What causes pain in the scrotum?
Pain in the scrotum is a nonspecific symptom of many possible diseases. Some of them are pathologies of the reproductive system of men directly, others have nothing to do with it and are irradiating( giving away) character. Be that as it may, it is impossible to understand the causes of the pain syndrome independently: it is fraught with the loss of sexual health. What do you need to know about such an unpleasant symptom, like a pain in the scrotum?
Contents
- 1 Why is there pain in the scrotum?
- 1.1 Diseases of the male reproductive system
- 1.1.1 Injuries of the scrotum area
- 1.1.2 Hydrocele
- 1.1.3 Varicocele
- 1.1.4 Inguinal hernia
- 1.1.5 Testicular torsion
- 1.1.6 Pathology of the epididymis
- 1.1.7 Orchitis
- 1.1.8 Testicular cancer
- 1.1.9 Prolonged abstinence
- 1.1.10 Prostatitis
- 1.2 Diseases not related to the reproductive system
- 1.1 Diseases of the male reproductive system
- 2 Differential diagnosis, characteristic symptomatology
- 3 Diagnostic methods
Why is there pain in the scrotum?
scrotal pain can be caused by two reasons groups, as has been noted:
- diseases of the reproductive system.
- Concomitant diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, urinary system, etc.
Each of the highlighted groups should be briefly reviewed.
diseases of the male reproductive
system presents a range of pathologies:
scrotal area Injuries
Main article: Injuries to the scrotum
first and most obvious immediate cause of pain, because you can easily keep track of a causal link between the mechanical effect on the testicles and the occurrence of discomfort. In this localization, bruises are most common. A bruise of the scrotum organs is a dangerous condition that requires timely treatment, because it is possible to develop complications.
hydrocele
Main article: hydrocele( hydrocele)
This dropsy shell egg when in the anatomical structure of the observed accumulation of fluid. As a result, there is a compression effect on the tissues of the sexual organ. Everything can end very badly: we are talking about conditions until the loss of reproductive function. Most often, the disease affects newborns and young people under the age of 30 years. The main factors which involve destruction of the described character are: trauma, testicular inflammation, congenital disorders of genital organs, and operations( as a complication).
varicocele
Main article: Operations on varicoceles - their types,
advantages and disadvantages of pathologically dilated( varicose veins), vessels testis and spermatic cord. It occurs both in children and in adults of any age. This disease is fraught with the formation of a persistent impairment of the circulation of genital tissues with the subsequent development of infertility and thrombosis. For life, such a pathology is not a threat, but is characterized by severe complications and an intense pain syndrome. The causes of varicocele are different, among them: congenital malformations, arterial hypertension, trauma, etc.
Inguinal hernia Main article: Inguinal hernia in men - symptoms and treatment
most often occurs in children. It develops as a result of protrusion or direct loss of parts of the abdominal organs into the cavity of the scrotum. It occurs often. The main factors of development are: trauma, malformations of the fetus. In the vast majority of cases it is a question of congenital pathology. Torsion of the testis
Main article: Testicular torsion and its hydatites
Represents a torsion of the spermatic cord with the subsequent development of a violation of normal blood circulation of the testicle. This is a dangerous condition requiring immediate correction, usually by surgical methods, as everything can end with acute ischemia of the genital organ and tissue necrosis. The immediate factor in the development of torsion of the testicle is its excessive mobility, caused by improper development of the fetus. That is why most often this pathology occurs in newborns and children under 10 years old.
Pathology of the epididymis
Inflammation( epididymitis), suppuration( abscess), etc.
Orchitis
Directly inflammation of the testis itself( orchitis).It is faced mainly by adult patients. Has a tendency to chronic, so delay with treatment in any case impossible. The causes are most often infectious. However, the effect of autoimmune factor, trauma, etc. is possible.
Testicular cancer
Rare, but extremely dangerous disease. Malignant tumors of the testicles can lead to an intense pain syndrome.
Long-term abstinence
And also sexual arousal without discharge in the form of sexual intercourse and ejaculation. In the absence of sexual discharge there is an excessive accumulation of seminal fluid in the structure of the testicles - stagnant phenomena that cause pain.
See also: Sexual abstinence in men - when useful and harmful?
Prostatitis
Inflammation of the prostate gland in the acute phase can cause intense pain in the scrotal area.
Diseases not related to the reproductive system
- colitis( inflammation of the large intestine);
- hemorrhoids;
- cystitis;
- pyelonephritis;
- is a stenotic disease;
- urethritis.
Differential diagnosis, characteristic symptomatology
Pain is a nonspecific symptom. Determine by it what pathology is simply impossible. The doctor will interview the patient for complaints in order to conduct differential diagnosis - by manifestations, to distinguish one disease from another. To determine a possible cause, one can listen to one's own organism and draw some conclusions based on the typical symptoms of various diseases:
- For traumas of the scrotal area, a dull, aching pain syndrome is characteristic. It increases during physical activity. In addition, swelling of the scrotum, blueing, and unilateral character of the lesion are observed. Moreover, it is easy to track the source of discomfort.
- The hydrocele - the testicle grows in volume, the character of the lesion is also one-sided, the pains are aching, pulling, do not depend on physical activity. To distinguish the hydrocele, it is necessary to press on the testicle( slightly).When edema occurs protrusion of the scrotum from the opposite side of the site of exposure. In severe cases, the size of the anatomical structures increases so much that it is difficult to wear underwear and even walking. Possible common manifestations in the form of increased body temperature, etc.
- Varicocele. Complex disease, because in most cases it does not manifest itself. Pain weak, stitching, aching. Strengthen in the period of walking, sexual arousal. Veins are well visible, their contours( in classical cases).Usually, this disease is detected by accident.
- Inguinal hernia. It is characterized by impaired urination, discomfort when walking, sensation of a foreign body in the scrotum( which does not happen in other diseases).When the size of the hernia is large, the shape of the scrotum changes, it becomes much larger. Probably curvature of the penis.
- Pathology of the epididymis. Seldom manifest than anything other than pain. Pain syndrome is usually very intense, intensified when walking, at the time of ejaculation. In the rest, without methods of objective diagnosis, it is difficult to identify problems with appendages.
- Testicular cancer. The symptomatology is obvious. The scrotum increases in size, a foreign body formation is found in the organ structure, usually soft to the touch and painful. Pain syndrome is intense, permanent. With advanced stages of cancer, there is general symptomatology in the form of fever, weakness, weakness, pathological thinness, etc.
- Orchitis or inflammation of the testicle is manifested by reddening of the genital organ, swelling of the testicle, extremely strong pain of shooting character. Also characteristic is the inability to perform a normal sexual intercourse, a scant amount of ejaculate, a violation of erectile function.
- Prostatitis. Characterized by: pain in the anus, perineal( between the anus and scrotum), the scrotum, the lower abdomen, frequent urination, urine flow, sexual dysfunction with a decrease in libido.
- Non-sexual diseases are characterized by myriads of concomitant symptoms of a specific nature: dyspepsia( heartburn, nausea, vomiting, etc.), urination, stool, pain in the primary source, etc. An experienced doctor will immediately determine the nature and nature of the pathological process.
It is possible to distinguish one disease from another, but the point in question is to put instrumental methods of diagnosis.
Diagnostics methods
Diagnostics, mainly instrumental, because laboratory methods give only general information about the patient's health. Among the survey methods, there are:
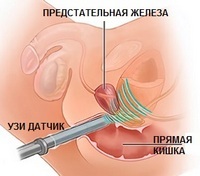
- finger prostate examination;
- palpation of the testis( physical examination);
- diaphanoscopy( probing of the scrotum for the purpose of evaluating its structure and condition);
- scrotal ultrasound, which makes it possible to identify a hernia, accumulation of fluid in the cavity of the described structure;
- dopplerography of vessels;
- puncture of the scrotum;
- CT / MRI, especially when suspected of a neoplastic( cancerous) process.
There are many causes of pain in the scrotum. Only in two cases can we talk about the option of the norm: with prolonged abstinence and sexual arousal without discharge. In all other situations it is necessary to speak about pathologies. Do not try to identify the source of pain yourself. It is necessary urgently to address to the urologist or the urologist-andrologu for carrying out of complex diagnostics. Treatment is symptomatic, and also aimed at eliminating the cause of pain.
Recommended for viewing: