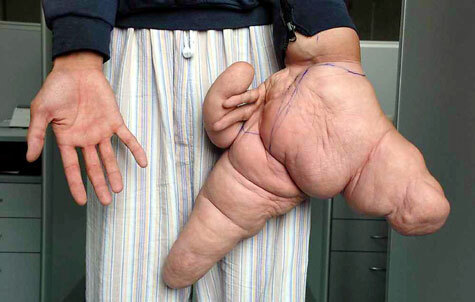
Hyperparathyroidism
 Hyperparathyroidism( generalized fibrotic osteodystrophy) is a disease caused by increased production of parathyroid hormones of parathyroid hormone, resulting in pathological changes in the kidneys and bones, as well as a chronically elevated calcium content in the blood. The most common disease occurs between the ages of 20 and 50, with women more often( 2-3 times) than men.
Hyperparathyroidism( generalized fibrotic osteodystrophy) is a disease caused by increased production of parathyroid hormones of parathyroid hormone, resulting in pathological changes in the kidneys and bones, as well as a chronically elevated calcium content in the blood. The most common disease occurs between the ages of 20 and 50, with women more often( 2-3 times) than men.
Causes of of hyperparathyroidism
The most common cause of hyperparathyroidism is parathyroid gland tumors. Depending on the reasons for this disease, there are primary, secondary, tertiary and pseudo-hyperparathyroidism.
Primary hyperparathyroidism .It occurs due to the formation of a benign tumor( adenoma) parathyroid glands: from 80 to 85% of cases
Secondary hyperparathyroidism .Reinforcement of function, enlargement and proliferation of glands with elevated phosphate content and prolonged decrease in calcium in the blood( hyperplasia, carcinoma): 10% of cases
Tertiary hyperparathyroidism
.Increased production of parathyroid hormone, due to the long existence of secondary hyperparathyroidism;Development of benign. Parathyroid glandsPseudohyperparathyroidism .Generation of parathyroid hormone by tumors that develop not from parathyroid gland cells.
. Hyperparathyroidism with .
. Clinical manifestations of this disease are grouped, depending on what was more affected( neurological and psychiatric spheres, gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, bones).Against this background, the disease is divided into forms, according to the clinical picture: mental - neurological, gastrointestinal, renal and bone forms.
However, for any form this disease is characterized by early common symptoms:
- lethargy, fast fatigue, severe weakness of the muscles of the legs and arms, general muscle weakness. Patients stumble when walking, it is difficult for them to climb stairs, walk, stand, sit
- A swinging "duck walk" appears( the person walks from side to side when walking)
- There are pains in the feet( due to foot muscle damage, or due to injuryFlatfoot development)
- Clear thirst and copious frequent urination( due to excess calcium blocking the work of the antidiuretic hormone responsible for the regulation of urination)
- There is a significant weight loss, sometimes reaching aAbout severe exhaustion of
-
begins to loosen and drop completely healthy teeth. Mentally - a neurological form is characterized by a decrease in mental abilities, frequent depressive states, drowsiness, rapid mental fatigue. In the acute course of the disease, auditory and visual hallucinations are observed, as well as a partial or complete loss of voluntary movements.
The gastrointestinal form is characterized by the following symptoms: lack of appetite( leads to significant weight loss), bloating, constipation, nausea, repeated vomiting. Possible formation of duodenal ulcers with pronounced symptoms, which does not heal even with prolonged treatment. Often observed the development of acute inflammation of the pancreas. Glands.
With renal form in the kidneys, calcium absorption decreases, which causes polyuria, thirst, kidney stones( nephrolithiasis);In the kidneys begin to be deposited crystals of calcium salts( nephrocalcinosis).This form can often proceed secretly, revealing itself only minor pain in the lower back.
Bone form is characterized by three main manifestations: pathological fractures, cyst formation and osteoporosis.
Characteristic symptoms of the bony form :
- Even with small physical exertion, spontaneous frequent fractures( most often bones of the ribs, shin, shoulder, neck of the thigh), after which the so-called false joints( absent in the normal human body) are formed.
-Load of pain in the bones( more often in the spine) of the aching, pulling character
- Due to incorrect fusion of fractures, the shape of different parts of the skeleton
changes. - As a result of osteoporosis and vertebral fracture, a decrease in the growth of
is observed. - Bones lose firmness and become more flexible.
Hyperparathyroidism. Diagnostics
. Diagnosis of hyperparathyroidism is determined by the presence of a characteristic symptomatology;To reveal a tumor on the gland, an x-ray of the parathyroid gland is performed;According to the blood test( there will be an elevated calcium concentration and a reduced phosphorus content);When the thyroid ultrasound is performed, the parathyroid glands increase.
Hyperparathyroidism
treatment Both operative and conservative treatment is used. Operative treatment is to remove the enlarged parathyroid glands or adenomas. With the development of the hyperparathyroid crisis, surgical intervention is required for emergency indications. Conservative treatment is aimed at lowering the level of calcium in the blood and consists in the use of certain drugs and adherence to a specially developed diet.
More articles on the topic:
1. Hyperinsulinism
2. Congenital disorders of sexual differentiation