Treatment of tooth granuloma
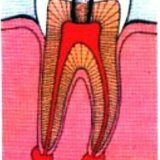
The granuloma of the tooth, in comparison with other dental diseases, is characterized by special cunning. It imperceptibly "attacks" the roots of the teeth, rapidly increases and destroys healthy bone tissue. At a later stage of the disease, the granuloma is already scarce, and it begins to "beat" the entire body. Exacerbation of lurking granulomas in the gums can cause hypothermia, colds, stress, heavy physical work. Uncontrolled reproduction of dangerous microorganisms begins in the root canal of the tooth, when medical intervention is inevitable.
Types of treatment
The most effective way to get rid of a granuloma is to remove the affected tooth forever. A few years ago, dentists did exactly this: they removed the tooth, cleaned the hole from the neoplasm cover in cases when it was not removed together with the tooth. However, today, with the latest methods of treatment, there are more sparing ways to get rid of the granuloma, retaining the tooth or, at least, its healthy part. There are only two methods of treatment: surgical and therapeutic. It happens that they are inextricably linked.
Cases in which the tooth can not be preserved:
- If the cause of infection in the tooth channel is the periodontal pocket.
- Wide vertical tooth crack.
- Strong tooth decay, making the forecast of its recovery unfavorable.
- Complete obstruction of the root canal.
- Multiple perforations of the root of the tooth.
Therapeutic treatment
It is possible with full preservation of the tooth, but under certain conditions. Endodontic treatment is performed only with the use of sterile disposable instruments and a cofferdam preventing the ingress of saliva and other biological fluids into the internal cavity of the tooth, and from it into the root canal system. During the treatment of affected root canals, it is mandatory to use ultrasound equipment and special irrigants( sodium hypochlorite 3-5%).The time factor is also important, because antiseptics work, it's necessary to stay in the channel for at least 15-30 minutes. If you need to treat a four or five-tooth tooth, then quality treatment can not take less than 1.5 hours. The tooth canals are sealed with a gutta-percha with a sealer( special paste for canals), the final picture is taken. Sometimes the treatment of affected dental canals is delayed by two or three visits for several hours each.
The protocol for the treatment of granulomas, which provides a favorable further prognosis, does not accept the unsealed restoration of the tooth. Therefore, a good doctor will never send a patient after endotherapeutic treatment home without setting a temporary seal. She provides hermetic until the next visit to the dentist. Then the fate of the tooth is completely in the hands of the doctor, who will try to restore this tooth. Restoration of the crown part of the tooth should always be reliable and accurate. This requires professionalism and experience.
Surgical treatment methods
Cystectomy with the resection of the apex of the tooth root is an operation in which the granuloma is removed and the infected part of the root is cut off. Resection can not be performed without a previously completed orthographic( right through the mouth) filling of the dental root canal. Otherwise, any resection will not be effective. Then there is a surgical stage of root tip resection and retrograde( to the new apex of the root) filling the root canal with tissue-resistant material( silver amalgam)
The root tip resection has its own indications:
- No endotherapeutic result in 2-4 years after the procedure.
- Obstruction of the dental root canal and greater strategic importance of the aching tooth.
The prognosis for the tooth after resection of the apex of the root is usually favorable.
Hemisection is another type of surgical intervention. Less sparing way of removing the granuloma in relation to the tooth. It is carried out if it is not possible to preserve the roots of the tooth. The doctor surgically removes the granuloma and the hopeless root with part of the tooth above it. According to the hemisection, the defect is corrected by the crown. The operation is shown to the teeth, in which at least one root can still have a positive prognosis, and the other can not be saved. The subsequent prognosis on the life of the tooth after the hemisection is relatively favorable.