Loss of consciousness: causes and first aid in fainting

Loss of consciousness is a symptom of many diseases.Sometimes it is a consequence of the acute transient shortage of blood circulation in the brain and then it is a question of "syncope", and sometimes it is a sign of much more terrible events in the body.Regardless of the reasons, any loss of consciousness frightens others who, panicking, begin to make mistakes in the provision of first aid.How will be correct?For this it is worthwhile to understand why there is a loss of consciousness.
Contents: Causes of unconsciousness Diagnosis First aid for unconsciousnessCauses of unconsciousness
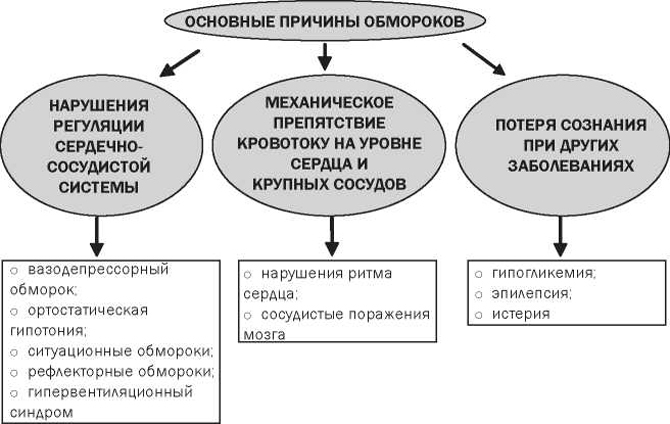
There are a lot of causes for loss of consciousness, but they can be grouped into 4 large groups:
- due toInsufficient blood flow to the brain;
- due to decreased oxygen saturation of blood;
- due to metabolic disorders( impaired brain nutrition);
- due to impaired transmission of impulses along nerve fibers in the brain or the appearance of pathological foci of excitation in it.
Loss of consciousness due to insufficient inflow occurs:
- As a result of the pathological reaction of the nervous system to the resulting stimuli( fright, fatigue).At this moment, the cerebral vessels expand, the pressure in them falls, the blood flow velocity slows down, as a result of which the nutrition of the brain structures deteriorates sharply.
- For heart diseases.This is due to a sharp decrease in cardiac output with the appearance of various arrhythmias, blockades.
- With orthostatic hypotension, in which a person loses consciousness at the time of a sharp transition from a horizontal position to a vertical one.This is due to the violation of pressure regulation, in which the blood does not have time to redistribute from the lower limbs to other areas of the body, including the brain.
- In any form of shock, when there is a sharp violation of the flow of blood to all organs.

Loss of consciousness due to lack of oxygen in the blood occurs in the following situations:
- long stay in a stuffy room;
- severe diseases of the bronchopulmonary system;
- poisoning with poisons blocking hemoglobin( carbon monoxide);
- anemia with a sharp decrease in hemoglobin levels.
Diabetes mellitus is the most common "metabolic" cause of unconsciousness.This disease with its inadequate treatment can easily lead to severe metabolic disturbances and coma.
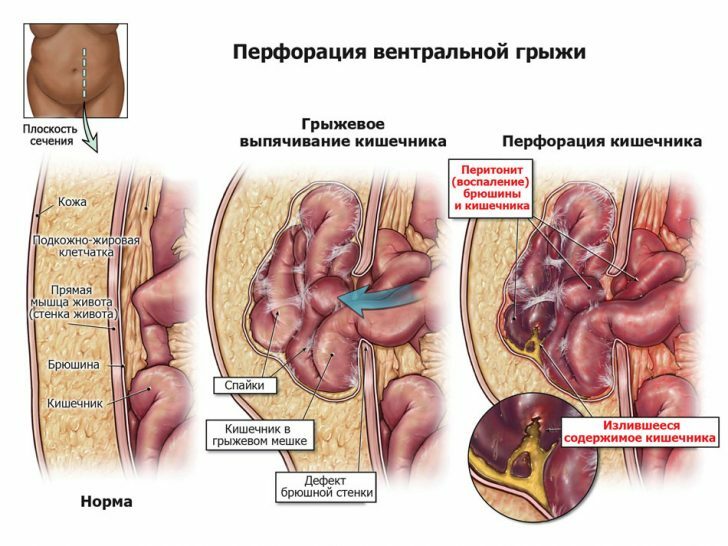
Pathological foci in the brain occur with epilepsy.This is the only type of loss of consciousness in which a person retains motor activity.Stroke, concussion - these conditions, accompanied by a sharp disruption of cell nutrition and their destruction, lead to a loss of consciousness due to the cessation of transmission of nerve impulses.
The most common loss of consciousness occurs in the following situations:
- ventricular tachycardia - 11%;
- syndrome of weakness of the sinus node - 3%;
- bradycardia, atrioventricular blockade of II-III degree - 3%;
- supraventricular tachycardia - 3%;
- aortic stenosis - 2%;
- epilepsy - 2%;
- transient ischemic attack - 2%.
Diagnosis
The loss of consciousness in itself is easy to diagnose - the lack of response to external stimuli, including painful, complete immobility( excluding convulsive syndrome) allows you to clearly identify the problem.But to determine the cause of it is sometimes quite difficult. For this, all the diagnostic studies that traditional science is capable of are used:
- study of an anamnesis during which it is possible to identify the presence of diseases that can lead to loss of consciousness or taking medications that lower blood pressure or affect the functions of the nervous system;In addition, if possible, it proves a provoking factor - a sharp rise, stay in a stuffy room, heat, physical overstrain, etc.
- laboratory tests:
- a general blood test can detect severe anemia;
- glucose analysis helps determine if the patient has developed hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia;
- analysis on oxygen saturation of blood helps to suspect problems that hinder adequate oxygenation.
- Instrumental research:
- electrocardiogram allows detecting the presence of cardiac arrhythmias and blockades;It is possible to carry out an "advanced" version of the ECG, Holter monitoring of the heart rate;
- ultrasound of the heart, which can detect changes in heart contractility, determine the condition of the valve apparatus;
- dopplerography of carotid arteries, which makes it possible to detect obstructions to the blood flow in these vessels;
- computer and magnetic resonance tomography helps to detect damage to the brain tissue.
First aid for unconsciousness
 In fainting, first aid should be given immediately, as the cause of this condition is often unknown, but can be very serious.The unconscious person should be taken out of a stuffy room to fresh air.It is necessary to unbutton the collar of the shirt.Check for a pulse on the carotid artery and spontaneous( self) breathing.If they are present, then bring to the nasal passages cotton wool soaked with ammonia.
In fainting, first aid should be given immediately, as the cause of this condition is often unknown, but can be very serious.The unconscious person should be taken out of a stuffy room to fresh air.It is necessary to unbutton the collar of the shirt.Check for a pulse on the carotid artery and spontaneous( self) breathing.If they are present, then bring to the nasal passages cotton wool soaked with ammonia.
Attention! Do not move the injured person if you can not rule out serious injuries( fall from a height, car crash).A person can have a broken spine and every extra movement increases the risk of disability or death.
If the patient does not regain consciousness, it must be laid on its side in a safe position.This is necessary in order to prevent language devaluation.In addition, in this state, vomiting is quite often observed, and a person can be choked with vomit.The only exception is cramps, in which you can not move the patient.Instead, you just need to insure his head so that he does not break it against solid objects and surfaces.
Attention! Do not try to give an unconscious person any pills or liquids!In such patients, the swallowing reflex is sharply reduced, so the medicine can get into the respiratory tract, causing asphyxia.
After the person comes to himself, he should be taken to the hospital for further diagnosis and treatment.However, if a syncope lasts more than 5 minutes, then most likely the cause of it is quite serious, and there is no time to wait for the restoration of consciousness.
Attention! Do not let a person come to himself nitroglycerin, if he does not complain of pain in the heart!This can cause a sharp drop in blood pressure and a second loss of consciousness.Practice shows that most of the fainting occurs against a background of sudden hypotension, in which nitrate-containing drugs are absolutely contraindicated.
If, along with a loss of consciousness, the patient has stopped breathing and palpitations - immediately begin cardiopulmonary resuscitation.Do not think that you will cope with this difficult matter, if everything that you know about it is derived from American films.There is a clear algorithm for cardiopulmonary resuscitation, and it is best to study it in advance under the guidance of an experienced emergency physician or paramedic of the same service.
Loss of consciousness is a rather formidable symptom, indicating a serious problem in the body.First aid should be started immediately - the "rescuer" does not have time for panic.The sooner you get back to normal and get used to work, the more likely the patient is to survive.
Bozbey Gennady Andreevich, ambulance doctor