Obstructive bronchitis: symptoms and treatment
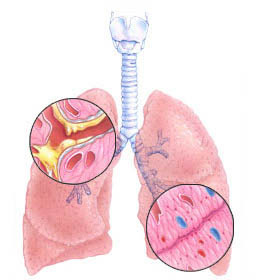
Inflammatory bronchitis, characterized by impaired airway patency, in medicine is classified as obstructive bronchitis.There are two forms of obstructive bronchitis, acute and chronic.According to medical observations, the acute form of the disease is most often diagnosed in pediatric patients, while chronic obstructive bronchitis is diagnosed in adults.The causes of the disease can become viral infections - for example, angina, rotovirus, rhinovirus and others.
Causes of obstructive bronchitis Symptoms of obstructive bronchitis How to treat acute obstructive bronchitis How to treat chronic obstructive bronchitisCauses of obstructive bronchitis
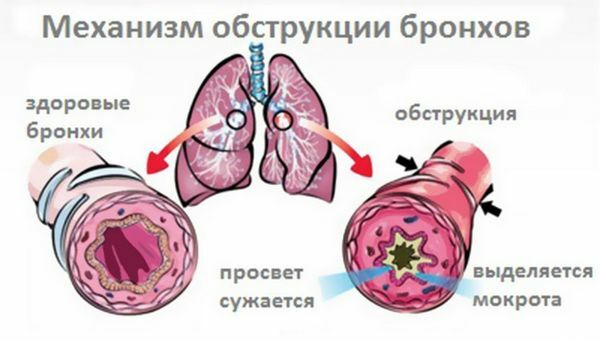
There are a number of factors that are not identified causes of obstructive bronchitis, but are quite capable of provokingIt:
- living in a region with adverse environmental indicators - polluted air, increased moisture level;
- smoking;
- work in harmful production - for example, with silicon, cement or in mines;
- genetic pathology, when it turns out that the patient has a deficiency of a1-antitrypsin.
Symptoms of obstructive bronchitis
If there is a development of the acute form of the disease in question, then it is worth paying attention to the following symptoms:
- body temperature increase;
- general weakness;
- cough.
It is the cough that is the main symptom of the development of the acute form of obstructive bronchitis - at the very beginning of the disease it is characterized as dry and paroxysmal, as the inflammation progresses the cough becomes moist, after each attack a large amount of sputum appears.
We recommend to read:Please note: if the patient does not begin to perform medical measures in case of symptoms of acute obstructive bronchitis, then he may have shortness of breath.This is due to the accumulation of a large number of sputum in the bronchi.In addition to dyspnea, with a severe course of the acute form of the disease under consideration, one can note wheezing with breathing, a wheezing air outlet.
The chronic form of obstructive bronchitis proceeds in a completely different "scenario":
-
 First, the course of the disease alternates with periods of remission and exacerbation.Moreover, during remission, there are no signs of obstructive bronchitis.Exacerbations occur on the background of acute respiratory infections, all symptoms begin to appear at once - cough, fever, weakness.
First, the course of the disease alternates with periods of remission and exacerbation.Moreover, during remission, there are no signs of obstructive bronchitis.Exacerbations occur on the background of acute respiratory infections, all symptoms begin to appear at once - cough, fever, weakness. - Secondly, dyspnea develops in a patient with a diagnosis of chronic obstructive bronchitis slowly and definitively formed only after 7-10 years.And if, at the very beginning of its development, dyspnea is characterized by sickness as a lack of air, then in the end it represents already full-fledged respiratory failure.
- Thirdly, chronic obstructive bronchitis has a peculiarity of the course: at the onset of the disease, the periods of remission are long, exacerbations occur extremely rarely and against the background of acquired infection.But in a few years the periods of remission are not only short, but also rarely happen, breathing becomes constantly wheezing, dyspnea worries the patient even in absolute calm.
How to treat acute obstructive bronchitis
To treat this disease, which occurs in an acute form, is necessary only under the supervision of a specialist. If acute obstructive bronchitis is diagnosed in childhood, the following physician recommendations should be considered:
-
 In order to release the respiratory tract from accumulated mucus, you can use a rubber cannula( a small enema) or a special electric suction.
In order to release the respiratory tract from accumulated mucus, you can use a rubber cannula( a small enema) or a special electric suction. - Positional( postural) drainage and / or vibrating massage are prescribed for better sputum discharge in childhood.
- Facilitates the condition of a patient with obstructive bronchitis so-called "distracting" therapy - hot foot baths.They can be carried out only in the absence of increased body temperature!
- The patient needs to be provided with an abundant drink - this helps to dissolve the sputum, which automatically facilitates the departure of accumulated mucus in the airways.
- Doctors recommend taking medicine with an expectorant effect - for example, tincture on the root of the althaea, licorice root.
- If the sputum turns green or strongly yellow, gets a more dense consistency, it is advisable to take antibacterial drugs( antibiotics) - they should be prescribed only by the doctor in charge.
- It is compulsory for a patient to undergo a course of vitamin therapy - this will strengthen immunity.
Please note: should strictly monitor the patient's well-being and when a very high body temperature, shortness of breath, prolonged coughing without leaving sputum should immediately call a doctor.The optimal option - treatment of acute obstructive bronchitis in the hospital, in a medical institution.
The treatment of obstructive and other types of bronchitis is devoted to the lecture of the doctor of restorative medicine - Prokofieva NV:
How to treat chronic obstructive bronchitis
It is impossible to compare the principles of treatment of obstructive bronchitis in acute and chronic form - they are radically different. The general principles of therapy for the disease under consideration are as follows:
- It is necessary to eliminate the factor that led to exacerbation of chronic obstructive bronchitis - cure acute respiratory viral infection, angina.
- The doctor should prescribe medications with a bronchodilator effect-for example, Salbutamol, Euphyllin, Atrovent, and others.
- For the liquefaction of sputum and to ensure its rapid withdrawal, the patient should take mucolytic medicines - for example, Bromhexine or Ambrobene.
Please note: antibacterial agents( antibiotics) are prescribed by a physician in chronic obstructive bronchitis only in case of detection of pus in sputum.
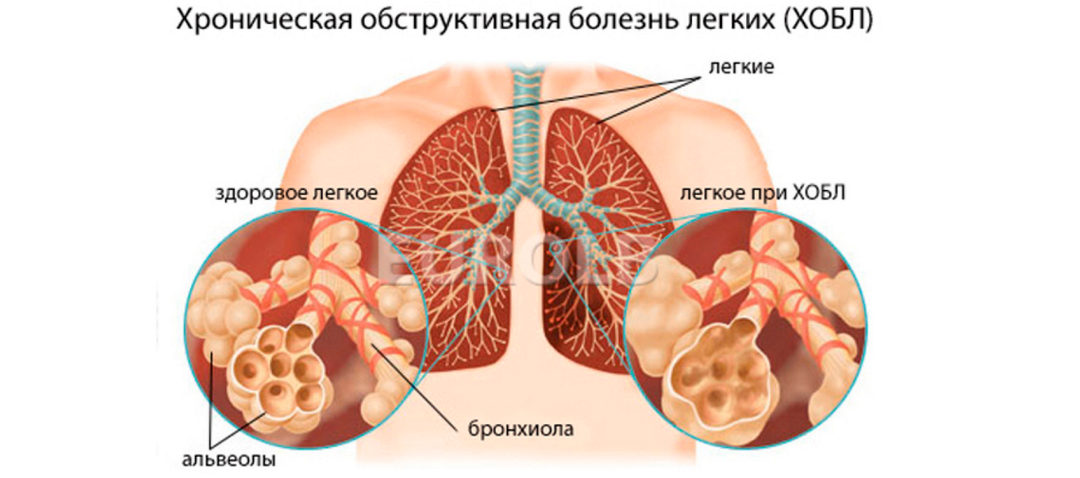
As part of the treatment of chronic obstructive bronchitis, official medicine allows the use of decoctions and infusions from medicinal plants, in some cases, help to relieve the patient's condition compresses.But any measures for the treatment of chronic obstructive bronchitis, not related to appointments from a specialist, should be agreed with the attending physician.
To prevent exacerbation of chronic obstructive bronchitis, patients should constantly engage in strengthening immunity - exercise, swimming pool, outdoor exercise.In addition, you need to periodically take courses of vitamin therapy, avoid hypothermia and promptly treat any viral / infectious diseases.
Tsygankova Yana Aleksandrovna, medical reviewer, therapeutist of the highest qualification category



