Bronchoectatic disease
 Bronchiectasis is a disease of the bronchi. It is characterized by their expansion or deformation. It is a chronic suppuration in infertile bronchi. Bronchi affected by this disease are called bronchiectasias.
Bronchiectasis is a disease of the bronchi. It is characterized by their expansion or deformation. It is a chronic suppuration in infertile bronchi. Bronchi affected by this disease are called bronchiectasias.
Bronchoectatic disease occurs in childhood and adolescence. The disease manifests itself in the form of repeated bronchopulmonary infections with a cough.
Types of the disease
Distinguish in terms of the appearance of congenital and acquired bronchoectatic disease.
Due to occurrence of isolated: atelektaticheskuyu( pulmonary atelectasis zone) destructive( sacculated bronchiectasis) postbronhiticheskaya( later chronic bronchitis), poststenotic( resulting from prolonged stagnation of mucus and atony walls) Retention( manifested in the case of changing the tone of bronchial walls)disease.
Causes and development of bronchiectasis
The first causes of bronchial development include congenital malformations. Underdevelopment of the bronchial wall takes place.
The second reason is the acquisition of bronchiectasis. It appears as a result of very frequent bronchopulmonary infections, which were transferred at a small age. The causes may be the consequences of tuberculosis, chronic bronchitis, bronchopneumonia, lung abscess.
The third reason is the ingress of foreign substances into the lumen of the bronchi, which can subsequently cause the development of the disease.
The development of bronchoectatic disease occurs as a chronic inflammation of the bronchial tree. It also leads to changes in the layers of the bronchi, namely, in the mucous and muscular, and in the peribronchial tissue. After the transferred diseases the walls of the bronchi become weak and deformed. The occurring processes affect the nerve endings, arterioles and capillaries.
bronchiectasis as cylinders and spindle affect large and medium-sized bronchi and saccular - small. Small in size may not appear for a long time. In case of joining other infections, the inflammatory process is accompanied by the appearance of purulent sputum. As a result, chronic inflammation occurs.
purulent process supported by sophisticated self-cleaning of the bronchial tree, reduced immunity, nasal inflammation complications.
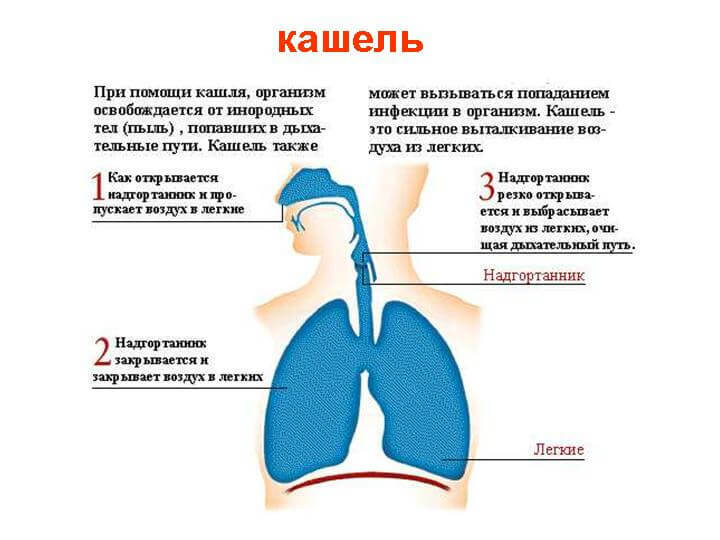
Symptoms The main symptom of bronchiectasis - a persistent cough with purulent sputum. It has an unpleasant smell. As accumulation in the bronchi, sputum provokes the resumption of cough. Such seizures often lead to the rupture of blood vessels, and eventually to blood cough or pulmonary hemorrhage.
Chronic inflammatory process leads to exhaustion of the body. As a result, anemia, dyspnea, weight loss, weakness, stopping physical and sexual development may manifest.
As a result of the exacerbation of the disease, the temperature rises, and the amount of sputum increases. When finding
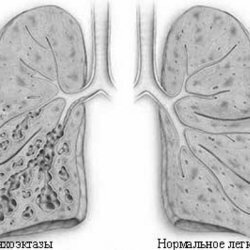
bronchiectasis occurs weakened breath, wheezing. When X-ray is detected deformation and cellularity lung atelectasis areas, reduction in the amount of diseased segments or lobes.
Bronchoscopy makes it possible to detect a purulent secret. Then the material for further investigation is taken from it, with the help of this method of diagnosis determine the cause of bleeding and carry out measures to sanitize the bronchial tree.
The next stage is bronchography. It makes it possible to determine the spectrum of the spread of the lesion. It is localized. Bronchography is used with the use of anesthesia or anesthesia. With this method of investigation, various bronchial dilatations, their deformation, and location are revealed.
Spirometry and peakflowmetry are used in the diagnosis of respiratory failure.
Treatment of bronchiectasis
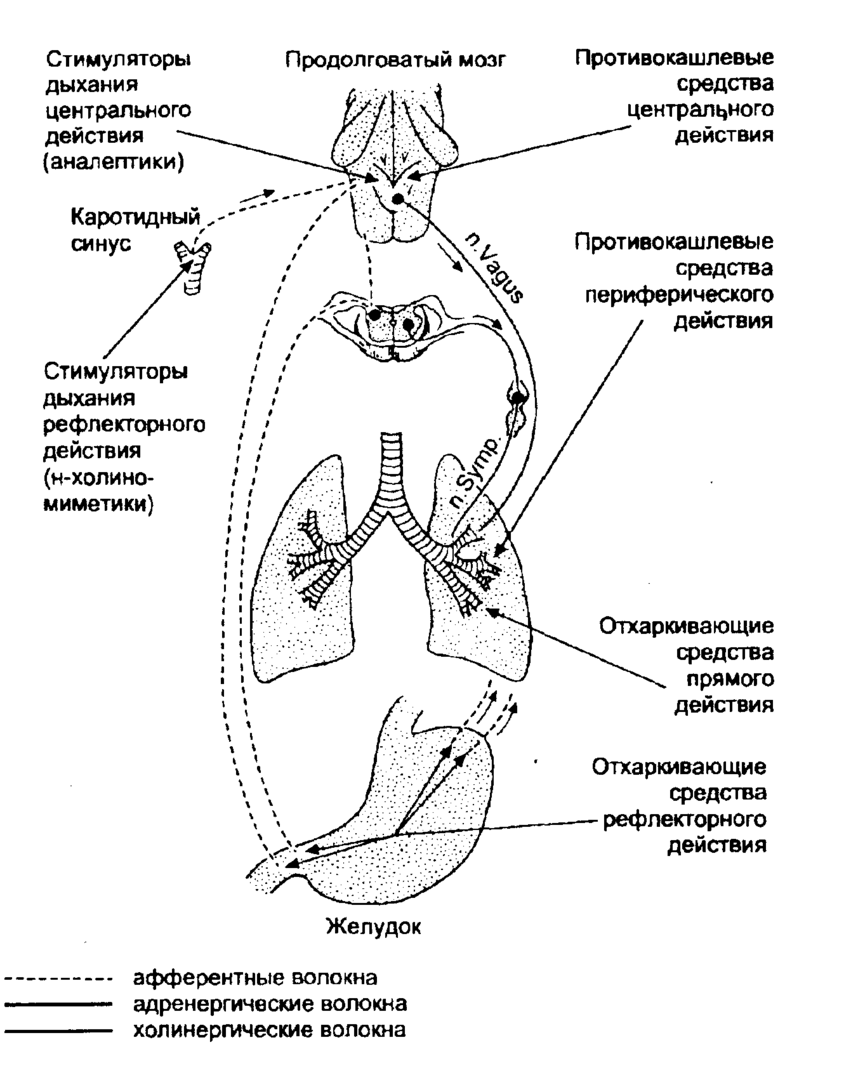
Treatment has two main activities. The first type consists in the sanation of the bronchi, and the second - in suppressing the purulent-inflammatory process.
Treatment includes antibiotic therapy and bronchoscopic drainage. When sanation is administered antibiotics intramuscularly or intravenously. If there is a chronic inflammation, then use cephalosporins, semisynthetic penicillins, gentamicin.
Chest massage, alkaline drink, inhalation, electrophoresis, respiratory gymnastics are measures for the effectiveness of excretion of sputum from the bronchi.
In the treatment of bronchiectasis, special gymnastics are used - drainage. Its peculiarity is that all exercises are carried out in the supine position: on the back, side, abdomen. All gymnastics is accompanied by coughing jerks, the purpose of which is excretion of sputum. To increase the effectiveness of exercises use unbuffled breath, frequent changes of position, easy pocking of the chest.
The use of medical bronchoscopy is to remove the purulent secret by flushing the bronchi. Also at the same time, antibiotics, mucolytics, bronchodilators are administered, ultrasound is used.
A special place in the treatment is proper nutrition. Food should be rich in proteins and vitamins. In the daily diet must be present meat, fish, cottage cheese, vegetables, fruits, natural juices. In the absence of exacerbations of the disease, respiratory exercises are performed, expectorants eat, and sanatorium-and-spa rehabilitation is mandatory.
In the treatment of bronchiectasis, surgical intervention takes place. During the operation, the affected lobe of the lung is removed. Such intervention is carried out only in the absence of contraindications and in terms of vital signs.
Complications of
On the background of a progressive disease, pulmonary insufficiency may appear. Subsequently, dyspnea occurs, which manifests itself not only under stress, but also at rest. Over time, there may still appear a "pulmonary heart", which contributes to the emergence of circulatory failure in a large circle.
An exacerbation can cause the development of perifocal pneumonia, an abscess of the lung. There is a danger and a breakthrough of pus in the pleural cavity, which ultimately leads to empyema of the pleura.
Prognosis and prophylaxis of the disease
In the case of surgery, the patient's complete recovery takes place. When using regular courses of anti-inflammatory therapy, it is possible to achieve a long-term remission. Cold weather, hypothermia, the consequences of colds can lead to an exacerbation of the disease. You should carefully monitor your health and warm clothes.
If treatment is not available, it will lead to adverse effects. One such is disability.
To prevent the development of the disease, follow-up care is used. In such cases, the pulmonologist monitors the course of chronic bronchitis, pneumosclerosis, and also prescribes adequate and effective treatment. A special place is occupied by the treatment of children's infectious diseases and everything depends on the correctness and adequacy of their treatment.