Polyhydramnios during pregnancy: causes, treatment and consequences
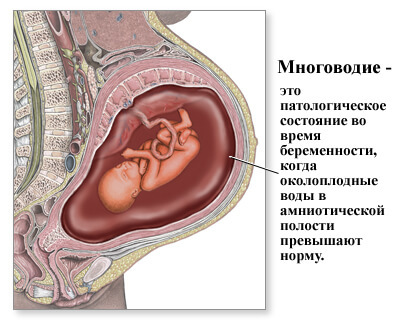
Polyhydramnios during pregnancy is a pathological condition in which the amount of amniotic fluid exceeds the figures considered to be the norm at a certain time.
The amniotic fluid provides a full intrauterine development of the baby's future.They protect the fetus from external influences and allow it to move, participate in the process of metabolism and prevent clamping of the umbilical cord.Amniotic fluid is regularly updated( about every 3 hours), and its amount gradually increases.If at 10 weeks the volume is approximately 30 ml, then in the prenatal period - already 1-1.5 liters.
On polyhydramnios speak, when in the late terms of a liquid more than one and a half liters.
Table of contents: Causes of polyhydramnios during pregnancy Symptomatic Consequences of polyhydramnios during pregnancy Diagnosis Treatment of polyhydramnios in pregnancy and prognosisCauses of pregnancy in many cases
The exact cause of polyhydramnios has not been established to date.There is an opinion that genetic( family) predisposition is of certain importance.Allocate a risk group;Among the women entering it, this pregnancy pathology is much more common.
Predisposing factors:
- large fetal dimensions;
- multiple pregnancy;
- kidney pathology;
- diabetes mellitus;
- Rh-conflict;
- infection;
- pathology of the excretory system of the unborn child.
Note: is more likely to develop a pathological condition when infected with rubella, herpes and cytomegalovirus viruses.To many-water often leads to toxoplasmosis.
Predisposing factors include impaired swallowing function in the fetus.In later terms, he daily absorbs up to 4 l of amniotic fluid.
Symptoms
There are a number of clinical signs that allow suspected polyhydramnios during pregnancy.
The following symptoms may appear:
- marked general malaise;
-
 is constantly pursuing a sense of weakness;
is constantly pursuing a sense of weakness; - shortness of breath amid minor stress;
- severity and discomfort in the abdomen;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- tachycardia;
- permanent swelling of the feet;
- abdomen circumference ≥ 100-120 cm;
- pronounced stretch marks( striae);
- fluctuation( gurgling fluid in the abdomen);
- vomiting.
Note: causes the dyspnea to become the so-called "high standing" of the dome of the diaphragm.
By nature of the current, polyhydramnios are divided into acute and chronic.Especially dangerous is the acute variant of development, most often diagnosed in the II trimester. It is characterized by a sharp increase in the volume of water in a very short time - from a few hours to 1-3 days.Circumference of the abdomen of the patient at the level of the navel increases rapidly, and in the inguinal and lumbar region there appears soreness of medium or high intensity.During the examination, the swelling of the abdominal wall and hypertension of the myometrium are determined.
In chronic form, the volume of the amniotic fluid increases gradually, but the likelihood of complications is also very high.
The severity of the pathological process is distinguished by a light, medium and severe degree.
Consequences of polyhydramnios during pregnancy
Polyhydramnios during pregnancy in many cases leads to severe consequences, especially in the absence of early diagnosis and adequate medical care.
Possible complications of the pathological condition are:
- spontaneous abortion( in almost 30% of cases);
- bleeding( in almost 40% of cases);
- fetoplacental insufficiency;
- early and massive water discharge;
- intrauterine malformations( most often the nervous system and the digestive tract of the fetus suffer);
- gluteal, oblique or transverse presentation;
- premature placental abruption;
- birth before the term.
Fetoplacental insufficiency leads to an inadequacy of the fetus of oxygen( hypoxia), which can cause the death of a future baby or serious developmental disorders.
If the pathology is caused by a bacterial or viral infection, the probability of infection of the fetus is high.
According to medical statistics, almost 20% of patients diagnosed with polyhydramnios develop late toxicosis( gestosis).
Important: pathology can lead to a weakening of labor in the 1st and 2nd period, as there is overgrowth of the uterine wall, which adversely affects muscle tone.When giving birth on the background of rupture of the bladder and a massive outflow of water, the umbilical cord or parts of the child's body may fall out.Often postpartum hemorrhage develops.
Diagnosis
 The basis for suspicion of polyhydramnios is the history( the presence of certain symptoms) and general examination( with measurement of the abdominal circumference).
The basis for suspicion of polyhydramnios is the history( the presence of certain symptoms) and general examination( with measurement of the abdominal circumference).
During the examination it is necessary to study the blood counts( UAC and sugar level) and urine.In the Rh factor, antibodies are examined.
The laboratory is also studying a smear for possible pathogenic microflora.
In palpation, the uterine tension is determined and its size( upwards) is not matched to the duration of pregnancy.The high mobility of the fetus is also characteristic;He constantly tries to change his position.
Important: is an excessively free position of the fetus and its active movements often lead to an umbilical cord entanglement, which is fraught with asphyxiation.
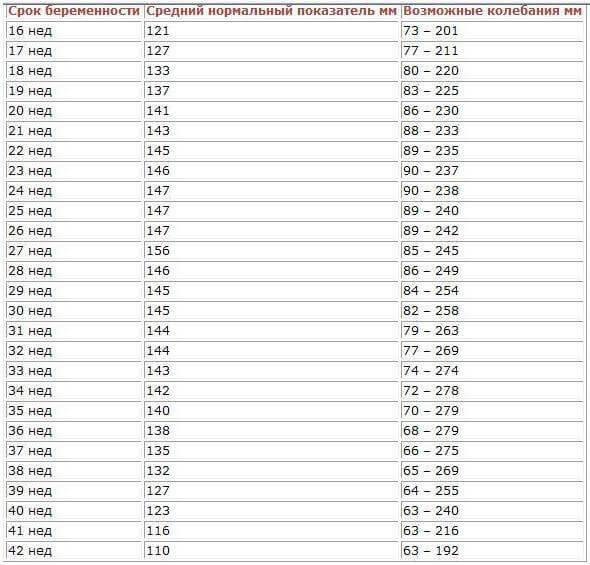
Verification of the diagnosis is made during ultrasound scanning. In ultrasound, the largest area between the uterine wall and the fetus is measured, resulting in the so-called."Amniotic fluid index."
Amniotic fluid table:
Very useful diagnostic methods include CTG( cardiotocography is needed to assess fetal status) and Doppler.
Treatment of polyhydramnios during pregnancy and prognosis
If an easy or moderate severity is detected, obstetrician-gynecologists make every effort to keep the pregnancy until the physiological delivery of .In severe cases, disorders of vital functions are possible, therefore, early( operative) delivery is often shown to preserve the patient's life.
To determine the medical tactics, it is important to identify the factors that triggered the pathological condition.
If multiplicity is caused by infection, antibiotic therapy is required to combat bacterial pathogens( it is advisable to prescribe broad-spectrum drugs - Rovamycin or Erythromycin).
Important: during pregnancy is unacceptable use of tetracycline antibiotics!
Diuretics( Hypothiazide, Furosemide), vitamins C, E and group B and immunomodulators are prescribed for indications.
For the improvement of uterine and placental blood flow, the agents of Actovegin and Curantil are recommended.
Note: pregnant women diagnosed with polyhydramnios need to carry out daily cardiotocography, to measure weight and blood pressure.Ultrasound and dopplerography for evaluation of uterine and placental blood flow are conducted at least weekly.
Polyhydramnios may be an indication for the procedure of abdominal amniocentesis, during which puncture is performed followed by a slow removal of excess amniotic fluid( pumped to 200 ml).
With weakened labor activity, its medicamental stimulation is carried out.
With mild degrees, therapy can be performed at home, but moderate severity already becomes an indication for hospitalization.
The prognosis for the chronic form of polyhydramnios is quite favorable.If there are no contraindications, childbirth is carried out naturally.
In order to prevent a sudden rupture of the bladder, a puncture of the membranes - amniotomy - is resorted to in advance.Thanks to this procedure, the amniotic fluid is poured out in a thin stream, and the uterus contracts.In emergency cases, a caesarean section is indicated.
Prophylaxis of this pathology presupposes early registration in a women's consultation, regular examination with a specialist, strict adherence to medical prescriptions.Pregnant is important to observe the regime of the day, eat right and take daily walks in the fresh air.
Vladimir Plisov, medical reviewer