Gallstone disease: symptoms, causes, diagnosis and treatment
Pain in the right upper quadrant can be caused by a variety of pathological conditions.But most often they are provoked by diseases of organs directly related to production and excretion of bile - liver, gall bladder and bile ducts.Statistics show that in the first place in this category of diseases is gallstone disease( CHD), which affects up to 25% of women and 10% of men of adulthood.
Table of contents Causes of cholelithiasis Symptoms of cholelithiasis Subsequent course of the diseaseCauses of cholelithiasis
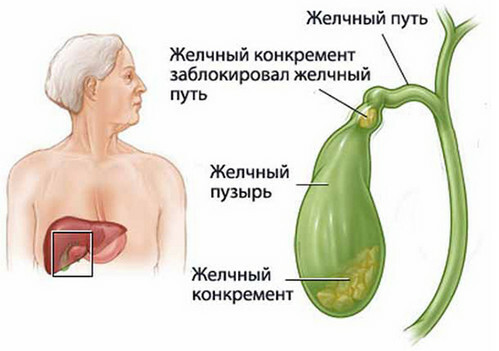
"Stones in the bile" - that's how sick people usually describe their illness and they are right.Stones( concrements scientifically) are formed mainly in the gallbladder and consist of components of bile - bilirubin, cholesterol, calcium salts - mixed in various proportions.
Scientists believe that stone formation occurs for three main reasons:
- Bile stasis.This is due to the appearance of a mechanical obstruction to a normal outflow of bile - cicatricial narrowing, hypertrophy of the mucous membrane of the duct or their muscle layer, tumors.
- Inflammation of the gallbladder wall.An active infectious process causes an increased necrosis of the cells of the mucosa, which come off and become precipitation nuclei, on which the components of the future stone settle.
- Metabolic disorders, namely cholesterol, phospholipids and bile acids.In this case, it is the imbalance between these substances that is important, and not the increase in the concentration of any of them.
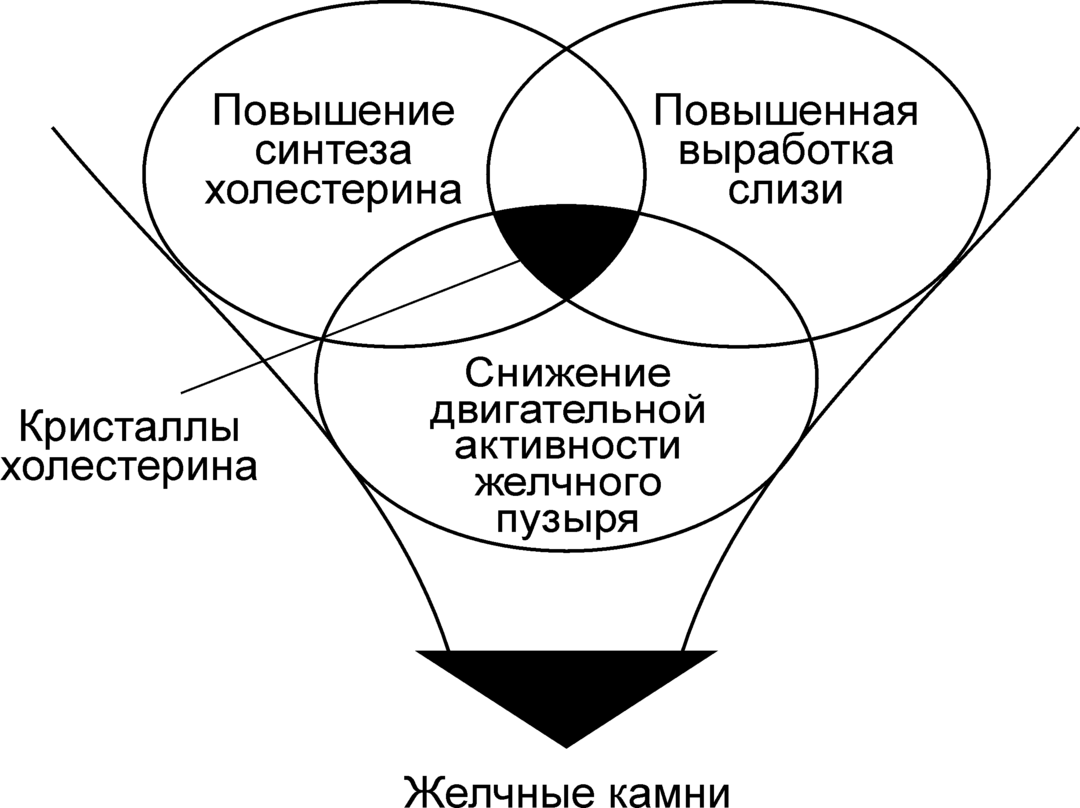
Three things usually work, but only one can prevail.But in any case, once started, stone formation does not cease never.
Symptoms of cholelithiasis
Gallstone disease is insidious - it has an asymptomatic course for a long time.With a successful combination of circumstances, stones in the gallbladder are sometimes found during a medical examination or in the presence of other diseases in which such diagnostic measures as ultrasound of the abdominal organs are shown.
However, most often LCB is only detected when it is manifested by biliary colic, which occurs if the stone is infringed either in the neck of the gallbladder or in the duct from the organ.Pain in this case usually appear after a plentiful feast, during which a large amount of food is used, which provokes an increased release of bile - oily, acute. Sometimes an attack provokes:
- physical load that changes intra-abdominal pressure;
- psychoemotional stress, causing spasm of the muscles of the cystic duct;
- driving on a bumpy road, capable of physically shifting still a fixed stone.
Pain in the right side with biliary colic is very strong, it has a cutting, stitching or tearing permanent character, although it can also be paroxysmal( less often).Its location is the right hypochondrium and epigastrium( in the stomach region), but sometimes it also gives in the lower back, and in the right arm, and the scapula, and even in the heart, simulating an attack of ischemia of the heart muscle.
A frequent "companion" of biliary colic is nausea, accompanied by repeated vomiting, which does not lead to improvement of well-being.In vomit masses there is an admixture of bile.
The duration of colic can vary from minutes to several hours.The behavior of the patient during this period is restless, he rushes from corner to corner, groans.The temperature for biliary colic is almost always normal, although the pulse may become more frequent.Perhaps a slight swelling of the abdomen, a weak tension of the right half of it, determined by palpation.
Ideally, the attack can stop on its own, but often requires the taking of antispasmodics( preferably in injection form).
Subsequent course of the disease
The disappearance of pain does not mean a cure.Gallstone disease is characterized by a chronic course, and therefore it should be more accurately called chronic calculous cholecystitis.
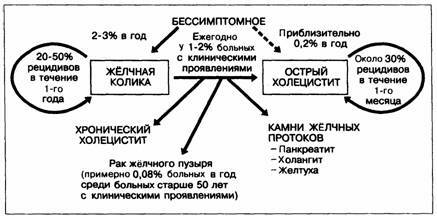
Chronic calculous cholecystitis
Constant presence of gallstones and bile stagnation create favorable conditions for the existence of chronic inflammation.It is them that explains why after the colic the patient's condition rarely normalizes completely. Usually at this time the patient notes the presence:
- pulling pains under the ribs on the right;
- their gain after taking fatty or fried foods, spices;
- bloating;
- diarrhea that occurs after a diet violation;
- bitter taste in the mouth and heartburn.
In the absence of treatment, chronic calculous cholecystitis can lead to complications such as:
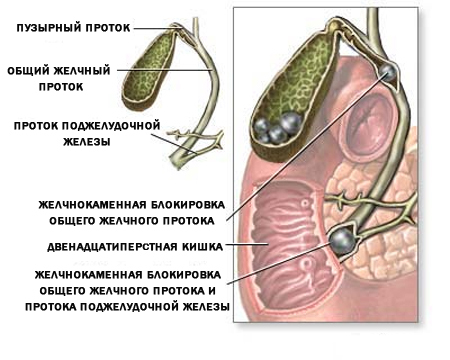
- choledocholithiasis - displacement of stones from the gallbladder into the common bile duct;
- cholangitis - the passage of inflammation from the bladder into the ducts( quite a serious complication);
- cicatricial strictures of the common bile duct - narrowing of its lumen due to scarring of the foci of inflammation in it;
- internal bioliodigestive fistula - the formation of a through hole between the duct wall and the intestinal wall;
- hydrocephalus of the gallbladder - a change in the body, completely turning it off from digestion: the gallbladder is filled with mucous contents, bile does not penetrate it.
Acute cholecystitis
This is one of the most common complications of CLS.It occurs when the microflora is highly aggressive, trapped in the gallbladder, where bile stagnation is present at this time.Symptomatic of acute cholecystitis is somewhat similar to biliary colic: pain of the same localization and intensity, also giving to the right side of the body, nausea and multiple vomiting.However, there are also differences - the temperature, depending on the stage of the disease, rises from an insignificant fever( 37-38 ° C) to very high figures.The abdomen becomes sharply painful, with the transition of inflammation to the peritoneum there is a protective tension.
The main and most dangerous complication of acute cholecystitis is peritonitis, an inflammation of the peritoneum, which sharply increases the severity of any abdominal disease and has high mortality rates.
Diagnosis
In cases of biliary colic, the diagnosis usually does not cause doubt.The typical complaints and data on the factors that provoked the attack allow one to suspect that the gall bladder is "guilty" of causing pain.The use of ultrasound and cholecystocholangiography puts an end to the diagnosis of cholelithiasis.
The same methods used by doctors and in cases with cholecystitis.However, laboratory methods of investigation also help here, with the help of which it is possible to detect the presence of an inflammatory process in the body.Linking the characteristic clinical picture with the data of analyzes and apparatus methods of research, it is possible to put a reliable diagnosis almost always.
Treatment of cholelithiasis
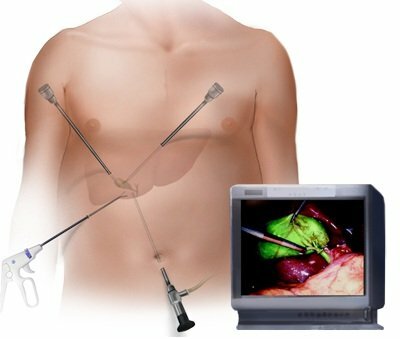
Whatever the supporters of alternative therapies( herbalists, psychics and other healers), the only method of complete healing of the patient is surgical.Once emerged, cholelithiasis never passes without a trace.Therefore, only removal of the gallbladder can completely relieve the patient of the disease.
However, at the peak of biliary colic and with mild forms of cholecystitis, doctors do not practice surgical treatment of the disease.In the first case, it is enough to use antispasmodics - baralgina, no-shpy, papaverine, to quickly relieve a person of pain.In acute cholecystitis also use a cold water bottle on the right hypochondrium, establish a strict diet without provoking the release of bile products and use antibiotics to kill microbes.In the early days, intravenous infusions of suitable solutions for the removal of intoxication are possible.
In severe cases of acute cholecystitis, an emergency cholecystectomy is indicated.This is done to eliminate the threat of developing peritonitis, in which the patient's chances of survival tend to zero.The operation is performed either by laparoscopic method( in the abdominal cavity microsurgical instruments are inserted through the punctures) or through a normal incision.
Gallstone disease is not a sentence, but an occasion for special attention to one's health.Avoidance of bias in the diet, constant monitoring of the gallbladder, and if necessary - removing it in a planned manner, can completely relieve a person of her unpleasant symptoms.The main thing is not to bring yourself to a serious condition, when even the best surgeons in the world will not give a guarantee of healing.
Is it worth it to remove the gallbladder and how to treat cholelithiasis?You will find the answers in this video review:
Bozbey Gennadiy, medical reviewer, ambulance doctor