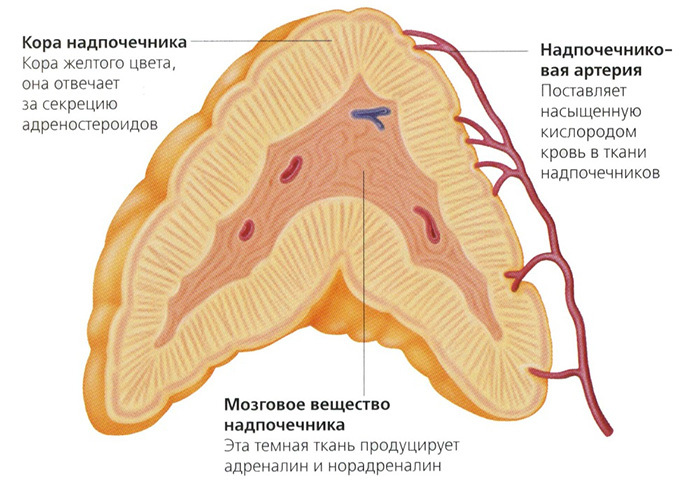
Thyrotoxicosis: a description of the disease
 Thyrotoxicosis is a disease caused by a significant increase in the thyroid hormone content in a person's blood for a very long time.
Thyrotoxicosis is a disease caused by a significant increase in the thyroid hormone content in a person's blood for a very long time.
Thyrotoxicosis, the description of the disease in the reference books contains the translation of the word "thyrotoxicosis" as "thyroid hormone poisoning".A constant excess of these hormones is the reason for the separation of both tissue respiration and oxidative phosphorylation. This process inevitably leads to a disruption of the energy exchange function, which is expressed in excessive generation of heat, a decrease in the amount of stored energy. Deficiency of energy in thyrotoxicosis is eliminated, due to the accelerated course of metabolic processes, which, in the end, determines its clinical picture.
In most cases, thyrotoxicosis is caused by diffuse toxic goiter. Also, this disease often occurs with toxic adenoma, autoimmune thyroiditis, pituitary adenoma. The risk of thyrotoxicosis increases in people with increased sensitivity of tissues to these hormones, as well as in infants whose mothers suffered from hyperthyroidism.
Causes and signs of thyrotoxicosis
The cause of thyrotoxicosis is also an overdose of hormones in the treatment, as well as self-administration of drugs containing these hormones and iodine.
Signs of thyrotoxicosis, provoked by excess thyroid hormones or overdose of drugs containing thyroid hormones, are almost identical. Are pronounced as a violation of fat metabolism, and changes in the cardiovascular and digestive systems, as well as endocrine glands.
Description of thyrotoxicosis disease has differences in sex and age. In the male, the combination of thyrotoxicosis with endocrine ophthalmopathy is more often detected. In addition, the size of the thyroid gland practically does not exceed the 3 degree of increase. In elderly people, heart rhythm disturbances occur more often, mental changes are possible. Thyrotoxicosis in children is characterized by neurotic manifestations. There is a progressive decrease in body weight with good appetite, tachycardia, emotional lability, sweating, discoloration( darkening) due to thyreigenic adrenal insufficiency. Despite the prevailing opinion, an increase in body temperature to 37-38 degrees is observed in patients with thyrotoxicosis, not always, as heat loss increases.
Thyrotoxicosis can occur in mild, moderate and severe forms. With a mild form, there is a moderate weight loss, tachycardia up to 100 beats per minute. The rhythm of cardiac contractions does not change, there are no signs of a violation of the glands of internal secretion.
Average thyrotoxicosis is characterized by pronounced weight loss, tachycardia up to 100-120 beats / min. And tachycardia has a stable character: it does not depend on the position of the human body, the previous period of sleep or prolonged. Short-term changes in heart rate, disturbances in carbohydrate metabolism, gastrointestinal disorders( liquid stools), a decrease in the amount of cholesterol in the blood, and growing signs of adrenal insufficiency are also observed.
The severe form of thyrotoxicosis is the result of a lack of treatment for a long time. There are significant violations of the function of individual organs and systems, violation of the heart rhythm, the development of cardiovascular insufficiency( soon there is shortness of breath, accelerated blood flow, elevated cardiac index), weight loss.
External signs of thyrotoxicosis
Thus, the description of the disease is characterized by the main external signs of thyrotoxicosis, at the appearance of which it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor. Among them: eye bulge, puffiness of the eyelids, double vision, skin moisture, sweating, in some cases, the identification of goiter, fever, weakness, increased excitability, a sharp change of mood, palpitations, shortness of breath, thirst, attacks of diarrhea.
Excess thyroid hormones reduce calcium stores in tissues, so the risk of osteoporosis and fractures increases.
When hyperthyroidism is suspected to be a blood test that can determine the level of thyroid hormones and the presence of antibodies that destroy the thyroid tissue. If in the area of thyroid palpable tumor, need to pass radionuclide examination to check for the presence of iron nodules.
According to the results of diagnostics endocrinologist naznachitt necessary treatment of the disease, taking into account the identified changes, pathological and individual characteristics of each patient.
Treatment of
To reduce the level of hormones, there are 3 main methods of treatment. The most popular of them is taking antithyroid medications. This method is used in the treatment of hyperthyroidism, which is caused by Graves disease. It is aimed solely at suppressing the secretion of these hormones. More effective treatment with radioactive iodine in the formation of nodules in the thyroid gland. Treatment consists of a course of taking doses of radioactive iodine used by the patient in the form of a solution. Iodine accumulates in the thyroid gland and destroys it.
Most patients recover as a result of this treatment almost completely. However, there is a chance of a relapse of hyperthyroidism, especially in patients with Graves' disease. After the surgery or treatment with radioactive iodine, the rest of the gland may not be able to cope with the production of the necessary amount of hormones. Therefore, after treatment, it is necessary to regularly check the level of hormones.
The forecast for the further life is rather favorable. Timely and adequate treatment of hyperthyroidism, depending on the severity of the disease, promotes healing, and causes rapid restoration of disability in most of the patients.