Balantidiasis: symptoms, treatment and prevention

Balantidiasis( infusor dysentery) refers to a group of intestinal parasitic diseases that occur with ulcerative defects in the large intestine and are accompanied by general intoxication complaints.
Table of contents: Table of contents: Aspirant Balantidiasis Balantidiasis symptoms Balantidiasis symptoms Balantidiasis complications How to determine the presence of balantidiasis in a patient Treatment measures Preventative measuresBalditidias causative agent
In the early 1980s balantidia were first detected in pigs.Subsequently, it turned out that the level of infection of these animals reaches 80%.
In 1897 the Swedish doctor Malmsten, examining the excrement of patients with diarrhea, found balantidium in them.The scientist first described in detail the disease, the clinical picture and complaints of patients.
N. Soloviev established the fact that balantidia are interstitial parasites, he also identified the disease in a separate nosological diagnosis.
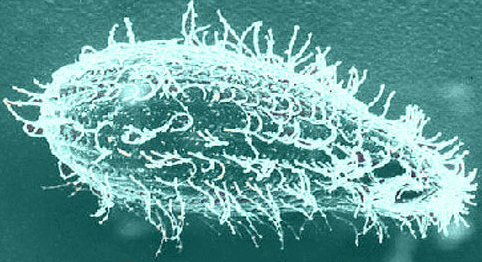
The bacterium causing the disease is balantidium coli, the ciliate ciliate, the largest causative agent of the disease in a person of the Protozoa type.
The cycle of microorganism development includes two stages:
- vegetative;
- cystic.
The vegetative is an oval-shaped balantidium, up to 80 μm in length and up to 60 μm in width.The external environment acts on microbes of this form is fatal.In feces they remain viable up to 6 hours.
Cysts balantidium rounded to 60 microns in diameter, also have two membranes, the structures of vacuoles with the core, are preserved in the natural environment for several weeks.
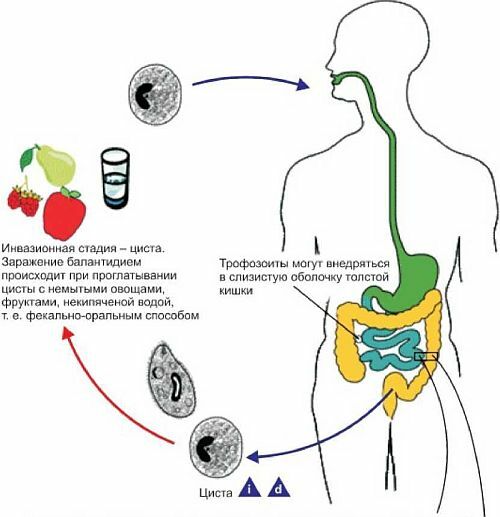
Note: infection with balantidiasis occurs through water, into which pig faeces enter, which are the main reservoir of pathogenic forms of microorganisms.Dogs can also be carriers of the disease.In special cases - a person.
In addition to water, balantidium may be contained in unwashed vegetables, soil.Transmission of infection sometimes occurs with synanthropic flies.
The disease is spread mainly among the inhabitants of rural areas, especially among those who are involved in the cultivation of pigs.Infection with caring staff can reach 30%.Balantidiosis is spread all over the world.
How is Baldithidiasis Infected
? Through the digestive tract, balantidiosis cysts enter the stomach, then the small intestine passes and multiplication and development begins in the lumen of the upper parts of the large intestine.At this point, the infected can have complaints that are characteristic of poisoning.
Balantidium secretes an enzyme - hyaluronidase, which promotes dissolution of the mucous membrane of the large intestine.In these "gaps" a pathogenic microbe is introduced.Over time, in place of the "entrance gate" there is redness and swelling, then erosions are formed, and subsequently - and ulcers.Cells of the epithelium give the response of the organism in the form of increased proliferation growth, but necrotic process also affects them.The ulcers become deep.
Bacteria balantidiasis are introduced into the submucosal layer, the immune forces of the body respond to activation of lymphocytes, histiocytic cells and congestion in the focus of segmented neutrophils.It is this process caused by edema, and in the subsequent - and purulent abscessing.
"Favorite" sites for ulcer localization are found in areas of bowel bends, especially in corners of the blind, as well as in sigma and rectum.Ulcerous defects can reach an area of several centimeters with pitted edges, loose, filled with dying cells.The contents of the bottom are of a dark color.
In practical medicine, there are cases of damage to the appendicitis, which resulted in purulent process and necrosis of the appendix.There are cases of involvement in the pathological changes of the small intestine, hepatic tissue and even the heart muscle.
The processes occurring in the body, caused by the vital activity of balantidium, provoke the release of toxins, which in turn cause symptoms of general poisoning in the patient.
Symptoms of Baldiatiasis
Disease can occur in forms:
- acute;
- subacute( latent);
- chronic permanent;
- chronic recurrent;
- subclinical( carrier).
The sharp shape is characterized by three degrees of gravity:
- light;
- average;
- heavy.
The disease develops rapidly - the fever rises, the patient shivering, then there is a fever.The temperature fluctuations on the daily chart are of a wrong nature.
Medium and severe degrees are characterized by severe intoxication with severe headache, accompanied by nausea and excruciating vomiting.Gradually, weakness grows.
 Against this background, intense pains in the abdomen occur, accompanied by abundant and frequent diarrhea, in which an admixture of bloody pus with a heavy smell of putrid character is found.The multiplicity of the pathological stool can reach up to 20 per day and more, as a result of which patients lose weight sharply, dehydration develops, and severe weakness.
Against this background, intense pains in the abdomen occur, accompanied by abundant and frequent diarrhea, in which an admixture of bloody pus with a heavy smell of putrid character is found.The multiplicity of the pathological stool can reach up to 20 per day and more, as a result of which patients lose weight sharply, dehydration develops, and severe weakness.
If within 2 months the symptoms of acute form do not pass, the disease passes into a subacute( latent) and chronic form.
Continuous flow lasts for several years with medium manifestations of the disease, which gradually leads to patient exhaustion.
The recurring variant can last up to 10 years, alternating flashes of exacerbations and fading.In a year there may be 2-4 exacerbations lasting from 1 week to a month.Periods of remission from 3 to 6 months.Prevalent pathological phenomena of intestinal distress.Intoxication syndrome malovyrazhenny.
If balantidiasis affects the appendix, the patient's complaints are characteristic of those with acute appendicitis, there are specific symptoms of irritation of the peritoneum.
Complications of baldiatiases
Emerging complications depend on the form, stage and duration of the disease.An important role is played by the body's resistance.
In balantidiasis, patients may develop:
-
 bleeding from the intestine;
bleeding from the intestine; - perforations of ulcers;
- development of forms of peritoneal inflammation( peritonitis);
- Malignancy.
Mortality from balantidiasis in foci of infection reaches 1%.Separate cases give a much more serious level of deaths - up to 30%.
How to identify the presence of balantidiasis in a patient
Diagnosis of the disease includes:
- epidemiological surveillance and analysis( a professional factor in pig workers);
- comparison of clinical complaints - fever of the wrong type, specific abdominal pain, putrefaction;
- intestinal endoscopy, with the detection of erosion and ulceration;
- parasitology data - detection of vegetative forms of balantidium in the patient's bowel movements;
- microscopic analysis of the contents of the bottom and edges of ulcers;
- parasitological study - isolation of vegetative cells of balantidium in smears from ulcerative contents;
- culturological research - cultivation of the colony in the culture of Rice.
These same diagnostic procedures make it possible to distinguish balantidiasis from cases of dysentery, intestinal amoebiasis, variants of dysbacteriosis and ulcerative colitis.
Treatment measures
 Balantidiasis is a specific infection, therefore the most common antibiotics are harmful to pathogens of this pathology in fairly low doses.
Balantidiasis is a specific infection, therefore the most common antibiotics are harmful to pathogens of this pathology in fairly low doses.
The first recommended drug for the treatment of balantidiasis is Monomycin, used for five-day cycles in the form of 4-time injections of 250 units.In total, two cycles are recommended with a break about a week.
Oxytetracycline also works well, which is prescribed in tablets of 0.25 grams 4 times per knock for a week in case of mild forms of the disease.
In severe cases in the treatment of balantidiasis, both antibiotics are given in combination with each other.
Additionally assigned:
- Trichopol;
- Yatren;
- Ampicillin;
- detoxification medicines;
- immunomodulators.
In a hospital, hemotherapy can be used.
Surgical treatment of balantidiasis is indicated in the development of the clinic of acute appendicitis, peritonitis, perforation of the ulcer, intestinal bleeding.
Recovering is the fact of repeated negative results of a study of feces and parasitological analyzes.
Preventative measures
In the possible foci of the disease, preventive examinations of residents, sanitary and hygienic measures and observation of their observance are necessary, especially in pig raising enterprises.No less importance should be given to monitoring the implementation of standards for the processing, decontamination and disposal of pig faeces.

It is very important to find the patient in time, to hospitalize and to prescribe adequate treatment of balantidiasis.
Alexander Lotin, medical reviewer



