of facial asymmetry, which in many cases may appear no earlier than about four years old.
Diagnostics
The diagnostic evaluation begins with a thorough medical history and physical examination of the child. Doctors prescribe various tests to diagnose Goldenhar syndrome and possible complications, including:
- X-ray, study of the internal structure of objects that are projected using X-rays onto a special film.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)which uses a combination of large magnets, radio frequencies and a computer to obtain detailed images of organs and structures within the body.
- Computed tomography (CT)which uses a combination of X-rays and computer technology to produce cross-sectional images ("slices") of the body.
- Genetic testingin which a sample of the patient's saliva is used for DNA identification.
Children with Goldenhar syndrome may also have other health problems, such as heart, lung, or kidney problems. This is due to the fact that the organs of the child may experience developmental impairment in the womb.
Consequently, ultrasound procedure - the use of high-frequency sound waves to create an image similar to those made in during pregnancy in a developing child - can also be carried out on the organs of the child to identify any anomalies. Additional tests that may be required include an assessment of the condition of the heart and a hearing test.
All of these medical tests allow doctors to gather a complete picture of the child's health and help determine an individualized treatment plan.
Standard treatments
Treatment for Goldenhar disease is based on the signs and symptoms that each person has. Ideally, the affected children should be handled by an experienced, multidisciplinary maxillofacial team. Treatment is age dependent, and specific measures may be recommended at different stages of growth and development.
The following are examples of medical problems that may need to be addressed in patients with Goldenhar disease:
- Feeding problems - Some children with Goldenhar syndrome have feeding problems caused by associated craniofacial disorders. Interventions may include special bottles, additional nasogastric feedings, and gastrostomy tube placement.
- Breathing problems - patients with an underdeveloped lower jaw may have breathing problems or develop sleep apnea. In these cases, it is recommended that you seek the appropriate medical professional to ensure proper care.
- Loss of hearing - A hearing test is recommended for all children with Goldenhar syndrome under 6 months of age. Hearing aids or other treatments are recommended for people with hearing impairments.
- Benign cysts and / or growths in the eyes - these tumors may need to be surgically removed if they are especially large or impair vision.
- Craniofacial anomalies (i.e. cleft lip and / or palate), congenital heart defects, kidney problems, and / or spinal abnormalities - some of the characteristic symptoms associated with Goldenhar's disease may require surgical treatment.
- Speech - Patients with Goldenhar syndrome are at increased risk of various speech problems due to a variety of associated craniofacial abnormalities. Therefore, some patients are advised to have speech examinations and work with a speech therapist.
Forecast
The prognosis for most children with Goldenhar syndrome is good. Children can live relatively normal lives and have a normal life span. They can get married, have children, and enjoy work and play.
Because multiple body systems are involved in Goldenhar syndrome, ongoing monitoring of complications and treatment - as needed - is essential to achieve optimal long-term results.
Andrey Zakirov/ article author
I am engaged in the prevention and treatment of coloproctological diseases. Higher medical education. On the site tvojajbolit.ru I will be responsible for the quality and literacy of articles.
Specialty: Phlebologist, Surgeon, Proctologist, Endoscopist.
More about the Author.