Ménière's disease: symptoms and treatment

Ménière's disease is a pathology of the inner ear, accompanied by increased production of the endolymph( labyrinthine fluid) in the cavities of the labyrinth, an increase in its pressure and a violation of the blood supply to the structures of the inner ear.As a result of the changes, there is edema, which provokes complaints in patients with this disease.The disease is named after the name of the doctor who first described it.Other names are endolymphatic hydrops, labyrinth hydrocephalus.
Meniere's disease manifests with attacks of increasing deafness, noise in the ears, periodic loss of balance, dizziness, nausea, vomiting.
Note : the disease is incurable, but with properly organized therapy, the progress of its development can be significantly slowed down.
Table of contents: Factors contributing to the onset of the disease Classification of the disease Complaints and clinical symptoms in Ménière's disease Methods for diagnosing Ménière's disease Treatment types and prognosisFactors contributing to the occurrence of Ménière's disease
Until now, the causes of this disease are not fully understood.
The development mechanism of endolymphatic gypsum is associated with:
- with dystrophic changes in membrane formations of the cochlear duct, resulting in a disturbance in the physiological movement of the fluid;
- is an available process of hyperproduction of the endolymph;
- pathological mechanism of impaired absorption of excess endolymphatic fluid.
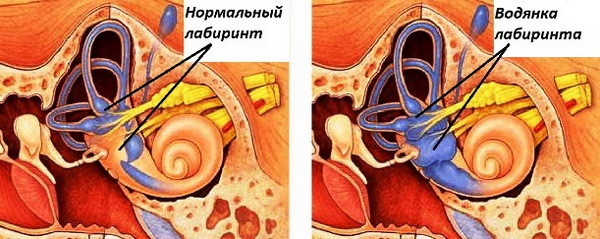
The causes that contribute to the onset of Ménière's disease development are:
- diseases in which water-salt metabolism occurs( chronic diarrhea, adrenal disease, etc.);
- allergic processes leading to a malfunction of autoimmune processes in the body that can cause hyperproduction of the endolymph;
- endocrine-hormonal pathology( insufficiency of estrogenic hormones);
- vascular diseases that cause both an increase in the production of the endolymph and a decrease in its absorption;
- viral diseases, which in some cases lead to ototoxic effect( lesion of tissues of the labyrinth apparatus);
- syphilis;
- traumatic and anatomical problems of the skull, especially the temporal bone, leading to a decrease in its airiness;
- anatomical defects in the structures of the labyrinth of the inner ear;
- problems with autonomic innervation of the inner ear.
Classification of the disease
According to the form of the labyrinth hydrocele, the following are distinguished:
- classic ( with hearing and balance impairment, this occurs in about 30% of cases);
- cochlear ( the disease begins to develop with primary auditory disorders, the most common form is 50% of cases);
- vestibular ( primary vestibular complaints occur, the frequency of this form is up to 20% of all cases of the disease).
The pathomorphologic-clinical classification includes the following disease variants:
- neurological - flowing with recurrent episodes of vestibular disorders and hearing problems.This form is most favorable for the development forecast;
- neuritic - characterized by paroxysmal, or permanent deafness in one ear;
- hemorrhagic .With this form, the blood cells penetrate the endolymph, the fluid pressure increases dramatically and leads to a complete "disconnection" of the vestibular functions with a loss of the ability to hear.Most often a one-sided process, but can affect both ears;
- double sided .The process extends to both ears.
Complaints and clinical symptoms of Meniere's disease
The severity of the manifestations of the physicians determine the stage( I, II, III) of the disease.
Patients experience:
- marked periodic attacks of dizziness, combined with severe nausea and multiple vomiting.A man with Meniere's disease experiences a painful sense of rotation, failure, displacement.The patient can not stand or sit at this moment.He lies down, closes his eyes and tries not to move his head;
- unpleasant sensations in the ear, noises and other sounds, a feeling of raspiraniya, zalozhennost.In this case, the hearing decreases, or is absent at all;
- shortness of breath, palpitations, paleness of the face, increased sweating, pendulum movements of the eyeballs( nystagmus).
The attack lasts from several minutes to several days.Most often its duration is within a few hours.
Note: may be preceded by an attack of Meniere's disease following a stressful situation, fatigue, alcohol intake, tobacco smoke poisoning, acute onset of any disease, high body temperature, trauma.
After an attack, the patient experiences some time auditory difficulties, weakness, gait disturbance.Each new paroxysm leads to an increasing loss of hearing and eventually turns into total deafness, at the occurrence of which attacks of dizziness and other vestibular disorders disappear.
At the onset of the disease, its phase is clearly discernible.The attack of the disease gives way to a period of good recovery.But with the progression of the disease of remission( periods between attacks) are becoming less pronounced, and the symptoms of Meniere's disease are steadily progressing, patients lose their efficiency and are partially desocialized.

Methods for the diagnosis of Ménière's disease
When interviewing and examining a patient, the otolaryngologist in most cases unerringly suspects Meniere's disease by characteristic complaints and symptoms.Additional diagnostic methods confirm the diagnosis.
The patient is assigned the following:
-
 auditory analyzer studies - conventional audiometry, examination of the ear perceived by the frequency tuning fork, other special tests( otoacoustic emission, impedanceometry, promontorial test, etc.);
auditory analyzer studies - conventional audiometry, examination of the ear perceived by the frequency tuning fork, other special tests( otoacoustic emission, impedanceometry, promontorial test, etc.); - otoscopy ( examination of visible anatomical ear formations);
- definition of nystagmus ( pendulum movement of eyeballs);
- electroencephalography;
- measurement of intracranial pressure;
- study of cerebral vessels by X-ray methods, MRI, dopplerography;
- glycerol test, which allows to determine the reversibility, or irreversibility of ongoing processes.
The patient is necessarily referred for a consultation with a neurologist.
In the process of diagnosis, the doctor excludes diseases that give similar complaints( otitis, eustachitis, etc.)
Treatment types and prognosis
The treatment measures for Meniere's disease are divided into 2 categories - withdrawal of acute attacks and planned treatment.
In most cases, treatment can be performed on an outpatient basis.Severe variants or anatomical defects requiring surgical treatment presume the presence of patients in the hospital.
For the removal or reduction of the complaints described in patients with Meniere's disease,
- uses neuroleptics( Triftazin, etc.), whose task is to reduce the psychophysiological component of the disease, remove the fear that arises during the attack, relieve agitation, dizziness;
- preparations that eliminate vomiting and nausea( Scopolamine and the like);
- medicines that dilate blood vessels( No-shpa, Papaverin);
- medications with antihistamine action( especially 1 generation - Dimedrol, Pipolphen);
- diuretics( contributing to the removal of excess fluid from the body, regulation of lymph).
A poorly amenable attack of Ménière's disease, with severe vomiting and with loss of fluid, requires inpatient treatment.
Between the attacks, patients are prescribed antihistamines if necessary, preference is given to 2 and 3 generations.For the regulation of sleep disorders, a hypnotic is selected individually.To eliminate attacks of fear and nervous excitement, sedatives and tranquilizers are given.
Note: , the use of the above medicinal groups should be performed under the supervision of a physician, as they have particular side effects and the potential for drug dependence.
 Properly prescribed treatment and the implementation of all recommendations to patients can significantly reduce the manifestations of the disease, make longer remissions, ease the period of the attack and reduce the rate of development of irreversible pathological changes at.
Properly prescribed treatment and the implementation of all recommendations to patients can significantly reduce the manifestations of the disease, make longer remissions, ease the period of the attack and reduce the rate of development of irreversible pathological changes at.
Unfortunately, drug therapy is not capable of completely curing Ménière's disease.
In cases where drug therapy does not give the expected effect and other indications are prescribed surgical treatment.
Surgical treatment of Ménière's disease
The mechanism of the operation can be:
- with drainage - performed by decompression techniques that improve the outflow of endolymphatic fluid from the labyrinth cavity( drainage of the labyrinth through the middle ear cavity, perforation and fenestration of bone structures,Drainage of the cavity of the endolymphatic sac);
- destructive - blocking by crossing the passage of pulses along the branches of the pre-collar nerve, labyrintectomy( removal of the labyrinth classically, using a laser or ultrasound);
- on the autonomic nervous system - intersection or resection of branches of the sympathetic nervous system, innervating the anatomical structures of the inner ear.
Additional procedures include chemical ablation - introduction of medicines that eliminate the complaints and have a therapeutic effect( alcohol-containing preparations, antibiotics) in the labyrinth structures.
Other methods of treatment
The diet for Meniere's disease should be highly vitaminized and with adequate mineral content.Do not abuse fatty and carbohydrate foods.
In periods between attacks, patients are encouraged to be active, should follow a healthy lifestyle, perform special gymnastics aimed at training the vestibular apparatus and the development of coordinated movements.
In case of development of depression, apathy and other pathological psychological reactions, you should seek help from a psychologist.Also, all relatives and relatives of the patient should be notified of Meniere's disease and the rules of behavior with the patient suffering from this ailment.Classes with them should be conducted by a psychologist, or specialist doctor, rehabilitologist.
Treatment of Meniere's disease is recommended to be conducted against the background of adequate nutrition, proper regimen and psychological support of the patient.In Meniere's disease, it is recommended not to limit physical activity during periods between attacks, to regularly perform exercises to train coordination and the vestibular apparatus.
Patients with hearing loss perform hearing care.
Prognosis for Ménière disease - steady progression, limiting the patient's professional capabilities, disability, partial and complete hearing loss.
Alexander Lotin, medical reviewer