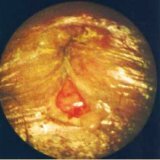
Proctitis: symptoms and treatment
 Proctitis is a pathology accompanied by an inflammatory process on the mucosa of the rectum.When the inflammation passes to the adipose tissue that surrounds the organ, a "paraproctitis" diagnosis is made.Pathology is equally often diagnosed in both sexes of different age groups.
Proctitis is a pathology accompanied by an inflammatory process on the mucosa of the rectum.When the inflammation passes to the adipose tissue that surrounds the organ, a "paraproctitis" diagnosis is made.Pathology is equally often diagnosed in both sexes of different age groups.
Anatomical structure of the rectum
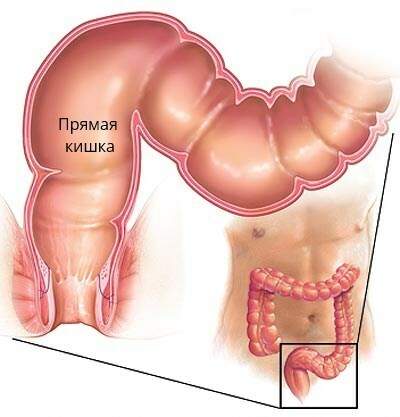 The rectum is the last part of the intestine and serves as the evacuation of digested food.It ends with an anal opening.The wall of the organ consists of muscles and mucous membrane, which produces a special mucus.This mucus serves as a lubricant for easier passage of feces.Also, the rectum has two sphincters, which are compressed to retain the feces and relax during the emptying of the intestine.
The rectum is the last part of the intestine and serves as the evacuation of digested food.It ends with an anal opening.The wall of the organ consists of muscles and mucous membrane, which produces a special mucus.This mucus serves as a lubricant for easier passage of feces.Also, the rectum has two sphincters, which are compressed to retain the feces and relax during the emptying of the intestine.
The composition of the mucus produced by the body includes digestive enzymes.They digest the remnants of food, and everything that can not be digested, is excreted from the body in the form of condensed feces.In the mucosa there is also a large number of nerve endings, which are involved in the process of defecation.
Proctitis causes
There are many factors that can provoke proctitis development:
-
 infectious diseases - intestinal infections caused by pathogenic microorganisms, syphilis, gonorrhea, helminthic invasions, tuberculosis, etc.;
infectious diseases - intestinal infections caused by pathogenic microorganisms, syphilis, gonorrhea, helminthic invasions, tuberculosis, etc.; - traumatic injuries of the rectum, resulting from surgical interventions for hemorrhoids or anal fissures, unconventional sexual intercourse, accidents, injuries during labor, accompanied by rupture of the perineum and rectum, insertion of foreign bodies into the anus or presence of sharp undigested particles in the stool;
- diseases of the digestive tract, in which unprocessed food remains enter the rectum.The mucous membrane begins to produce mucus in excess, which provokes inflammation.Such diseases include hepatitis, cirrhosis of the liver, cholecystitis( inflammatory disease of the gallbladder), pancreatitis( inflammatory process in the gallbladder), gastritis, peptic ulcer, intestinal dysbiosis;
- supply errors: the so-called alimentary proctitis may occur in people whose diet is dominated by spicy and spicy dishes.Also, one of the causes of this disease is often the abuse of alcohol.The development of the pathological process occurs due to irritation of the intestinal mucosa and the production of excessive amounts of mucus;
- vascular pathologies are also able to become a provoking factor for proctitis development.Infringement of outflow of blood is promoted by stagnant phenomena in hemorrhoidal veins.In this case, the mucosa does not receive enough oxygen and can not fully perform its functions.Also, it becomes more vulnerable to various kinds of infectious agents.Thus, among the causes of proctitis may include such pathological conditions as hemorrhoids, varicose veins, venous insufficiency, which develops mainly in people leading a sedentary lifestyle, heart failure;
- malignant processes in the rectum;
- long-term radiation therapy in the treatment of malignant tumors of any location;
- intoxication of an organism due to poisoning with heavy metals;
- some diseases of autoimmune nature( chronic ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease).
It is also possible to identify a number of risk factors that do not cause inflammation of the rectum directly, but contribute to the creation of favorable conditions for the development of the pathological process.Thus, the risk of proctitis increases in people with weakened immunity, prone to frequent infectious diseases, in people with inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary sphere( cystitis, vaginitis, etc.) and stool disorders.
Clinical picture with proctitis
 Proctitis can occur in acute and chronic form.Acute illness is accompanied by constant and periodic symptoms sometimes with an increase in body temperature and typical signs of intoxication of the body.There is a disease due to infections and traumatic injuries.
Proctitis can occur in acute and chronic form.Acute illness is accompanied by constant and periodic symptoms sometimes with an increase in body temperature and typical signs of intoxication of the body.There is a disease due to infections and traumatic injuries.
In the chronic course of the disease, clinical signs are poorly expressed.As a rule, periods of exacerbations alternate with remissions.The disease develops against the backdrop of chronic infectious diseases, autoimmune diseases, malignant neoplasms in the rectum and problems with the vessels.Sometimes chronic inflammation develops as an independent pathology, in other cases it becomes a consequence of an incomplete acute disease.
The classification of acute proctitis includes such forms of the disease as catarrhal, erosive, polyposis, ulcer and radiation.Chronic proctitis can occur in hypertrophic, normotrophic and atrophic forms.
Typical signs of acute proctitis are usually the following:
- pain, burning and itching in the anus.Acute pain becomes more intense with bowel evacuation;
- discomfort and heaviness;
- pain in the perineum, radiating to the genitals;
- is likely the appearance of pain in the lumbar region;
- appearance of purulent discharge with blood impurities from the anus;
- rise in temperature to 38 degrees, general weakness;
- constipation or diarrhea;
- increased urge to defecate, which can be quite painful;
- admixture of blood in the excrements.
Attention ! In the acute form of the disease, pathological manifestations usually occur in just a few hours.If the therapy is started in a timely manner, they disappear rather quickly, most importantly - do not delay with the reference to the doctor-proctologist.
Symptoms of proctitis chronic include mild pain and burning sensation in the rectum.In a number of patients, these symptoms may not be present at all.A slight increase in temperature is possible.In the chronic form of the disease, mucous or purulent discharge from the anus is present permanently, with certain types of pathology also spotting impurities in the feces.
Patients suffering from prolonged haemorrhage in the intestine are characterized by characteristic poor skin and general weakness.With proctitis, provoked by oncological and other serious diseases, exhaustion occurs.
Possible complications of
If at times you do not seek medical help, acute proctitis may go into a chronic form, which is much more difficult to treat.As complications of the disease are considered rectal fistulas, formed as a result of purulent tissue damage, colitis and sigmoiditis, the spread of the inflammatory process to the pelvic peritoneum( pelvioperitonitis).
Polyposis proctitis can be complicated by the transition of the pathological process into a malignant form.Because of cicatricial changes, the lumen of the rectum narrows in the patients.With a long-term inflammatory process in the body, inevitably there is a weakening of the overall immunity, which can become a starting point for the development of many pathologies.
Proctitis diagnostics
Proctitis diagnostics is handled by a proctologist doctor.In the process of examining the patient, he analyzes his complaints and anamnesis, and also assigns a number of studies:
-
 cytological analysis of intestinal contents;
cytological analysis of intestinal contents; - fecal culture for assessment of intestinal microflora;
- digital rectal examination;
- rectoscopy is a visualization method that allows to examine the walls of the affected organ from the inside with the help of a rectoscope.The device is inserted into the rectum through the anus and allows you to see the pathological changes in its mucosa, as well as differential diagnosis with hemorrhoids or anal fissures;
- biopsies of the wall of the intestines to determine the degree of inflammation and differential diagnosis with tumor neoplasms.
Proctitis Treatment
Proctitis treatment can be conservative and surgical depending on the severity of the disease and the presence of complications.In the early stages of development of the disease, doctors try to dispense with non-surgical methods.Patients are recommended to follow a special diet with the exception of those foods that are irritating to the mucous - salty, spicy, spicy, sour and fatty foods.When the disease worsens, it is also necessary to abandon fresh fruits and vegetables.Also, you should completely eliminate the use of alcohol.
A special role in the therapy of the ailment in question belongs to physical stress.Patients can not be long in the sitting position, as the lack of dynamics leads to a weakening of the pelvic muscles and stagnation in the pelvic region and legs.That is why even a severe course of pathology is not a contraindication for the performance of even a minimal set of exercises.
Important ! In most cases, proctitis treatment does not require hospitalization.An exception is the polyposis and ulcerative-necrotic form of the disease.Also, hospitalization may be required in case of exacerbation of chronic inflammation of the rectum.
The drug treatment of proctitis is prescribed by the physician on an individual basis and can include the following medicines:
- antibiotics - a specific type of antibiotic is assigned after laboratory tests in which the exact type of pathogen is identified.The action of antibacterial drugs is directed directly at suppressing pathogenic microorganisms;
- antispasmodic drugs can eliminate spasms and pain, and also normalize the stool;
- for relaxing the muscles of the rectum and eliminating the pain syndrome may also be prescribed antihistamines;
- also provides patients with cleansing and treatment enemas.For the latter, decoctions of medicinal herbs are used, which allow eliminating inflammation and irritation in the intestines, purifying and antiseptic treatment of the rectum;
- also antiseptic effect is achieved when taking sedentary baths with the addition of potassium permanganate;
- as an additional treatment for patients may be prescribed rectal suppositories, accelerating the process of regeneration of the affected mucosa and normalizing metabolic processes;
- if proctitis is caused by ulcerative colitis, there may be a need to prescribe glucocorticoids( hormones of the adrenal cortex).
Self-medication proctitis medication is unacceptable, the selection of medicines and their dosage should be performed only by a qualified specialist.
In case of chronic forms of the disease, the patients are shown sanatorium treatment, observance of a certain diet, exercise therapy, massage, physiotherapy( radon baths, mud therapy, diathermy, etc.).
Surgical treatment of proctitis
 A complication such as paraproctitis can serve as the basis for an operative intervention.In this case, during surgical intervention, excision of adipose tissue along with an inflammatory focus is performed.Also, surgical treatment is required when narrowing the rectum.The operation allows to expand its lumen and to ease the patient's condition.
A complication such as paraproctitis can serve as the basis for an operative intervention.In this case, during surgical intervention, excision of adipose tissue along with an inflammatory focus is performed.Also, surgical treatment is required when narrowing the rectum.The operation allows to expand its lumen and to ease the patient's condition.
Other indications for surgical intervention include long-term proctitis, which is not amenable to conservative therapy, and the presence of neoplasms in the rectum.According to the indications, surgery for nonspecific ulcerative colitis can be prescribed.
Prevention measures
Primary prophylaxis of proctitis involves adherence to a healthy rational diet.It is strongly recommended not to abuse alcohol, as well as fried and spicy food, various spices and spices.It is equally important to strictly observe the hygiene of the genitals and the anal area.At sexual acts it is obligatory to use means of barrier contraception.At the first signs of inflammatory diseases in the pelvic area, you need to see a doctor as soon as possible.
If proper therapy has been performed and remission is achieved, correct personal hygiene and a healthy lifestyle in general will also help to avoid further exacerbations.People with an increased risk of developing the disease in question should monitor the work of the intestine and stool, as well as the state of the genitourinary system.
Chumachenko Olga, medical reviewer