How to treat bleeding gums
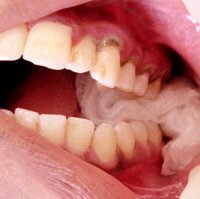
Gum bleeding is a problem that most of the world's population has faced. About 75% of people of mature age and 40% of children are familiar with inflammation and bleeding gums, have repeatedly detected their puffiness, irritability to light mechanical effects. Many are wondering how to treat bleeding gums? To do this, you first need to determine the cause of this phenomenon. And in most cases, the cause of these symptoms is gingivitis.
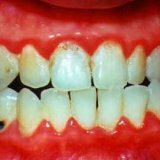
The first thing that is observed with gingivitis is a specific plaque on the gums, a certain film that is formed by oral bacteria from saccharides. When the teeth are cleaned, this film is destroyed, but after it is destroyed later the time appears again. If you do not brush your teeth too often, or do not brush your teeth at all, the film hardens, and then gradually turns into tartar. Stones of teeth can not be removed with a toothbrush, professional cleaning is required. Following the gums begin to bleed.
How to treat bleeding
Under no circumstances should gingivitis be ignored, it must be treated in a timely manner. The next stage of the pathological process is periodontitis. It causes periodontitis to the loss of teeth, and this is a much more serious problem. On the condition of the whole body periodontitis has an adverse effect. Increased risk of strokes, heart attacks, and in pregnant women, he can provoke premature birth.
Treatment is usually performed by periodontists or hygienists. The first stage is a survey. Further, professional hygienic cleaning of the oral cavity is appointed, the purpose of which is to remove plaque, which is the primary cause of gingivitis. After that, the doctor will select you the means for further use at home to care for the gums and teeth, tell you how to effectively use them.
To treat gingivitis caused by the appearance of plaque - it means to properly care for the gums, as well as teeth.
Ulcerative necrotic gingivitis
Two kinds of bacteria cause this type of gingivitis, normally there should be a small amount of gingivitis in the oral cavity.
In addition to bleeding gums, swelling, a leading symptom of the disease is the appearance of very painful sores on the gums, which are covered with a touch of white.
Do not remove the plaque by yourself, leave it only to a specialist. With the defeat of not only the gums, but also the oral mucosa, the disease is called ulcerative necrotic gingivostomatitis.
Treated ulcerative-necrotic gingivitis usually longer.
In addition to professional oral hygiene, various pain relievers and medications are used. The effect after treatment comes quickly enough: approximately on the second-third day the pain goes away, the inflammation decreases. It is impossible to stop treatment completely, the entire course must be completed to avoid relapse of gingivitis. When there are repeated signs of gingivitis to the periodontist, you need to contact as soon as possible.
Hypertrophic gingivitis
Soft dental plaque affects the gums in such a way that the gum extends, overlapping part of the tooth. This can occur against a background of some diseases. The disease is hypertrophic gingivitis.
In the case of this disease, bleeding gums are insignificant, but the gums are enlarged, painful and compacted.
Most often, hypertrophic gingivitis develops in young children, adolescents, women "in position", and may also occur during orthodontic treatment.
Other causes of the disease can be certain diseases, it happens that it appears as a consequence of the side effects of certain types of medication.
Doctors divide the treatment of hypertrophic gingivitis into stages.
The first stage is to conduct professional hygiene of the oral cavity.
In the next step, usually starting two weeks after the end of the first, areas of the enlarged gum are removed under local anesthesia surgically.
Gum healing occurs on the order of five to ten days, two months after surgery, it is necessary to check the results. If the cause of the onset of the disease was the taking of medications, then they must be canceled or replaced with one drug for another, for this, consult a specialist treating you.