Infectious colitis: symptoms and treatment
Infectious colitis is a disease of the large intestine, which is inflammatory.It arises from the ingress of pathogenic microorganisms into the human digestive system from the environment or by activating the opportunistic flora already present in the intestine.The patient is diarrhea with the presence of mucus and sometimes - with blood, pain in the abdominal cavity, dehydration and intoxication of the body.
Table of Contents: Structure and function of the colon What is infectious colitis Causes of the disease Symptoms of the disease Diagnosis Treatment of the disease Prevention and prognosisStructure and function of the colon
This part of the intestine is located in the abdominal cavity.
It includes:
-
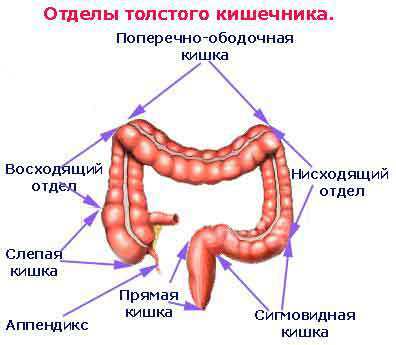 the caecum;
the caecum; - Colon ascending colon,
- Colon cross section;
- descending part of the colon,
- sigmoid colon;
- rectum;
- anus.
The blind and ascending gut are located to the right of the thick, the transverse segment of the sigmoid is located on the left relatively thick.
The main purpose of the large intestine is the collection and storage of waste resulting from the digestive process.
The bowel itself is a multi-layered tube, which includes:
- A layer consisting of smooth muscles, whose task is to move the undigested food residue along the colon to the anus for subsequent defecation.
- Mucous membrane( inner layer), necessary to absorb liquid and electrolytes from the intestinal slurry of food residues.Thanks to this process, the feces solidify.
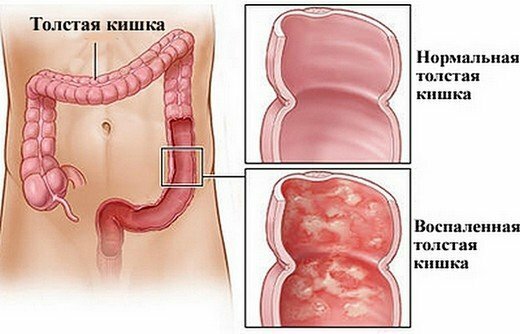
Inflammation occurs precisely in the mucous membrane, which provokes the symptoms of infectious colitis.
What is infectious colitis
This colon disease, manifested in two forms: chronic( usually less common) and acute - occurs due to different types of bacteria, protozoa, viruses and parasites. Pathology is accompanied by dehydration of the body, its intoxication.In the inflammation process, other parts of the gastrointestinal tract are sometimes involved.Infectious colitis is prevalent everywhere and absolutely every person has experienced this disease at least once in a lifetime.
Most often, this disease can be "picked up" in the warm season, in hot countries or where the amount of drinking water is limited, and communications are poorly developed.The most dangerous regions include the countries of Central and South-East Asia, Africa. The addiction to the disease and its symptoms manifest in the same way as in the male and female half of the population.Children are more prone to infectious colitis.
Infectionists deal with the treatment of this disease.
Causes of the disease
 To the main cause of the manifestation of infectious colitis include various bacteria: staphylococci, shigella( causative agents of dysentery), clostridia, proteus, E. coli, Campylobacterium, Yersinia, Salmonella and other .Symptoms of the disease can occur with enteroviral or adenoviral infection, less often when a rotavirus gets into it.Among the parasites that can cause infectious colitis, you can distinguish lamblia, amoeba and others.Infectious colitis can develop from syphilis or tuberculosis.
To the main cause of the manifestation of infectious colitis include various bacteria: staphylococci, shigella( causative agents of dysentery), clostridia, proteus, E. coli, Campylobacterium, Yersinia, Salmonella and other .Symptoms of the disease can occur with enteroviral or adenoviral infection, less often when a rotavirus gets into it.Among the parasites that can cause infectious colitis, you can distinguish lamblia, amoeba and others.Infectious colitis can develop from syphilis or tuberculosis.
If the patient's immune system is weakened, actinomycetes, candida( fungi) may act as pathogens of the disease. The disease caused by fungi is sometimes a marker of HIV infection .Also fungal infectious colitis occurs due to chemotherapy in cancer patients or in patients taking steroid hormones for a long time.Conditionally pathogenic microorganisms, for example, Clostridium bacteria, can cause infectious colitis in case the patient takes antibiotics or undergoes a course of chemotherapy.
Depending on the morphological changes, the disease has several forms that depend on the pathogen: fibrotic, catarrhal( with viral pathogens), phlegmonous, catarrhal-hemorrhagic( dysentery), phlegmonous gangrenous and necrotic( the causative agent are clostridia).The process of flow is rapid, with the transition from one form to another, otherwise - it stops at one of the stages.
Symptoms of the disease
With the development of pathology, intestinal motility is disrupted, endothelial cells begin to secrete fluid in large quantities, deterioration of fluid absorption back, toxins become easier to penetrate through the intestinal walls, cause intoxication.
Symptoms of infectious colitis largely depend on the cause of the disease.
For any form of this disease is characterized by:
- diarrhea with abundant mucus;
- spasmodic abdominal pain;
- high body temperature;
- white coating on the tongue;
- general weakness;
- dryness of mucous membranes.
Depending on the symptoms, you can find out whether the small intestine and stomach were involved in the process.For the first( enterocolitis) is characterized by an increase in the release of fecal matter, dehydration of the body is further aggravated.Vomiting indicates gastroenterocolitis - involvement in the process of inflammation of the stomach.
The sigmoid colon is affected by dysentery.In this case, the patient has diarrhea, in which minor amounts of fecal masses of are isolated.Desires for defecation in the patient arise from 3 to 20 times a day, and sometimes more.The feces contain blood and mucus.If the case is neglected, mucus in feces - in a small amount, with veins of blood.The abdominal pain has a sharp character, the body temperature rises, the symptoms of an organism's intoxication are strongly manifested until the loss of consciousness.
Amebiaz has a similar clinic.It develops in the blind and ascending colon and is less acute.Sometimes the whole colon is involved in the process.Feces contain a large amount of mucus and blood.Outwardly it resembles a raspberry jelly.Intoxication is not expressed strongly.Amoebiasis is recurrent or chronic.
The unpleasant smell of diarrhea, the color of which is similar to swamp dust, is characteristic of infectious colitis, the causative agent of which was Salmonella .In this case, the small intestine is affected.As a consequence - liquid stool.The patient's body temperature sharply increases.Severe form of the disease can be complicated by septicemia and sepsis.
Clostridia cause the manifestation of pseudomembranous colitis that occurs with chemotherapy or treatment with antibiotics, with severe dysbiosis.It is characterized by severe diarrhea, feces have a putrefactive smell, patients complain of severe abdominal pain, which has a cramping character, and fever occurs.This disease can recur, lead to necrosis of intestinal tissues.
Diagnostics
Laboratory diagnostics, in which bacteriological, virological and parasitological studies are carried out, are important for clarifying the etiology. To test for antibodies to pathogens, a serum test can be performed.If septic complications occur, make the patient's blood culture sterile.Increased ESR and leukocytosis with a shift of the formula to the left are characteristic for the bacterial form of the disease.If colitis is caused by parasites, the level of eosinophils in the blood increases, viruses - of lymphocytes.
To differentiate infectious colitis from other diseases of the colon, endoscopic examinations of are carried out.In view of the fact that the picture of morphological changes is not specific, this study has only an auxiliary character.
Bacterial dysentery and pseudomembranous colitis are detected by a rectographic examination, conducted by infectionists or proctologists.If there are suspicions of complications from the disease, ultrasound is prescribed.
Specialists distinguish infectious colitis from diseases with similar symptoms: diverticulitis and diverticular disease, dysbiosis and Crohn's disease .It is very important to differentiate different types of infectious colitis, because therapy directly depends on the cause of the onset.
Treatment of the disease
 Specific treatment is performed by taking oral antibiotics. If the causative agent of colitis is Shigella, patients are prescribed 8-oxyquinoline and fluoroquinolone.When colitis occurs due to the activity of E. coli, cephalosporins 3 and 4 generations are prescribed, which act on the gram-negative flora.Metronidazole is used for pseudomembranous colitis.Amoebocides, metronidazole, preparations of antibiotic action of tetracycline are prescribed for amoebiasis.
Specific treatment is performed by taking oral antibiotics. If the causative agent of colitis is Shigella, patients are prescribed 8-oxyquinoline and fluoroquinolone.When colitis occurs due to the activity of E. coli, cephalosporins 3 and 4 generations are prescribed, which act on the gram-negative flora.Metronidazole is used for pseudomembranous colitis.Amoebocides, metronidazole, preparations of antibiotic action of tetracycline are prescribed for amoebiasis.
Rehydration is the most important direction in the treatment of colitis a.If the fluid loss of the patient is of a minor or moderate nature, and if there is no vomiting, the administration of rehydron or oralit( saline solutions) is prescribed.Disintoxication therapy, infusion rehydration can be prescribed in severe conditions.Patients with infectious colitis are recommended taking enzyme preparations such as festal, mezim and pancreatin, as well as probiotics.
Prevention and prognosis
As etiotropic therapy for infectious colitis is successfully used today, the prognosis is often favorable. It worsens when the disease has a severe form, which is characteristic of HIV-positive patients, oncological patients, if the causative agents are salmonella or clostridia.The disease is also difficult for young children.

The main preventive measure is hygiene, in which it is necessary to control the shelf life and purity of foods, mostly those that are eaten without heat treatment.Water quality should also be monitored.
Совинская Елена, medical reviewer