Increased ESR in the blood: what does it mean?
 The abbreviation "ESR" stands for "sedimentation rate of erythrocytes".This is a nonspecific laboratory indicator that is determined by examining the patient's blood.
The abbreviation "ESR" stands for "sedimentation rate of erythrocytes".This is a nonspecific laboratory indicator that is determined by examining the patient's blood.
ESR refers to methods of initial diagnosis.Correct interpretation allows to determine the algorithm of further actions of the doctor.
Table of contents: History and essence of the method Panchenkov study Method by Vestergren method Normal ESR indices in adults and children What is the increase in ESR?History and essence of the
method In 1918, it was found that in women during pregnancy, ESR changes.Later it was found out that the change of the index is observed with inflammatory diseases.One of the methods for determining the index, which is still widely used in clinical practice, was developed by Westergren back in 1928.
The density of red blood cells is higher than that of plasma, and if the blood does not coagulate, the red blood cells gradually fall to their own gravityThe bottom of the laboratory tube.
Note:
to prevent blood clotting, anticoagulant-sodium citrate( 5% - or 3.8% solution) is added to the tank before carrying out the test.The leading factor affecting the sedimentation rate is the aggregation of erythrocytes( i.e., their clumping together).Formed indivisible particles known as "coil bars" have a smaller area-to-volume ratio, so they more easily overcome the resistance of the liquid( plasma) and settle faster.The larger the sizes and the number of aggregates, the higher the ESR.
 The protein composition of the plasma and the surface potential of the erythrocytes affect the aggregation.When the pathology of infectious and inflammatory genesis develops, the electrochemical composition of the blood changes.The main reason for increasing aggregation is the presence in the blood of the so-called."Acute phase proteins" - immunoglobulins, fibrinogen, ceruloplasmin and C-reactive protein.Agglutination is normally prevented by a negative charge of red blood cells, but it has the property of changing upon the addition of antibodies and acute phase fibrinogen.
The protein composition of the plasma and the surface potential of the erythrocytes affect the aggregation.When the pathology of infectious and inflammatory genesis develops, the electrochemical composition of the blood changes.The main reason for increasing aggregation is the presence in the blood of the so-called."Acute phase proteins" - immunoglobulins, fibrinogen, ceruloplasmin and C-reactive protein.Agglutination is normally prevented by a negative charge of red blood cells, but it has the property of changing upon the addition of antibodies and acute phase fibrinogen.
Note: modified electric charge and increased tendency to aggregation are characteristic for atypical forms of red blood cells.
Slight decreases in albumin content do not affect the sedimentation rate, but a significant decrease in concentration causes a decrease in serum viscosity and an increase in the index.
Panchenkov method
To assess the ESR using this technique, a special laboratory vessel is used - so-called.A capillary of Panchenkov.Initially, sodium citrate is taken up to the "P" mark, and the anticoagulant is transferred to the glass.Then, twice consecutively, the test blood is drawn up to the "K" mark, and it is combined with citrate.The citrated blood is again recruited into the capillary, which is fixed in an upright position.ESR is determined after 60 min.Or after 24 hours;The indicator is expressed in millimeters.This method, which is most often used by doctors in our country, gives high accuracy in single studies.Its main drawback is that it takes a relatively long time to perform the analysis.
The Vestergren test
 The European method is somewhat more sensitive to an increase in ESR.For the analysis, use Vestergren tubes with a diameter of 2.5 mm and a graduating of 200 mm.Venous blood mixed with sodium citrate( 3.8%) in a ratio of 4: 1 serves as a material for research.A reagent such as ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid( EDTA) can be added to the blood.The indicator is expressed in mm / hour.
The European method is somewhat more sensitive to an increase in ESR.For the analysis, use Vestergren tubes with a diameter of 2.5 mm and a graduating of 200 mm.Venous blood mixed with sodium citrate( 3.8%) in a ratio of 4: 1 serves as a material for research.A reagent such as ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid( EDTA) can be added to the blood.The indicator is expressed in mm / hour.
Important: studies on Panchenkov and Westergren can give different numbers, and, the higher the ESR, the greater the possible difference.Therefore, in deciphering the analysis, it must be indicated, by what method the analysis was done.If you received the results in a laboratory that determines ESR by international standards - be sure to specify whether the results were reported to Panchenkov's standards.
Decoding results: normal ESR in adults and children
Normal ESR values vary depending on gender, age, and also some individual characteristics of the subject.
Adult adult limits:
- for men - 2-12 mm / hour;
- for women - 3-20 mm / hour.
Important: increases with age, significantly exceeding the limits of the norm.Elderly people can determine the speed of 40-50 mm / h, and this is not always a sign of infection, inflammation or other pathology.For women over 60 years of age, the figures are within the range of 2-30 mm / hour, and for men of the same age -2-20 mm / hour.
Limits of the norm for children of different ages( in mm / h):
- newborns - up to 2;
- from 2 to 12 months - 2-7;
- from 2 to 5 years - 5-11;
- from 5 to 12 years - 4-17;
- boys over 12 years old 2-15;
- girls over 12 years old - 2-12.
The most common deviations in the direction of increasing numbers.Inaccuracy of the analysis may be due to violation of the rules of conduct.Blood is transferred to the ESR on an empty stomach in the morning.If the examinee the day before was starving or, conversely, too tightly dined - the results are distorted.In such situations it is recommended to retake the analysis after 1-2 days.The result of ESR is influenced by the storage conditions of biological material prior to the study.
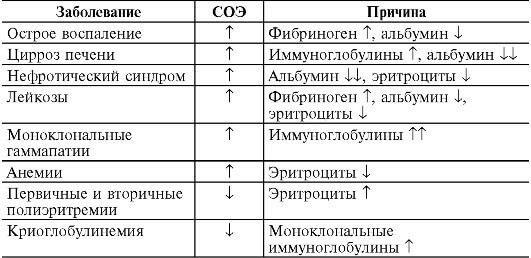
What does the increase in ESR mean?
 The analysis on ESR is famous for its simplicity and cheapness, but the interpretation of results often presents certain difficulties.Figures within the limits of the norm do not always indicate the absence of an active pathological process.
The analysis on ESR is famous for its simplicity and cheapness, but the interpretation of results often presents certain difficulties.Figures within the limits of the norm do not always indicate the absence of an active pathological process.
It is established that in a number of patients with diagnosed malignant diseases this indicator is less than 20 mm / hour.With regard to cancer patients, a significant increase in sedimentation rate of red corpuscles is more typical for individuals with solitary tumors than for patients with malignant blood diseases.
In some cases, no disease is detected in the subjects with an ESR of 100 mm / h or more.
The main causes of increased ESR:
- acute and chronic bacterial infections( infectious diseases of the respiratory and urinary system, as well as tuberculosis);
- viral infections( including hepatitis);
- fungal infections( systemic candidiasis);
- Malignant diseases( tumor neoplasms, leukemias, lymphomas and myeloma);
- rheumatological diseases;
- kidney disease.
Increased ESR is also characteristic for some other diseases and conditions, including:
- anemia;
- inflammation of the middle ear;
- sinusitis;
- chronic granulomatous periodontitis;
- inflammation of the pelvic organs( eg, prostate or appendages);
- pancreatitis;
- enterocolitis;
- phlebitis;
- myocardial infarction;
- significant injuries( including bruises and fractures);
- high immunity;
- diabetes;
- states after the performed operations.
Important: the increase in the rate of erythrocyte sedimentation more than 100 mm / h is most often detected with active infection( including sepsis), malignant tumors, oncohematological diseases, systemic lesions of connective tissue and kidney diseases.
Increased ESR does not necessarily indicate the presence of pathology.Within 20-30 mm / hour, it increases in pregnant women, with menstruation, and also with the intake of certain pharmacological preparations - in particular salicylates( Acetylsalicylic acid, Aspirin), complexes containing vitamin A and oral contraceptives.The increased rate of erythrocyte sedimentation may be due to the recent introduction of the hepatitis vaccine.
 Note: increase in numbers is often observed with obesity in the absence of acute processes, as well as against the background of high blood cholesterol.
Note: increase in numbers is often observed with obesity in the absence of acute processes, as well as against the background of high blood cholesterol.
In the first hours and days of the disease, the indicator may remain normal, since it takes a certain amount of time( 24 to 48 hours) for the serum proteins to change.At the onset of the infectious process, leukocytosis, that is, an increase in the number of leukocytes, occurs much earlier.It also takes time to normalize the indicator.After complete cure, increased ESR can persist for several weeks and even months.In this case, the indicator simply reflects the period of convalescence( recovery).
An increase in the ESR index is the basis for further research.In particular, for the diagnosis of inflammation, a biochemical blood test is needed to evaluate the indices of C-reactive proteins that are markers of inflammation.
Betsik Julia, medical reviewer