X-ray and lung fluorography: indications, rules for the interpretation and interpretation of the results
 Despite the availability of modern lung research methods, X-rays and lung fluorography are still valid.Modern X-ray technology and the level of specialists can detect pathological processes in these ways very accurately and quickly.
Despite the availability of modern lung research methods, X-rays and lung fluorography are still valid.Modern X-ray technology and the level of specialists can detect pathological processes in these ways very accurately and quickly.
An important advantage of radiation diagnosis is the relative cheapness of the study in comparison with MRI.If we compare the possibilities of X-ray methods and ultrasound, then, undoubtedly, in the case of chest organs, the X-ray is much more informative.In practice, it is convenient to combine both types of examination of patients, as they complement each other.
We recommend to read:Let's try to understand what distinguishes classical X-ray examination of lungs from fluorography, what are the advantages and disadvantages of each method.In which cases it is necessary to choose one of them, and when it is better to assign both studies.What type of radiation diagnosis is more informative and safe for health.
Table of contents:Fluorography - method of mass population survey
Soon after the discovery of X-rays in 1895, A.Bartelly and A. Carbasso scientists came close to developing a fluorographic method.J. Bleyer created the first photographic fluoroscope, providing the learned community with fluorograms.Alas, the low quality of these images did not allow the introduction of the diagnostic method into practice at that time.But the theoretical discovery of the new methodology was held.
The practical application of fluorography was organized by the Brazilian doctor M. Abreu in 1936.It was they in Rio de Janeiro for the first time in the world created a fluorographic station for the study of chest organs.
Two years later, he published a scientific paper with a detailed description of his technique( indirect image) and the specifics of the equipment used.The results of this work almost instantly spread throughout the world.In Russia, fluorographic research became massively applied at the end of the 30s of the last century.
What is a fluorography
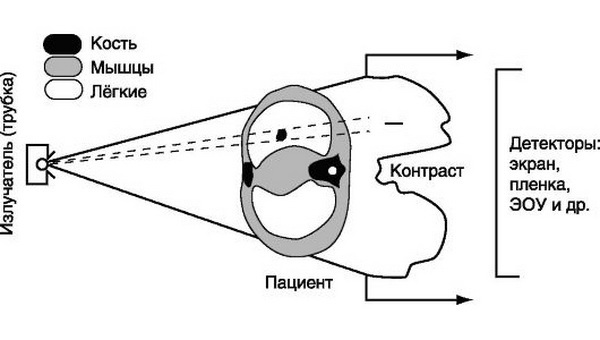
 Fluorography is the photographing of an image obtained on a fluorescent screen that occurs when X-rays emanate from the tube of the device passing through the patient's tissues.From the screen, with the help of special optics, the image is transferred to the film in a reduced form.Obtained images are examined by a radiologist through a magnifying technique.
Fluorography is the photographing of an image obtained on a fluorescent screen that occurs when X-rays emanate from the tube of the device passing through the patient's tissues.From the screen, with the help of special optics, the image is transferred to the film in a reduced form.Obtained images are examined by a radiologist through a magnifying technique.
Modern fluorographs use digital technology, greatly simplifying and facilitating the work of the doctor, reducing the radiation burden on the patient, but the method remains essentially the same.
Note: is the main goal of fluorography - the mass examination of the chest organs in the population.
The fluorograph is able to skip a large number of patients per day.With proper organization, a fluorography room can serve 100-150 patients per hour.Also, the study requires less material costs than classical radiography.
Preventive diagnosis of diseases of the chest with the use of fluorography has risen to a fundamentally new level.
At one time the method of fluoroscopy came into use, in which the photographs were not fixed on the film, but were recorded visually by a radiologist with direct observation of the fluorescent screen.The method gave a high radiation load to the doctor, and did not allow, if necessary, to evaluate the picture to other doctors.Over time, he completely vytisnilsya film version.
Indications for fluorography and thoracic examination
Fluorography is performed:
- for preventive purposes, all people over 16 years of age, at least 1 time in two years;
- primary patients of polyclinics and other medical institutions in the absence of a preliminary study;
- persons living together with pregnant women and newborn children;
- conscripts of military registration and enlistment offices - both conscripts and contractors;
- HIV infected.
If additional diseases are suspected,
The doctor directs the unscheduled fluorography to the patient if they suspect:
- pulmonary tuberculosis;
- neoplasms of the lungs and mediastinal organs;
- inflammatory and other diseases of the lungs and pleura( pneumonia, pleurisy, etc.);
- heart disease and large vessels.
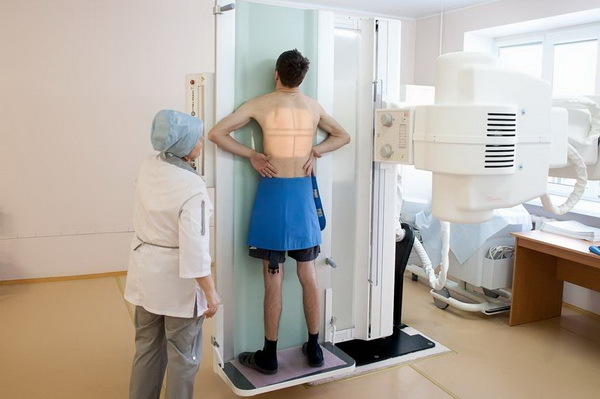
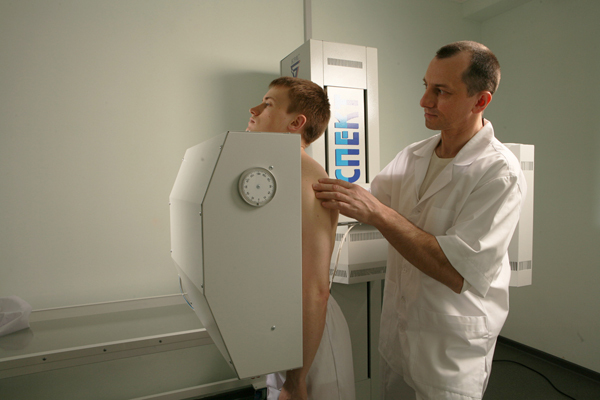
How is fluorography performed by
No special preparations for fluorography or X-ray of the lungs are required.The patient is asked to take off his clothes above the belt and decorations.
Then it is necessary to tightly press chest against the fluorograph screen, put the chin on a special stand for it.Next, a snapshot is taken on inhalation and respiratory arrest.
Disadvantages of fluorography
The main drawback of the method is the too small size and low resolution of the image in comparison with the survey X-ray.That is why, in doubtful cases, the doctor sends the patient after passing the fluorography for refining radiography / -scopy.
Decoding of results of X-ray and X-ray of the lungs
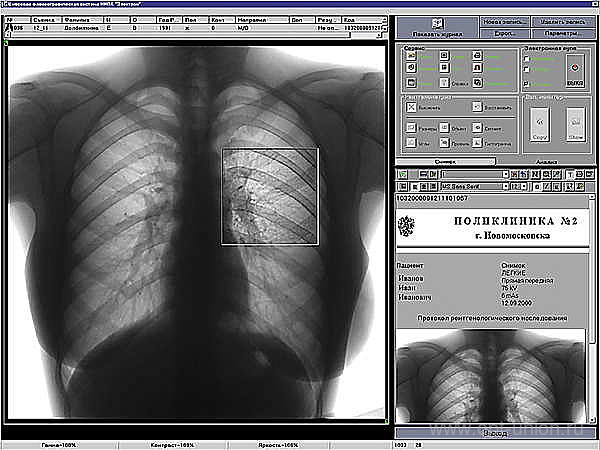
Note: is normal, no pathological processes and lung formation should be determined.
What changes( symptom-complex) can be seen on the fluorogram( roentgenogram):
- is an intensified pulmonary pattern formed by the lung vessels.It is observed with inflammation, tumor processes, sclerotic changes in blood vessels;
- enlargement, tightness and consolidation of the roots of the lungs, which consist of large bronchi, arteries, pulmonary veins.Pathological changes in them lead to a specific picture;
- fibrotic changes . Indicate previously transmitted inflammatory lung diseases;
- focal shadows.They can be single and multiple.The size of the hearth usually does not exceed 1 cm in diameter.Characteristic for pneumonia, tuberculosis, combined with other X-ray symptom-complexes;
- calcinates.Specific shadows formed from deposits of calcium salts at the site of primary foci of infections that did not develop into the disease and were isolated and rendered harmless by the action of human immunity.Calcinates - traces of the introduction of tuberculin rods, nonspecific infection;
- accumulation of fluid in the pleural sinuses.It is observed in pleurisy, some other processes.The picture clearly shows the liquid level;
- displacement of the mediastinal organs( heart, large vessels, trachea, bronchi, lymph nodes, esophagus).The shadow of the mediastinum can deviate or increase in diseases of the heart( vices, hypertension, inflammation of the heart muscle).Also, the displacement occurs when the air or fluid is accumulating in the pleural cavities.The appearance of this sign requires additional examination of the patient;
- change the position of the diaphragm.It is observed with an abnormal type of its structure, with obesity, deformation processes after injuries, diseases, surgical interventions.
Radiography and X-ray of the lung: rules for the procedures
Classical radiography of the lungs( chest organs) is the fixation on the film of data obtained by "radiographing the chest X-rays coming from the radial tube.Unlike fluorography in this method, there is no "intermediary" - a fluorescent screen.
Pictures in the standard version are made in direct and lateral projections, if necessary - oblique.Sometimes focusing is used for a more detailed survey of a particular site.
Therefore, the radiography can be:
- overview;
- sighting.
Fluoroscopy is a dynamic view of the result of X-rays passing through the patient's body and registration is not on the film, but on a special amplifier, which allows to transfer the image to the monitor screen.In digital fluoroscopy, the signal is processed by special computer programs, and then displayed.The entire process can be recorded as video on the storage medium.X-ray examination allows you to view the organs of the chest in the most convenient projection for the doctor.
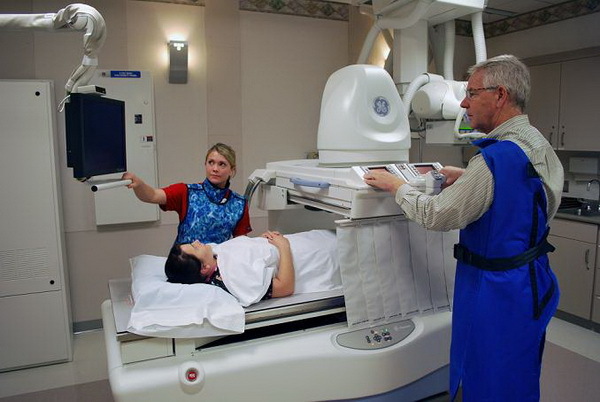 If necessary, a combination of both methods is possible.
If necessary, a combination of both methods is possible.
To obtain correct results, the equipment must be in good working order and configured.This will help to avoid unnecessary strain on the patient and the doctor and will eliminate diagnostic errors.Another important point is observance of the conditions of correct time exposures.The physician must select adequate radiation regimes.
Indications for radiography
The reasons why a doctor sends a patient to an X-ray examination of the lungs are similar to those for fluorography.
A classic radiograph - radiography or visual observation at the time of irradiation on the screen of the monitor - fluoroscopy is used to diagnose diseases of the lungs and the entire thorax.They are also prescribed for the justified necessity of refining the data of fluorography.
X-ray of the lung is indicated if suspected:
- pneumonia, pleurisy;
- tuberculosis in the lungs;
- new processes in the tissues of the lungs, the organs of mediastinum;
- occupational lung diseases;
- heart defects, and other cardiac pathology;
- traumatic injuries of the chest.
Rules for X-ray examination
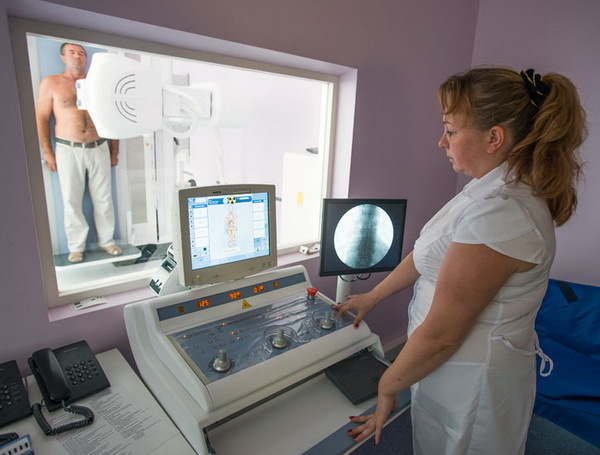 The rules for X-ray and fluoroscopy are similar to those for fluorography.The patient must undress above the waist, take off all metal objects and jewelry, in the presence of long hair, collect them above the examination field.
The rules for X-ray and fluoroscopy are similar to those for fluorography.The patient must undress above the waist, take off all metal objects and jewelry, in the presence of long hair, collect them above the examination field.
During the procedure, behave calmly, listen carefully to the doctor or laboratory technician and accurately follow their instructions.
Note: often ask patients: does it have the right to refuse x-ray examination.Of course have.If the doctor insists, and the patient does not want, then the patient can always write a refusal.In this case, he assumes responsibility for the wrong diagnosis and possible consequences of the disease.
After writing a refusal, no doctor has the right to ask you to provide fluorography for admission.
Without human consent, it is permissible to perform an X-ray examination of the lungs only in the case of an existing disease that can be dangerous for the surrounding people, as well as for patients with mental illness who are in a serious stage of the disease, in the absence of contraindications.A separate category of persons who are subject to compulsory examination are prisoners in places of deprivation of liberty and who are under investigation.
Interpretation of X-ray results of
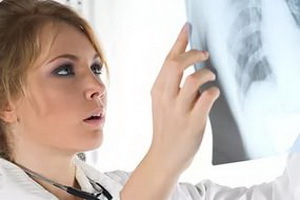 X-ray and fluoroscopy results are interpreted in the same way as evaluation of fluorography data.But these methods allow more detailed study of visible pathological changes, localization, size, limitation.
X-ray and fluoroscopy results are interpreted in the same way as evaluation of fluorography data.But these methods allow more detailed study of visible pathological changes, localization, size, limitation.
The shadows and formations in the survey picture show more clearly.X-ray of the lungs is more informative both due to a much higher resolution of the image, and because of the possibility of visual observation of the patient.Fixation of fluoroscopy on the information carrier allows you to see the results of the study to other specialists.
Fluoroscopy makes it possible to observe the patient in different positions and planes, as a result of which invisible pathological processes can appear, fluid can be detected and their levels changed.These manifestations are especially characteristic for purulent processes, when the liquid and viscous contents of the cavities can not always be clearly defined on the fluorography.
A lot of information for radiologists gives an assessment of the roots of the lungs, where there are large vessels, the evaluation of various rashes in the pulmonary fields, the extent of which exceeds 2 segments.In this case, lesions are called focal dissemination.
Contraindications to the appointment of X-ray and fluorography of the lungs
Fluorography and X-rays of the lungs are not carried out by pregnant women and breast-feeding women.In special cases of this category of patients, the study can be used, but according to strict indications and after a consultation consisting of several specialists.
Comparison of the doses obtained with fluorography and conventional radiography of the lungs
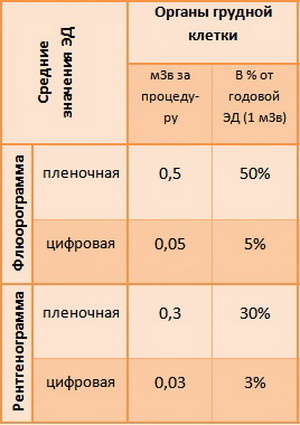 An important property of fluorography is a lower dose of received radiation compared to the conventional radiographic method.
An important property of fluorography is a lower dose of received radiation compared to the conventional radiographic method.
Thus, the average radiation dose for radiographic imaging and fluorography of the chest organs is:
- 0,15-0,4 mSv - review radiography;
- with fluorography: 0,15-0,25 mSv;
- modern digital fluorographs have reduced the level of radiation load to 0.03-0.06-0.002 mSv;
- the old fluorographs produced 0.6-0.8 mSv.
Note: lack of fluorographic method is the impossibility of identifying all variants of tuberculosis.
To solve this problem, in doubtful cases, large-frame fluorography was used, which significantly increases the diagnostic capabilities, and also use fluorography as soft and hard rays.
More detailed information on the rules of fluorography and lung radiography you will get by watching the video review:
Lotin Alexander, radiologist