Pneumonia: classification, symptoms, treatment characteristics
Pneumonia( pneumonia) is an inflammatory process that develops in the lung tissue.There are several types and forms of this disease, doctors classify pneumonia as an acute infectious disease.
Table of contents: Classification of pneumonia Causes Symptoms and signs of pneumonia Methods for diagnosing pneumonia Treatment of pneumoniaClassification of pneumonia
In medicine, there are differences in several main types of the inflammatory process under consideration, which in turn are divided into several subspecies:
- Home( community-acquired) pneumonia:
- typical - develops in people with a normal immune system;
- atypical - patients are characterized by pronounced impairments of the immune system( for example, there is a diagnosed human immunodeficiency virus);
- Aspiration pneumonia - occurs when foreign objects or substances enter the lungs.It often develops in people with strong alcohol intoxication, who are in a coma or under the influence of narcotic substances;
- caused by mycoplasmas, chlamydia and legionella - is characterized by the attachment of atypical symptoms: vomiting, nausea, diarrhea and other signs of digestive disorders.
- Hospital / hospital-acquired( nosocomial) pneumonia:
- developing after hospital stay for more than 2 consecutive days;
- occurs in patients who are on artificial ventilation( ventilator-associated pneumonia);
- is diagnosed in patients with impaired immune system - for example, after organ transplantation.
- Associated with first aid:
- for persons permanently staying in nursing homes;
- for patients who are on long-term dialysis( hardware blood purification);
- for patients with wound surfaces.
In addition, the acute infectious disease under consideration is classified according to the severity of the course:
- is easy to flow;
- medium-heavy current;
- heavy current.
Important : The severity of pneumonia can only be determined by a specialist - the withdrawal will be based on the severity of symptoms and the level of lung tissue damage.
Reasons

The inflammatory process in the lung tissue can develop due to the ingestion of a pathogenic microorganism. But in order for this microorganism to "work" in the pulmonary tissue, certain factors must be present:
- supercooling;
- Alcohol consumption;
- long-lasting bed rest;
- infection with viral etiology;
- conducted in the recent past operational interventions;
- presence in the body of a pathological focus - for example, chronic diseases of the lungs, cardiovascular system, bronchi;
- old age.
The main causative agents of the acute infectious disease under consideration are:
- viruses;
- E. coli;
- pneumococcus is considered to be the most frequent pathogen;
- Haemophilus influenzae;
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa;
- pneumocysts - they can only be in the human immunodeficiency virus;
- chlamydia / mycoplasma - refer to atypical pathogens;
- enterobacteria.
Symptoms and signs of pneumonia

Symptoms of pneumonia in adults are increasing gradually, so early diagnosis is very rare.This acute infectious disease always begins with sudden fever and chills. In this case, the symptoms of general intoxication of the body are pronounced:
- weakness in the whole body;
- decrease( in some cases - loss) of performance;
- decreased appetite, up to total refusal of food;
- increased sweating - most often this symptom is manifested at night;
- pain syndrome in muscles and joints - "twists, breaks";
- is a headache of a non-intensive, but permanent nature.
Then pulmonary manifestations of the disease begin:
- a strong cough - the first few days it has a dry character, and then it becomes wet;
- dyspnea - at the onset of the disease there is only physical effort( for example, after walking or climbing the stairs), then noted and in complete rest;
- pain in the chest - a symptom does not necessarily manifest itself in every case of pneumonia, it is more typical for the disease, when inflammation occurs in the pleura.In addition to the above symptoms, in some cases there may be other symptoms of pneumonia:
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract( diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, intestinal colic) - are inherent only in pneumonia, caused by E. coli;
- herpes on the affected side - typical for pneumonia of viral etiology.
Methods for diagnosing pneumonia
It is extremely difficult to diagnose the acute infectious disease as it is symptomatic - they can also indicate other diseases of the respiratory tract. The doctor, after examining and interviewing the patient, usually conducts the following diagnostic measures:
- laboratory blood test - general and biochemical analyzes;
- sputum analysis;
-
 X-ray examination of the chest - the doctor determines whether one or both of the lungs is affected by the inflammatory process and in which parts of the paired organ there are pathological changes;
X-ray examination of the chest - the doctor determines whether one or both of the lungs is affected by the inflammatory process and in which parts of the paired organ there are pathological changes; - fibrobronchoscopy - examination of the lungs and other organs of the respiratory system using a special optical device.This procedure is performed only with diagnosed pneumonia, which is not amenable to standard treatment;
- computed tomography of chest organs - performed only by the doctor's decision;
- blood culture - allows you to identify a particular pathogen.
Note: on rare occasions, when the therapist has doubts in diagnosing or reveals a complicated course of the disease, a pulmonologist is invited for a consultation.
Treatment of pneumonia
Therapy aimed at getting rid of the inflammatory process in lung tissue should be complex - doctors prescribe medications, they also refer the patient to physiotherapy procedures and approve of some methods from the category "traditional medicine".
Medical treatment of pneumonia
In the treatment of the acute infectious disease in question, doctors use several types of medications:
- Antibiotic( antibiotics) - are mandatory for the appointment, but the choice is made individually and depends on which causative agent was the cause of the developmentPneumonia.
Recommendations for the administration of antibiotics are given below. Important: : any medication should be prescribed exclusively by the doctor in charge.
- Expectorants - appointed with a damp cough, the presence of viscous sputum, when its exit from the body is difficult.
- Detoxification - are prescribed only for severe pneumonia.
- Glucocorticosteroids - are aimed at eliminating infectious-toxic shock in case of complicated inflammation of lung tissue.
- Antipyretics - are prescribed only at temperatures above 38 degrees.
- Cardiovascular - are necessary for severe dyspnea and severe oxygen starvation.
During the recovery period, the patient is assigned immunomodulators and multivitamin complexes - this will significantly increase and strengthen the immune system of the body.
Physiotherapy
It is very important for pneumonia to provide relief for the patient - during the development of the inflammatory process under consideration, it is difficult for the patient to breathe, he feels a fear of dying during dyspnea. Therefore it is advisable to conduct:
- oxygen therapy - through a special mask the patient is supplied with air with a high oxygen content.Excellent helps to get rid of respiratory failure and helps to cope with volume damage to the lungs;
- is an artificial lung ventilation - is indicated in case of severe disease.
- Inhalations
Surgical treatment of pneumonia is carried out in especially severe cases when there is a congestion of purulent contents in the organs.
Treatment of pneumonia with folk remedies
 Treatment of pneumonia with folk remedies should in no case be regarded as the only true one - it is always necessary to get advice from a doctor and combine traditional recipes with medication.
Treatment of pneumonia with folk remedies should in no case be regarded as the only true one - it is always necessary to get advice from a doctor and combine traditional recipes with medication.The most effective methods of supporting the body during the pneumonia are:
- Honey with birch buds.It is necessary to take 750 g of honey( buckwheat) and 100 g of birch buds, mix and boil for 10 minutes in a water bath( warmed).Then drain and take honey on a teaspoon three times a day for 20 minutes before eating.
-
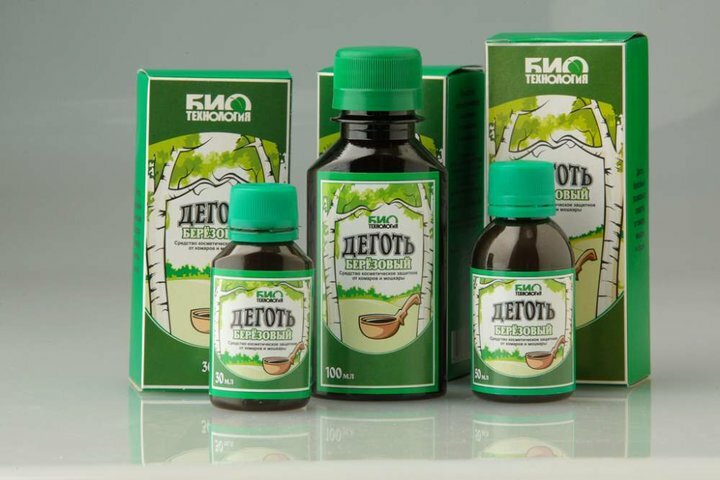 Medical tar.In a three-liter jar should put 0.5 ml of medical tar and top up with warm boiled water.The pot is closed with a lid and put on for 9 days in a warm but dark place.Then you need to take the remedy on a tablespoon three times a day before meals.Tar has an unpleasant taste, so you can drink medicine with water or drink it in a snack with sugar / honey.The same water you need to gargle - twice a day.
Medical tar.In a three-liter jar should put 0.5 ml of medical tar and top up with warm boiled water.The pot is closed with a lid and put on for 9 days in a warm but dark place.Then you need to take the remedy on a tablespoon three times a day before meals.Tar has an unpleasant taste, so you can drink medicine with water or drink it in a snack with sugar / honey.The same water you need to gargle - twice a day.
-
 Compress honey + vodka.It is necessary to lubricate the skin from the side of the lesion with honey, then moisten the rag or gauze with vodka and attach it to honey, warm it all and leave it overnight.Such compresses can be done only in the case of usual inflammation of the lung tissue, when there is no accumulation of pus.
Compress honey + vodka.It is necessary to lubricate the skin from the side of the lesion with honey, then moisten the rag or gauze with vodka and attach it to honey, warm it all and leave it overnight.Such compresses can be done only in the case of usual inflammation of the lung tissue, when there is no accumulation of pus.
Diet for pneumonia
Diet during the acute course of pneumonia and during recovery is very important - properly selected food helps to reduce the burden on the body, in particular the gastrointestinal tract, which will give strength to fight infection.
Recommended diet during exacerbation of the inflammatory process:
- fish of lean varieties( not greasy) - steamed, boiled, but not fried;
- meat is not fatty varieties - boiled, steamed, but not fried;
-
 broths on chicken meat, vegetable broth;
broths on chicken meat, vegetable broth; - vegetables - cabbage, greens, potatoes, garlic, onions, carrots, beets;
- fruit fresh - apples, grapes, pears, watermelon, all citrus;
- dried fruits - prunes and dried apricots;
- juices and fruit drinks from fruit and berries, jelly;
- puddings, vegetable and fruit casseroles;
- honey and any jam;
- tea and rose hips.
Very important for patient pneumonia to introduce into the diet milk and all milk / dairy products - cottage cheese, yogurt, cream, yogurt. For example, during the exacerbation of pneumonia, the menu for one day can be as follows:
- breakfast - a glass of semolina porridge in milk and a glass of milk( all warm);
- 2 breakfast - fruit or berry jelly( 1 glass) or decoction of rose hips( 1 glass) with honey;
- lunch - 200 ml of pearl soup on chicken broth, about 100 g of mashed potatoes with butter and milk( cream), 100 g of boiled / parboiled fish, 200 g of watermelon or any fresh fruit;
- snack - 200 g of any fruit or berries( apple, cranberry or raspberry);
- dinner - 100 grams of cottage cheese with honey and raisins, 100 g of bitter chocolate;
- second dinner - a glass of milk with honey, dry biscuits.Of course, the presented menu is very approximate, but it can be clearly seen that the food of a sick pneumonia at the peak of the disease differs by a small number of the products themselves, but high caloric content is necessary to replenish energy in the body.
It is recommended to eat in small portions, but often.If the patient does not have enough food, then its amount can be increased safely - in general, for pneumonia, a decrease in appetite is characteristic, so that the slightest desire to have a snack should be satisfied.
During the recovery period, you can introduce more saturated foods - for example, increase the amount of bread and baking, put more meat or fish on the portion, instead of the usual butter, use ghee in cooking.But you need to closely monitor the patient's condition - a weakened organism may refuse to take heavy food.Therefore, with the appearance of nausea or vomiting, stop the introduction of saturated, high-calorie foods and continue to adhere to the diet recommended at the stage of the disease.
After recovery, immediately take fat and "heavy" food to patients is not recommended - to introduce the usual foods in the diet should be gradually and in small doses.
Possible complications and consequences
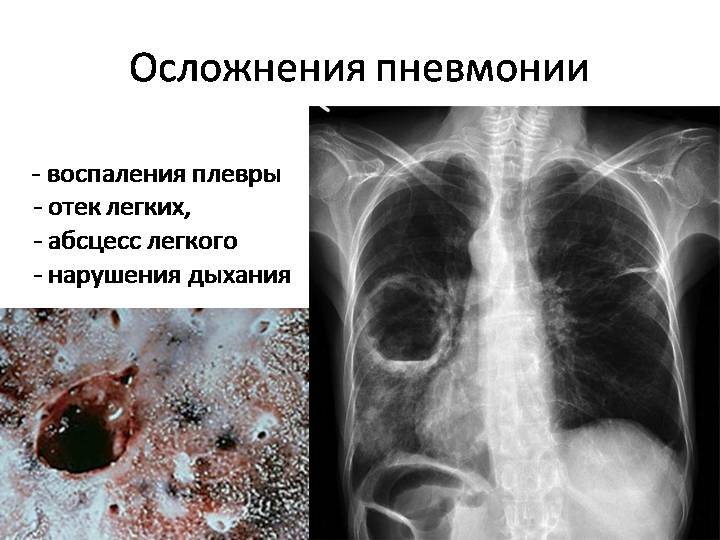
The most common recovery is complete without any serious consequences or complications, but in some cases localized pneumosclerosis may develop - it is a proliferation of connective tissue and lung compaction.To pay attention to such changes doctors can only at a roentgenological inspection of lungs, any influence on functionality of easy pneumosclerosis does not render.
Possible complications:
- pleural inflammation - pleurisy;
- lung abscess - the process of formation of a cavity with purulent contents due to melting of a localized site of the inflammatory process;
- gangrene of the lung - disintegration of lung tissue;
- bronchoobstructive syndrome - the patient experiences shortness of breath, lack of oxygen;
- acute respiratory failure - the lungs are not able to provide the necessary amount of oxygen to the body.
In addition to exclusively pulmonary complications, there may be other:
- infectious-toxic shock - pathogenic microorganisms and products of their vital activity( toxins) enter the bloodstream;
- myocarditis is an inflammatory process in the heart muscle;
- endocarditis - an inflammatory process on the inner shell of the heart;
- meningitis is an inflammatory process in the meninges;
- encephalitis is an inflammatory process of the brain;
- mental disorders - occur extremely rarely and only in people of senile age or abusing alcohol, drugs;
- anemia.
Prevention of pneumonia
Vaccination is an effective prophylaxis for the development of the acute infectious disease in question.It is carried out by influenza vaccine, pneumococcal vaccine, and also against Pseudomonas aeruginosa.It is recommended to carry out immunization in October-November, the period when outbreaks of acute respiratory-viral diseases and influenza are most often recorded.
To avoid the development of pneumonia, it is necessary to treat ARVI and colds in a timely manner, the flu - if you prefer the disease on the go( that is, do not follow the recommendations on bed rest and the intake of specific medicines), then the susceptibility of the organism to bacteria and viruses that can provokePneumonia, it rises.
Pneumonia is not considered a dangerous disease for human life, but it is necessary to get medical help in time to avoid the development of possible complications.It is advisable after the treatment to undergo a rehabilitation course in specialized sanatorium-and-spa institutions - this will help not only to restore the work of the respiratory system, but also to strengthen immunity.
For more information on the signs of pneumonia, methods of treating pneumonia and possible complications, you will receive a video review:
Tsygankova Yana Aleksandrovna, medical reviewer, therapeutist of the highest qualification category.