Ulcerative nonspecific colitis: symptoms and treatment
Ulcerative nonspecific colitis refers to severe pathologies.It affects only the mucosa of the large intestine in the form of destructive inflammatory and ulcerative processes of varying intensity.Pathology affects the rectum and gradually spreads to all parts of the large intestine.It begins slowly and the first sign of its development can be a bleeding from the rectum.The difficulty of treating this disease in its poorly understood and, as a rule, it lasts a long time.
This disease is most common among residents of megacities.It manifests itself usually in the elderly( after 60 years) or at a young age of 30 and is not contagious.
Table of Contents:Causes of Nonspecific Ulcerative Colitis
Scientists have not established the exact cause of ulcerative colitis, but they highlight a number of causal factors. These include:
- hereditary predisposition;
- infection of unknown genesis;
- genetic mutations;
- improper power supply;
- infringement of intestinal microflora;
- reception of certain medications( contraceptives, some anti-inflammatory drugs);
- frequent stress.
In a patient with ulcerative nonspecific colitis, immunity begins to work not against pathogens, but against the cells of the mucous membrane of the intestine, which in togus leads to ulceration.The immune mechanism of this pathology gradually spreads to other organs and systems.This is manifested by lesions and inflammations of the eyes, skin, joints, mucous membranes.
Forms of non-specific ulcerative colitis
 In view of the clinical picture, the following forms of this pathology are distinguished:
In view of the clinical picture, the following forms of this pathology are distinguished:
- chronic ulcerative colitis;
- sharp;
- chronic recurrent type.
Chronic ulcerative colitis has a constant course, without periods of remission.Together with this, it can have both a compensated and a heavy nature of the flow.The degree of severity of this disease directly depends on the extent of damage to the healthy intestinal mucosa.This form is lethargic and continuous, duration depends on the state of health of the patient.The disease itself greatly depletes the patient's body.If the patient's condition reaches critical, then a mandatory surgical operation is indicated.When such a colitis has a compensated form, it can last for many years.At the same time, conservative therapy makes it possible to improve the patient's condition and gives a good effect.
The acute form of of ulcerative colitis differs by a rather sharp and rapid onset.Inflammatory and ulcerative processes in the large intestine develop from the very beginning of the disease, so it proceeds quite heavily, but it is very rare in practice.Pathological processes develop lightning fast and spread to the entire gut, which is called total colitis.It is very important to begin the prompt start of treatment.
The recurrent form of of ulcerative colitis occurs with phases of remission and exacerbation.In some cases, seizures spontaneously stop and do not appear for a long time.
Symptoms of ulcerative colitis
There are many signs of ulcerative colitis and they can have varying degrees of severity depending on the severity of the disease and its shape.In this regard, one part of patients throughout the life of a normal state of health, and among the symptoms manifested only blood in the stool( which is often incorrectly associated with hemorrhoids).The other part of the patients has a more severe condition with bloody diarrhea, fever, abdominal pain, etc.
Specific symptoms of ulcerative colitis include the following complaints:
- bleeding from the rectum, accompanied by pain, diarrhea;
- diarrhea( up to 20 times per day);
- spasmodic abdominal pain;
- constipation( it happens very rarely, usually diarrhea is observed);
- lack of appetite;
- body temperature elevation;
- weight loss due to persistent diarrhea;
- decreased hemoglobin levels in the blood( due to persistent bleeding);
- blood in fecal masses( this symptom occurs in 9 out of 10 patients and can have the appearance of both a blood stain on toilet paper and a massive bloody stool);
- an admixture of mucus in the stool;
- frequent false urge to bowel movement - "rectal spitting"( when pus from the rectum comes pus and mucus);
- defecation at night( the patient wakes up at night because of an uncontrollable desire to defecate);
- flatulence( bloating);
- intoxication of the body( vomiting, tachycardia, dehydration, fever).
There are a number of extraintestinal symptoms of ulcerative colitis that are not related to the digestive tract:
- joint pain;
- eye pathology;
- liver disease;
- appearance of rashes on the body and mucous membranes;
- blood clots.
These signs may appear before the symptoms of the colitis itself, depending on its severity.
Complications
As a result of nonspecific ulcerative colitis, the following complications can develop in patients:
- intestinal perforation;
- intestinal profuse bleeding;
- toxic megacolon( a fatal complication, as a result of which the large intestine in a certain place increases in diameter up to 6 cm);
- rupture of the intestinal wall;
- anal fissures;A fistula or abscess ;
- narrowing of the lumen of the large intestine;
- paraproctitis;
- colon cancer( the risk of getting sick in a patient with colitis is increasing every year after 10 years of illness).
Diagnosis of nonspecific ulcerative colitis
Confirming the diagnosis requires a very thorough examination of the patient.First of all, it makes it possible to distinguish ulcerative colitis from other pathologies of the intestine, which have a similar symptomatology.
Inspection
With an objective examination, the doctor can both note the presence of typical signs of the disease, and their absence.Finger rectal examination allows the doctor to determine the presence of such pathologies as a thickening of the rectal mucosa, anal fissures, rectal fistulas, abscess, spasm of the sphincter, etc.The doctor should prescribe all the necessary studies to ultimately conduct differential diagnosis with pathologies in the form of irritable bowel syndrome, diverticulitis, colon cancer, Crohn's disease.
Laboratory tests for ulcerative colitis
- Blood test.In it, with nonspecific ulcerative colitis, anemia, leukocytosis, hypoproteinemia will be detected.
- Coprogram.This is an analysis of stool, which allows you to detect the blood( hidden or obvious) in it, the uniform elements of the blood.
- C-reactive protein.An increase in its level in the analysis indicates the activity of the disease.
- The number of autoantibodies pANCA.In 7 out of 10 patients, antineutrophil perinuclear cytoplasmic antibodies are detected.
- Bakposev.It is prescribed to exclude the dysenteric and pseudotuberculous nature of the disease.
- PCR or molecular genetic study.Its task is to exclude the viral and parasitic genesis of the disease.
- Histological examination.In colitis, it helps to identify typical for him microscopic signs, as well as exclude precancerous conditions and cancer itself.
- Assay for fecal calprotectin.This study of feces, which provides an opportunity to obtain information about inflammatory processes in the intestine.
Instrumental Research
- Fibroileo-colonoscopy - is today the main method of diagnosis.This is an endoscopic examination of the entire large intestine with the help of optical instruments.This method allows you to explore the extent of colitis, its severity, the presence of strictures, that is, narrowing of the intestine, polyps on the wall.Parallel to this, a material for histological examination is also taken.
- USED .The task of ultrasound diagnostics is to determine the presence of indirect symptoms of ulcerative colitis in the form of thickening of the intestinal wall and its expansion in diameter.At the same time, ultrasound is inferior in informativeness to endoscopic research.
- Irrigoscopy . It is an X-ray examination method.It is carried out with the introduction of contrast medium.With her help, a doctor can determine the presence of inflammatory modifications in the intestine, exclude strictures, swelling.Typical signs on the roentgenogram are narrowing of the lumen of the intestine, small ulceration, disappearance of the gestation, uneven pattern on the mucosa, pseudopolypes.But this method is not suitable for patients with a toxic megacolon.
- HydromRT .This is a method for diagnosing the state of the intestine to be carried out to clarify its state of surrounding tissues.
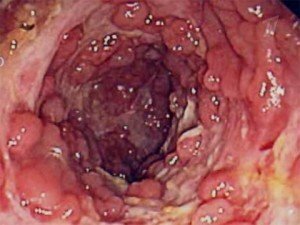
- Recto-Maskoscopy .This examination of the rectum with the help of an endoscope.It is carried out necessarily, taking into account the fact that in ulcerative nonspecific colitis in 90% of cases there is a lesion of the rectum.With it will be found mucus, erosion, blood, ulcers, pus on the intestinal mucosa, as well as its swelling and redness.
Pathomorphological diagnostics
When examining the material taken, a mucosal lesion is detected in the form of ulcers penetrating deep into the submucosal layer, sometimes even to the muscular layer.Ulcers have dug flat edges.In those areas of the intestine where the mucous membrane is preserved, excessive regeneration of the glandular epithelium can be detected, resulting in pseudopolypes.Also, a characteristic feature in the form of "crypt abscesses" is often found.
Treatment of nonspecific ulcerative colitis
The type of therapy for ulcerative colitis is completely dependent on its severity and the patient's condition.In most cases, it means taking special drugs, to correct diarrhea, the digestive process.In more severe cases resort to the use of additional medications and surgical treatment.
Hospitalization is extremely necessary for the newly diagnosed diagnosis, this allows doctors to determine the amount of necessary treatment for concomitant hematologic and metabolic disorders.Among them most often is hypovolemia, acidosis, prerenal azotemia, which develop as a result of a large loss of electrolytes and liquid through the rectum.Because of this, infusion therapy and blood transfusion are simply mandatory for such patients.
The task of treatment of ulcerative colitis:
- Elimination of complications( anemia, inflammation of an infectious nature).
- Purpose of special nutritional supplements( they provide an opportunity to ensure normal sexual development and growth of children).
- Weakening and elimination of the symptoms of the disease.
- Control and prevention of seizures.
Conservative treatment includes, in addition to drugs, also a diet.It should be sparing mechanically, contain an increased amount of easily digestible proteins in the form of cottage cheese, meat and fish( low-fat).But the consumption of fresh fruits and vegetables is prohibited.To eat should be divided, in small portions.The food should be normal temperature, not cold and not hot.Parenteral nutrition is indicated in the case of severe disease.
Medication therapy includes:
- Intravenous infusion for the removal of intoxication of the body, normalization of water-electrolyte and protein balance.
- Antibiotics.Preparations are prescribed taking into account the sensitivity of the microflora of the large intestine.
- Tranquilizers.With the purpose of a sedative effect appoint Seduxen, Elenium.
- Antidiarrhoeic drugs.In the scheme include anticholinergic drugs( Platifillin, tincture of Krasavki, Solutan), herbal astringents( decoction of pomegranate crusts, blueberries, alders).
- Sulphosalazine( Salophthalmic) is a drug that is absorbed in the terminal section of the colon.It is administered topically or systemically and( suppositories, enemas).
- Corticosteroid hormones.They are administered systemically or in the form of an enema in the case of a severe form.
Surgical treatment
It is used in connection with complications in the form of severe bleeding, colon cancer, the lack of therapeutic effect from conservative methods, intestinal obstruction, lightning-fast form of ulcerative colitis with tolerance to treatment, perforation.
Typically, the following operations are used:
- reconstructive reconstructive;
- radical, when the total resection of the thick part of the thick is performed, followed by the imposition of stoma( sigmo- and ileo-);
- palliative( ileostomy).
Operations are often performed in children in the case of severe ulcerative colitis without a lack of positive dynamics in treatment.In adults, however, surgery is usually performed because of complications.In this case, it allows you to save the patient from many suffering.
Viktorova Julia, medical reviewer