Computed tomography of abdominal organs
 This type of radiation and computer diagnostics is used for layer-by-layer examination of the structure of the abdominal cavity organs, determination of the pathology present in them.For the examination, X-ray radiation is used, which is given by a tomograph and allows to obtain layered sections of tissues.The data is recorded by special sensors that transmit a signal to a computer equipped with a special package of signal processing programs and outputting the result to the monitor with a fixation on the storage medium.
This type of radiation and computer diagnostics is used for layer-by-layer examination of the structure of the abdominal cavity organs, determination of the pathology present in them.For the examination, X-ray radiation is used, which is given by a tomograph and allows to obtain layered sections of tissues.The data is recorded by special sensors that transmit a signal to a computer equipped with a special package of signal processing programs and outputting the result to the monitor with a fixation on the storage medium.
Which organs can be examined and what is the computerized tomography of the abdominal cavity?
Diagnostics allows you to know in detail the structure:
- organs consisting of parenchymal tissue - the liver with vessels, the gallbladder with common bile duct, the pancreas with surrounding tissues and the spleen;
- hollow organs of the gastrointestinal tract - stomach, 12 duodenum, parts of the small and large intestine;
- bone tissue of the lower thoracic and lumbar spine;
- of the abdominal parts of the nervous and vascular systems;
- abdominal( abdominal) lymphatic formations.
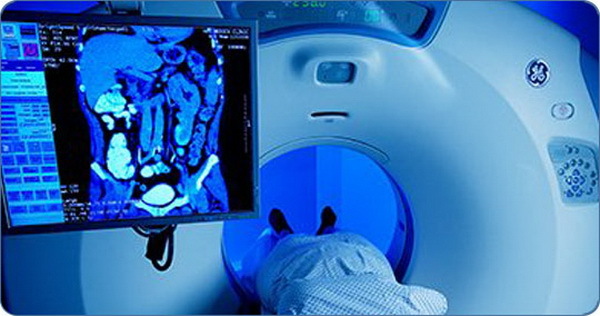
After the examination, it is possible to draw conclusions about: the dimensions and relative position of the abdominal organs;
- ;
- state of parenchyma( specific organ tissue) and smooth muscle walls of hollow formations;
- has available inflammatory changes in the tissues, their volume and phase of the disease;
- presence and quantity of parasitic organisms;
- available neoplastic processes( tumoral formations);
- traumatic injuries of the abdominal organs and their consequences;
- abnormalities of the structure of the parenchymal and hollow organs contained in the study area;
- state of the vascular system, blood supply tissues and abdominal organs;
- pathological changes in the nervous tissue providing functions of the digestive, urinary and bone systems;
- structure of the inferior thoracic and lumbar spine, ribs and sternum.
Indications for the appointment of computed tomography of the abdominal cavity
The study is recommended for patients who seek medical advice about:
- liver diseases - inflammations( hepatitis), cirrhosis, which occurs with the replacement of hepatocytes( hepatic cells)Neoplasms, parasites;
- problems in the gallbladder - acute and chronic cholecystitis( inflammation), cholangitis( a painful process in the ducts), the presence of stones in the bladder and ducts;
- pathological changes in the pancreas - pancreatitis( inflammation), neoplastic processes( benign and malignant formations);
- malaise associated with the spleen - infarction( clotting of blood vessels with thrombi, or emboli with subsequent necrosis of tissue), tumors;
- of the neoplastic processes of the stomach and intestines( benign and malignant), metastases;
- purulent complications in diseases of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space( abscesses, phlegmon), cystic formations;
- inflammations and tumors of lymph nodes, hemoblastoses( tumorous processes in retroperitoneal lymphoforming);
- Vascular thrombosis, blood supply to the abdominal cavity, vascular aneurysm;
- trauma, bleeding, internal organ hemorrhage;
- evaluates the conducted antitumor treatment;
- anomalies in the size, position and development of the abdominal organs.
Contraindications to computed tomography of the abdominal cavity
Contraindications to the study of the conditional, rather, they can be called limitations.
It should be refrained from conducting the diagnosis in the following cases:
- pregnancy at any time;
- of the patient's mental illness in the phase of aggravation;
- body weight more than 200 kg;
- allergies to preparations containing iodine;
- decompensated diseases of kidney and liver;
- severe complications of diabetes mellitus;
- progressive thyroid disease;
- skin tumors;
The necessity of computed tomography in these cases is discussed by the doctors collectively for each patient.
Preparatory measures before the procedure
If necessary, preliminary research methods are performed - ultrasound, gastroscopy, conventional X-ray examination, colonoscopy.
Before conducting a CT scan with a patient, a conversation should be conducted in which it is necessary to explain the reason for the procedure, the safety and painlessness of the method.It is necessary to dwell on the rules of behavior of the patient during the session.If a contrast medium is used, the physician should interview the patient for allergic reactions.
In addition, a few days before the computer tomography should appoint a diet that eliminates the use of products that cause increased gas production and constipation.
Two days prior to the examination, the patient is assigned adsorbents( usually activated charcoal).On the eve, and if necessary, before the procedure make cleansing enemas.The examination is carried out on an empty stomach.It is not recommended to drink, as water provokes peristalsis( movement) of the intestine.
During the examination, it is necessary to lie without moving, calm and even breathing.Listen and execute the radiologist's commands.If there are unpleasant sensations, worse itching of the skin, dizziness, nausea, vomiting or pain - report immediately to the doctor.
The patient should be warned that during the introduction of contrast, an unpleasant aftertaste in the mouth, a burning sensation and warmth at the site of administration of the solution are possible.
Important: patient must give a written receipt of consent for the survey.
More information on the rules for preparation for CT of abdominal organs - in the video:
Sequence of passage of CT of the abdominal cavity.
Prepared for research, the client is laid on the table, instructed and starts the session.The duration of the examination is an average of 30 minutes.
During the procedure, the table frame moves relative to an arcuate scanner containing sensors that record data in the form of snapshots and video images and transfer them to a computer.The resulting "slices" are processed with the help of programs and are visualized on the monitor screen.Simultaneously, they are written to the data storage device.
Data analysis is carried out by an x-ray physician for one and a half to two hours and is given to the hands of the patient or treating physician.
Spiral computed tomography( CTD) of the abdominal cavity

The most modern and accurate method for diagnosing diseases.A distinctive feature of this survey is the rotation of the radiator along a spiral trajectory with simultaneous rectilinear motion.As a result, images are obtained that can be viewed in any planar direction, which is also provided by a large number of detectors.The thickness of the sections( usually about 10 mm) is adjusted in this case depending on the diagnostic task.Contrasting can be used together with spiral tomography.
The multislice ( multislice) computed tomography is more accurate.
Note: The method of MSCT( multispiral computed tomography) of the abdominal cavity is considered the most informative when detecting and following oncologic problems.
The advantage of MSCT in front of the SCT of the abdominal cavity is:
- reduces the amount of interference caused by movements of the internal environment of the body, which gives a more contrasting picture of the images and video;
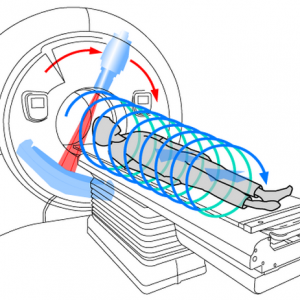
- creating slices about a millimeter thick, which improves the spatial representation of the organ or pathological focus;
- increase in the study area;
- reduced radiation exposure by approximately 30%;
- decrease in the amount of contrast medium required to produce the result;
- the possibility of creating complex three-dimensional( 3D) and multiplanar( multi-plane) reconstructions of organs, vessels, foci of the disease.
In addition to MSCT and SCT, patients can be assigned an MRI: many questions arise - what is the difference and which diagnostic method is more reliable?You will get the answers by viewing the video review:
Alexander Lotin, radiologist,