Bacterial tonsillitis: symptoms and treatment at home
 Bacterial tonsillitis( angina) is the inflammation of the tonsils caused by bacteria.In most cases, the development of bacterial angina leads to infection with streptococcus, less often - staphylococcus.It is a disease that occurs with severe intoxication and requires active treatment.
Bacterial tonsillitis( angina) is the inflammation of the tonsils caused by bacteria.In most cases, the development of bacterial angina leads to infection with streptococcus, less often - staphylococcus.It is a disease that occurs with severe intoxication and requires active treatment.
Causes of
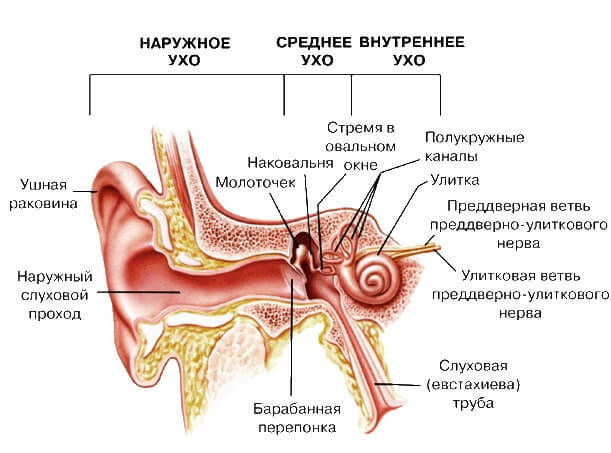
Palatine tonsils( tonsils) is a small paired organ located in the pharynx.They consist of lymphoid tissue, the main purpose of this tissue is to protect the human body from all kinds of alien agents.So, palatine tonsils are a kind of obstacle-filter for penetration of harmful microorganisms with inhaled air consumed by food.
Inflammation of the tonsils occurs when bacteria get into them, while an important role is played by the aggravating factors.These are such circumstances as reduced immunity, hypothermia.
Angina is an infectious disease and it can be infected by a patient with angina or a carrier. There are such forms of bacterial sore:
- Catarrhal;
- Follicular;
- Lacunar;
- Fibrinose;
- Phlegmonous.Symptoms of bacterial tonsillitis
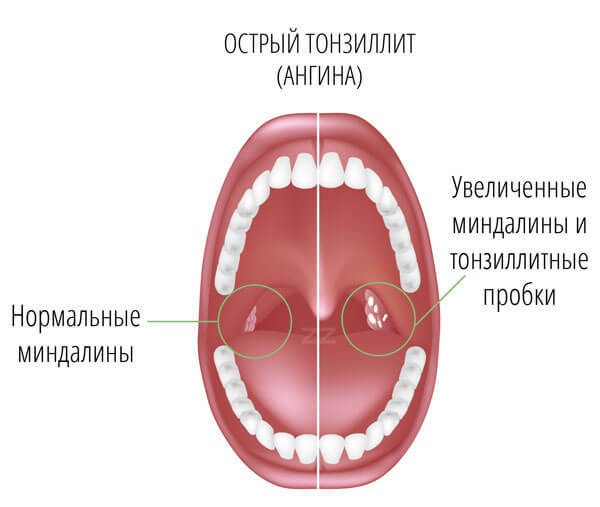
The presence of bacterial tonsillitis in a person can be determined by general and specific characteristics.To general symptoms, physicians include fever, chills, and weakness.To specific - a sore throat at attempts of a swallowing, and also external changes of tonsils.Various forms of bacterial angina are characterized by typical changes in the tonsils, as well as the severity of general symptoms.
Biliary angina
This is perhaps the easiest form of angina .The ailment catches man suddenly.First, a feeling of perspiration, dryness appears in the throat, then there is pain when swallowing.At the same time, a person feels weak, broken, and can be bothered by a headache.There is an increase in body temperature of not more than 38 degrees.
When examining the pharynx, enlarged, swollen, red palatine tonsils are visualized.The surface of the tonsils is clean without purulent deposits.Palpator can detect an increase in cervical lymph nodes.The disease usually lasts about three to five days.
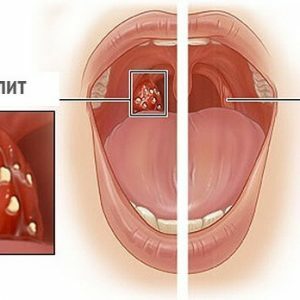
Follicular angina
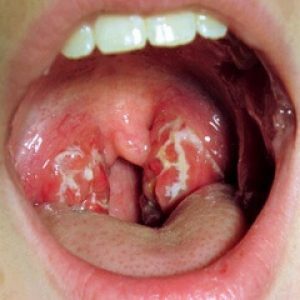
The disease manifests itself with a temperature rise of 38-39 degrees.It is worth noting that in some patients the temperature does not rise to such high figures.At the height of the temperature a person feels weakness, aches in the whole body, chills, headache.In infants with follicular angina, severe symptoms can be observed: vomiting, symptoms of meningism, dullness of consciousness.
Immediately there is an intense pain in the throat when swallowing, because of which a person tries not to eat or drink again.By touch, you can determine the increase in cervical lymph nodes. When examining the pharynx, it is possible to detect an increase, reddening of the tonsils.On their surface, yellowish points with a millet grain are visualized.These are festering almond follicles, which in people are called purulent plugs.As a rule, purulent follicles are opened on the third day of the disease.This is accompanied by a decrease in body temperature, as well as some improvement in well-being.In general, follicular angina lasts about a week.
Lacunar angina
The course and general symptoms of this form of the disease are exactly the same as with follicular angina. But at the same lacunar angina proceeds still heavier.The peculiarity of this form of bacterial tonsillitis is that on enlarged, edematic tonsils pus does not accumulate in the plugs, but spreads over the entire surface of the organ.
Externally it looks like the appearance on the surface of the tonsils of yellowish islets of pus.In this case, the islets can merge with each other, so the purulent coating can cover almost the entire surface of the tonsils.It is characteristic that the plaque never spreads beyond the tonsils.Lasts lacunar tonsillitis about a week, but in case of complications, the duration of the disease increases.
Fibrinous angina

Fibrinous angina is a consequence of follicular or lacunar angina.A characteristic feature of the disease is the appearance on the tonsils of fibrinous white-yellowish plaque in the form of a film .Plaque covers the entire surface of the tonsils, and sometimes even spreads beyond their borders.
When trying to remove plaque, it is rejected easily, without damage to the tonsils.The total plaque on the tonsils is also observed in diphtheria.But with this disease, the plaque is removed with difficulty, and in place of the exfoliated scurf there is a bleeding surface of the tonsils.
Phlegmonous tonsillitis
Phlegmonous tonsillitis is rare, in fact is an intrathonylar abscess.That is, there is a build-up of pus in the near-modal fiber.The formation of an abscess is associated with purulent melting of tonsil tissues in bacterial angina.As a rule, only one amygdala is affected by phlegmonous angina.
With phlegmonous tonsillitis the amygdala is enlarged, edematous, its surface is tense, and palpation is painful to .Subjectively, phlegmonous tonsillitis manifests itself with growing pain in the throat, an even greater difficulty in swallowing, an increase in signs of intoxication.Intratonsillar abscess requires surgical treatment with the opening of the cavity and its drainage.
Treatment of bacterial tonsillitis
Patients with bacterial tonsillitis in the early days of the disease must always comply with bed rest .In case of severe illness the patient is sent to the infectious department.Since swallowing is accompanied by severe pain in the throat, a person can use non-irritating, soft, but nutritious food.The abundant drink is shown, it can be water, fruit juice, compote.
Medical therapy
Because bacterial tonsillitis is caused by bacteria, it is necessary to fight it with antibacterial agents .Only these drugs kill germs and stop the infectious and inflammatory process.No folk methods are able to eliminate the infection, they can only improve their state of health, for example, to reduce the pain in the throat.So, the treatment of bacterial tonsillitis necessarily implies the appointment of antibacterial agents.
Among all antibiotics, preference is given to:
- Penicillin( Amoxicillin, Flemoxin Solutab, Ampiox);
- Macrolides( Azithromycin, Erythromycin);
- Cephalosporins( Cefix, Ceftriaxone).
 Antibiotics are prescribed in tablets or injections depending on the severity of the bacterial tonsillitis.The duration of treatment, as a rule, is seven days. It is very important to go through the entire course of treatment, you can not stop antibiotic therapy only by the fact that a person began to feel better.
Antibiotics are prescribed in tablets or injections depending on the severity of the bacterial tonsillitis.The duration of treatment, as a rule, is seven days. It is very important to go through the entire course of treatment, you can not stop antibiotic therapy only by the fact that a person began to feel better. To prevent the formation of an allergic reaction against antibiotherapy, antihistamines are prescribed( Loratadin, Suprastin).At temperatures above 38 degrees, antipyretic agents can be used - Paracetamol, Ibuprofen.
Local treatment( rinsing with angina)
Local treatment has an antiseptic effect on the tonsils, as well as surrounding tissues. To this end, rinse with special solutions for the preparation of which you can use such components:
- Soda;
- Cookery or sea salt;
- Furacilin;
- Calendula tincture;
- Decoction of the drug daisy.
The rinse solution must always be warm.You can rinse your throat several times a day.
Recommended to read:Grigorova Valeria, medical reviewer