Leishmaniasis: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention
 Leishmaniasis - diseases of man and some species of mammals.
Leishmaniasis - diseases of man and some species of mammals.
There are two main forms of pathology:
- cutaneous;
- with internal involvement( visceral).
Two geographic characteristics of the disease are distinguished: leishmaniasis of the Old World and leishmaniasis of the New World.Diseases are caused by leishmania - microbes from the Protozoa type.Transmission of the pathogen occurs with the participation of mosquitoes.
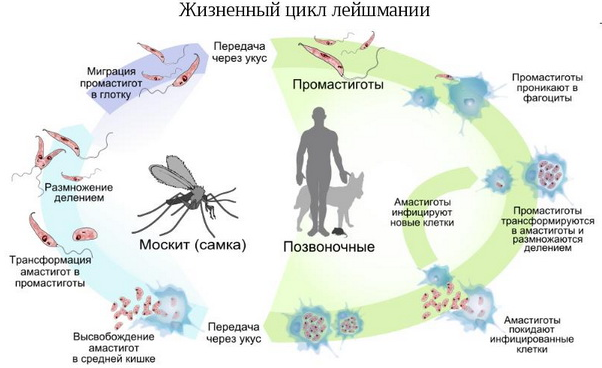
Table of contents: Leishmania development cycle History of disease study Changes in the body in case of illness Visceral leishmaniasisLeishmania development cycle
Leishmania changes their habitat two times during their life period.The first owner is vertebrate animals( foxes, dogs, rodents, ground squirrels) or man.In their body, there is a no-fat( amastigot) stage.The second owner is a mosquito.In it, leishmanias are flagellate( promastigotnuyu) stage.
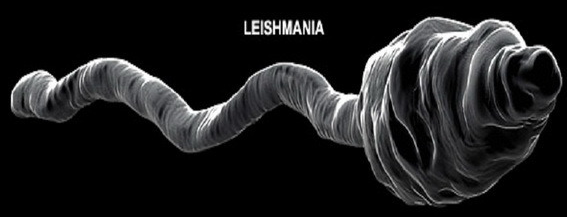
Note : amastigots live in blood cells and blood-forming organs.
History of the disease
For the first time a scientific description of the cutaneous form of leishmaniasis in the XVIII century was given by the British physician Pocock.A century later, works on the clinic of the disease were written.In 1897, P.F.Borovsky discovered the causative agent of the cutaneous form from the Pendin ulcer.
In the years 1900-03.In India, identified leishmania, causing visceral form of the disease.After 20 years, a link was found between the transmission of leishmaniasis and mosquitoes.Further studies have shown the presence of foci in nature and the role of animals, as reservoirs of the microbe.
As leishmaniasis is transmitted
The carriers of the disease are several species of mosquitoes, the favorite habitat of which are nests of birds, burrows, animal den, rock clefts.In cities, insects actively inhabit damp and warm cellars, piles of rubbish, rotting dumps.
The activity of bloodsucking parasites comes in the dark, especially at sunset.When sucking the blood of a sick animal or human leishmania penetrate into the mosquito.After 5-8 days, the insect becomes infectious for the rest of its life.
Note: people are very susceptible to infection, especially - weakened and people with low immunity.
After a mosquito bite, Leishmania penetrates into the body of the new host, where it transforms into a non-combustible form.At the site of the bite there is a granuloma, filled with pathogens and cells of the body, causing an inflammatory reaction( macrophages, giant cells).Then the formation resolves, sometimes leaving behind a scar tissue.
Changes in the body in case of
Dermal leishmaniasis from the outbreak spreads through the lymphatic vessels to the lymph nodes, causing inflammation in them.On the skin there are specific formations, called specialists leishmanioms.
There are forms( in South America) with lesions of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity and larynx, the development of which forms polypous structures that destroy cartilage and tissue.
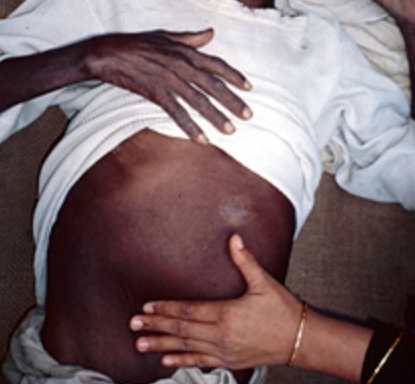
With leishmaniasis of internal organs( visceral), microorganisms from the lymph nodes penetrate into the organs.Most often - in the liver and spleen.Less often their goal is the bone marrow, intestines, kidney tissue.Rarely do they penetrate into the lungs.Against this background, the clinical picture of the disease develops.
 The infected organism responds by the reaction of a delayed-type immune system that gradually destroys pathogens.The disease goes into a latent form.And with a weakening of the defensive forces, it manifests itself again.Leishmania can begin active reproduction at any time, and the silent sickness clinic flares up with renewed vigor, triggering a fever and marked intoxication caused by the products of the leishmania.
The infected organism responds by the reaction of a delayed-type immune system that gradually destroys pathogens.The disease goes into a latent form.And with a weakening of the defensive forces, it manifests itself again.Leishmania can begin active reproduction at any time, and the silent sickness clinic flares up with renewed vigor, triggering a fever and marked intoxication caused by the products of the leishmania.
Particularly exposed to destruction of liver and spleen cells, which leads to the development of anemia in the patient.This is facilitated by the defeat of the bone marrow by parasites.
Leishmania parasitize mainly within cells, which makes them inaccessible to body protection factors.
The survivors have a persistent appearance of immunity.
Visceral leishmaniasis
There are 5 main types of visceral leishmaniasis:
- Indian kala-azar;
- is Mediterranean;
- East African;
- Chinese;
- American.
Mediterranean visceral leishmaniasis
 Other names of the disease are children's leishmaniasis, child kala-azar.
Other names of the disease are children's leishmaniasis, child kala-azar.
This form is mostly used by children aged 1 to 5 years.In general, single cases of the disease are common, but focal outbreaks occur in cities.Infection occurs in the summer, and clinical manifestations of pathology develop by autumn.Cases of the disease are recorded in the area of the Northwest of China, Latin America, in the countries washed by the Mediterranean Sea, in the Middle East.Visceral leishmaniasis also occurs in Central Asia.
The period from the bite of the vector to the beginning of the development of complaints is from 20 days to 3-5 months.At the site of the bite, the formation( papule) is covered with a flake.
Three periods are observed in the course of the disease:
- Initial manifestations - the patient is growing: weakness and lack of appetite, lack of mobility, apathy.When examined, you can find an enlarged spleen.
- The height of the disease - there are specific symptoms of visceral leishmaniasis.
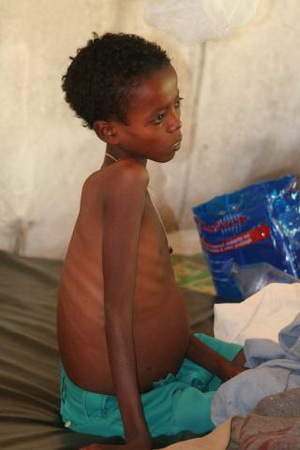
- Terminal - the patient looks depleted( cachexia) with thin skin, sharply reduced muscle tone, while examining the abdominal wall, the contours of the spleen and liver appear.
Specific symptoms of visceral leishmaniasis arising at the height of the disease:
- Appears expressed undulating fever, the temperature reaches high digits, the liver is enlarged and compacted.
- Still more strongly the process of organ damage affects the spleen.Sometimes it takes up more than half of the abdominal cavity.Inflammation of surrounding tissues shows soreness of the affected organs.
- Lymph nodes are also enlarged, but painless.
- Skin with a "porcelain" shade as a result of developing anemia.
- Patients lose weight, their condition worsens.
- Mucous membranes are necrotic, die.
- A strong increase in the spleen results in a marked increase in pressure in the hepatic vein( portal hypertension), which contributes to the development of fluid in the abdominal cavity, edema.
- The heart from the pressure of the spleen is shifted to the right, arrhythmia develops, blood pressure is falling.Heart failure develops.
- Enlargement of the lymph nodes in the trachea region causes severe coughing attacks.Often they are joined by pneumonia.
- The activity of the gastrointestinal tract is impaired.Diarrhea is observed.
The course of the disease in visceral leishmaniasis can be:
- acute( is rare, occurs with a violent clinic);
- subacute( occurs more often, duration - up to six months, without treatment - fatal outcome);
- protracted( the most common, with a favorable outcome against the background of treatment, occurs in older children and adults).
Indian cala-asar
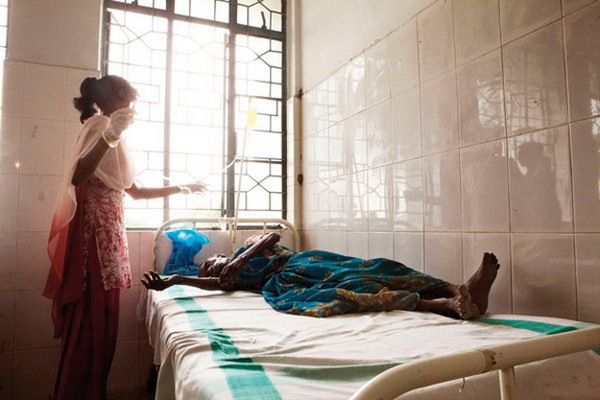 The historical names for this variant of leishmaniasis are "black disease", "dum-doom fever".The age contingent of patients is from 10 to 30 years.Basically - the rural population, among which there are epidemics.The disease is common in India, northeastern China, Pakistan and surrounding countries.
The historical names for this variant of leishmaniasis are "black disease", "dum-doom fever".The age contingent of patients is from 10 to 30 years.Basically - the rural population, among which there are epidemics.The disease is common in India, northeastern China, Pakistan and surrounding countries.
The period from infection to clinical manifestations lasts about 8 months.Complaints and clinical picture are similar to Mediterranean leishmaniasis.
Note: is a distinctive feature of kala-azar is a dark, black-hued skin color( adrenal damage).
Kala-azar is characterized by the appearance of nodules and eruptions that appear 1-2 years after infection and can last for several years.These formations are reservoirs of leishmania.
Cutaneous leishmaniasis( Borovsky's disease)
Flows with local lesions of the skin that then ulcerate and scar.
Skin leishmaniasis of the Old World
Known in two forms - anthroponous - I type of Borovsky disease and zoonotic - II type of Borovsky's disease.
I type of Borovsky disease( late ulcerated) .Other names are Ashgabat, year, city, dry leishmaniasis.
 The peak of infection occurs in warmer months.It occurs mainly in cities and urban settlements.Susceptibility to it is universal.Epidemic outbreaks are rare.After the illness, life-long immunity is produced.This form of cutaneous leishmaniasis is known to spread in the countries of the Middle East, India, Africa, Central Asia.Achieved the disease and Southern Europe.At the moment it is considered liquidated.
The peak of infection occurs in warmer months.It occurs mainly in cities and urban settlements.Susceptibility to it is universal.Epidemic outbreaks are rare.After the illness, life-long immunity is produced.This form of cutaneous leishmaniasis is known to spread in the countries of the Middle East, India, Africa, Central Asia.Achieved the disease and Southern Europe.At the moment it is considered liquidated.
Leishmanioma is formed at the site of parasite infestation.It includes macrophages, fibroblasts, lymph cells and other factors of body defense.Leishmania is absorbed by macrophages.A few months later, a leishmanioma begins necrosis.Then there is an ulcer, which gradually cicatrizes.
The incubation period( from the moment of infection before the onset of the disease) can last from 3-8 months to 1.5 years.
There are 4 types of typical clinical symptom of this type of cutaneous leishmaniasis:
- primary leishmanioma.There are three phases of development: tubercle, ulceration, scar;
- sequential leishmanioma;
- diffuse-infiltrating leishmanioma( rare);
- tuberculoid dermal leishmaniasis( rare).
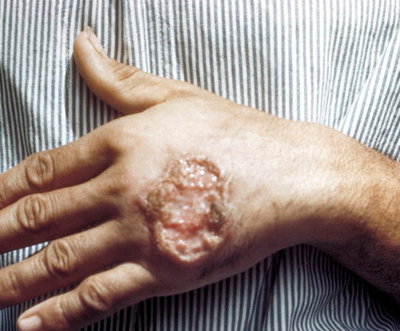
A pink papule( 2-3 mm) is formed at the entrance gate of the infection.After a few months, it grows to a diameter of 1-2 cm. At its center, a flake forms.Under it, after falling away, remains a granular ulcer with elevated margins.Ulceration gradually increases.By the end of the 10th month of the disease, it reaches 4-6 cm.
A scarce secret stands out from the defect.Then the ulcer will scar.Usually, these ulcers are located on the face and hands.The number of ulcerative formations can reach ten.Sometimes they develop non-simultaneously.In some cases, tubercular thickening of the skin without ulceration is formed.In children, the tubercles can merge with each other.This process is sometimes delayed up to 10-20 years.
Please note : this option is prognostically safe for life, but leaves after itself defective defects.
Zoonotic is a type II disease of Borovsky( early ulcerated ).Also known as is desert-rural, moist leishmaniasis, pendin ulcer.
The source and vector of zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis is similar to the previous types of disease.It occurs mainly in rural areas, the disease is characterized by a very high susceptibility of people.Particularly sick children and visitors.The distribution area is the same.Zoonotic leishmaniasis gives epidemic outbreaks.
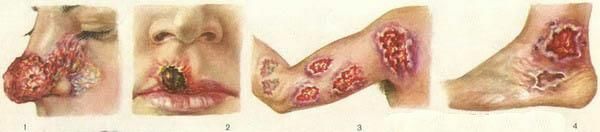
A distinctive feature is the faster phase flow of the leishmanioma.
The incubation period( from infection before the onset of the disease) is much shorter.Usually - 10-20 days, less often - up to 1.5 months.
Clinical variants are similar to the anthroponous type.The difference is the large size of a leishmanioma resembling a boil( boil).Necrosis develops in 1-2 weeks.The ulcer takes on huge dimensions - up to 15 cm or more, with loose edges and pain when pressed on it.Around the leishmanioma, nodules are formed, which also ulcerate and merge.The number of leishmaniom in some cases reaches 100. They are located on the legs, less often on the trunk and very rarely - on the face.After 2-4 months begins the stage of scarring.From the beginning of development to the rumen, it takes about six months.
Cutaneous leishmaniasis of the New World
American cutaneous leishmaniasis .Other names are Brazilian leishmaniasis, skin-mucous leishmaniasis, espudia, uta , etc.
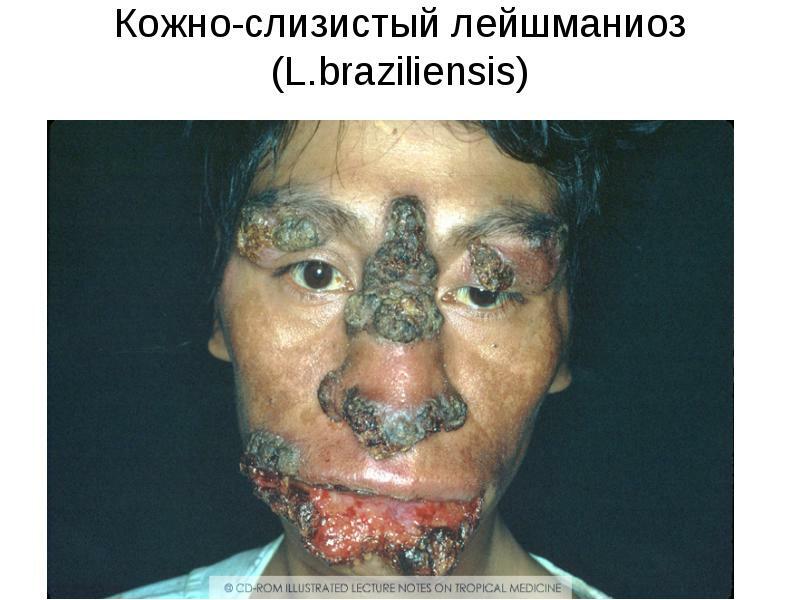
The main feature of this variant of the disease is pathological changes in the mucous membranes.Long-term consequences - deformation of the cartilage of the nose, ears, genitals.The course is long and heavy.Several species of this disease are described.
Diagnosis of leishmaniasis
Diagnosis is established based on:
- of the available disease focus;
- specific clinical manifestations;
- laboratory diagnostic data.
 When visceral leishmaniasis in the blood - the phenomenon of anemia( sharply reduced hemoglobin, erythrocytes, color index), reduced the number of leukocytes, neutrophils, platelets.In clinical analysis, the pathological variability of blood cell forms is observed.Blood clotting is reduced.ESR increases sharply, sometimes reaching a level of 90 mm per hour.
When visceral leishmaniasis in the blood - the phenomenon of anemia( sharply reduced hemoglobin, erythrocytes, color index), reduced the number of leukocytes, neutrophils, platelets.In clinical analysis, the pathological variability of blood cell forms is observed.Blood clotting is reduced.ESR increases sharply, sometimes reaching a level of 90 mm per hour.
In biochemical analysis - increasing gamma globulins.
In most cases:
- parasitological analysis of bone marrow punctures to detect leishmania;
- study of a thick drop and a blood smear - are additional methods, since microorganisms in them are not so often determined;
- blood culture on the NNN medium;
- serological diagnosis.A method for determining fluorescent antibodies( ELISA-RNIF), complement fixation reaction( RSK), latex agglutination reaction with a protein isolated from the detected leishmania( RLA), biological tests using laboratory animals is carried out.
For the diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis, blood culture is performed.Less commonly used biopsy of lymph nodes, liver tissue and spleen.
Diagnosis of cutaneous variants of leishmaniasis is supplemented by examination of the contents of ulcers.Collected scrapings and biopsy of the skin, allowing to detect the pathogen.
To the recovered patients carry out preventive tests( the reaction of Montenegro with leishmanin).
Treatment of leishmaniasis
Conservative treatment of visceral forms of leishmaniasis:
-
 Initially Neostibozan is used.The injection course involves 20 infusions intramuscularly or intravenously;
Initially Neostibozan is used.The injection course involves 20 infusions intramuscularly or intravenously; - Glucantim - 12-15 injections;
- Solustibazan, Stibanol, Pentostan, Solyusurmin and other preparations of pentavalent antimony.They are used in injections according to the schemes up to 2 weeks.
- , with insufficient effect to treatment, Lomidine is added( 10-15 daily injections at a dose of 0.004 g / kg of patient weight);
- if necessary, use antibiotic therapy, in case of secondary infections;
- with lesions of internal organs to the classical scheme of treatment of leishmaniasis, cardiovascular agents, respiratory, hepatoprotectors are added;
- restorative and stimulant drugs.
Skin forms of leishmaniasis are additionally treated:
- with antibiotic therapy;
- with aminoquinol, antimonil, glucantim;
- with leechmania mitacrine in solution, urotropin;
- powders and ointments of berberine sulphate, therapeutic ointments with these preparations are also used;
- by removal of tubercles by electrocoagulation;
- by removal of formations by cryotherapy.
In stubbornly unreachable cases, interferon preparations are administered.
Important: for prompt readings of spleen removal.
Preventive measures
As a preventive measure for outbreaks of leishmaniasis, a set of measures is carried out, including:
- treatment or destruction of sick animals;
- landscaping with the removal of desert areas and dumps;
- drying of premises;
- application of mosquito repellent;
- mechanical bite protection;
- detection and treatment of carriers and sick people;
- immunoprophylaxis, especially among those leaving for foci of leishmaniasis.
Alexander Lotin, Phyto-Therapeutist