Tumor of the larynx: symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
The laryngeal tumor can be both malignant and benign. Malignant tumor is the most common disease after a skin tumor( malignant) and is more common in men. In addition, a malignant tumor of the larynx is associated with the abuse of alcohol and smoking. Benign tumors are visible, most often, with the naked eye, but differ in small sizes. Tumor of the larynx: symptoms, diagnosis, treatment depend on whether you have cancer or a benign tumor.
Symptoms of a malignant tumor.
Malignant neoplasm of the larynx has the following symptoms:
- Neck swelling;
- Hoarseness and other voice changes;
- Feeling of discomfort when swallowing;
- Sore throat;
- Pershing;
- Persistent cough;
- Sensation of swallowing in the larynx of a foreign body;
- Pain in the ear;
- Respiratory depression;
- Weight Loss.
Cancer of the larynx affects usually the vocal cords, causing hoarseness in this case. If you wheeze for more than two weeks, consult a doctor. Other subspecies of tumors cause pain and difficulty breathing. Sometimes, before there are other symptoms, you can notice a swelling on the neck, which arises from the spread of a malignant tumor( metastasis) to the lymph nodes.
Symptomatic of this disease also depends on the size of the tumor and on what department it appeared in. So, the sensation when swallowing a foreign body is usually associated with the appearance of densification( rigidity) of the epiglottis( cartilage of the larynx) due to infiltration of this organ with a tumor. In later stages of cancer, pain in the ear appears, which is associated with metastases and sprouting into the nerves of the tumor. Weight loss is also associated with sore throat in the patient( pain increases with swallowing, which causes a person to stop taking food often).Hoarseness is associated with a loss in the patient of the vocal cords due to a violation due to a mechanical obstruction of the tight closing of the vocal folds( this is a tumor).In cancer of the larynx, hoarseness increases with the progression of the disease. In later periods, the patient may also have difficulty breathing associated with tumor growth, narrowing of the laryngeal lumen and immobility of the larynx halves( both or one).Further, the tumor can spread with the appropriate clinical manifestations to the neighboring larynx and germinate into the soft tissues of the neck forward.
Diagnosis of laryngeal tumor.
Tumor of the larynx, its diagnosis depends on the stage of the disease the patient turned to the doctor. At the very beginning, the doctor interrogates the patient, is interested in his complaints and makes an anamnesis, that is, he collects the necessary information about the patient's illnesses and risk factors( for example, about smoking, drinking alcohol, the nature of work and profession) for diagnosis of the larynx tumor. After this, the doctor examines the patient: first he conducts a physical routine examination conducted by any doctor in any disease( during this examination the doctor examines the patient's neck, thyroid gland, lymph nodes and other swelling on the neck, and also with a spatula looks at the patient's throat), Then the doctor conducts laryngoscopy, which can be both direct and indirect, computed tomography and biopsy.
Indirect laryngoscopy consists of examining the larynx by a doctor using a small round mirror on a long handle that is inserted into the patient's throat. At this time, the tongue is pushed aside by a spatula. Before this procedure, the doctor should spray the patient's throat with a special anesthetic to avoid triggering the emetic reflex. Direct laryngoscopy( also called fibrolaringoscopy) is performed using a flexible thin laryngoscope, which is inserted through the nasal entrance to the larynx( first it is necessary to spray the nasal cavity with an anesthetic).Thanks to this procedure, the doctor will be able to examine the vocal cords and laryngeal walls.
The method of computed tomography is based on obtaining X-ray images of the larynx, which are sections of tissue at different depths. Then the received pictures get for further processing in the computer and form a "layered" picture. Before this procedure, the patient is administered a special contrast agent that will enhance the contrast of the tumor compared to other surrounding tissues.
Biopsy is the main method of diagnosing tumors( not only tumors of the larynx) and consists in taking a small piece of tumor tissue and further histological examination under a microscope. This method makes it possible to clarify the structure of the tumor and its nature and is carried out during indirect laryngoscopy. For a biopsy, local anesthesia( eg anesthetic spraying of the larynx) or general anesthesia should be used. The duration of this procedure, its kind and anesthesia should be discussed with the doctor in advance.
In other words, to make a correct diagnosis, the doctor first examines with a laryngoscope the larynx and makes a biopsy of the site, which is suspected for the presence of a tumor. After this, the doctor conducts all the studies to determine whether the tumor is malignant, and if it is a positive outcome, classifies it in 4 stages based on the width of its spread.
Treatment of a larynx tumor.
Tumor of the larynx, its treatment depends on the exact location of the tumor and the stage of its development. In an early stage, an operation or radiation therapy is performed to treat a malignant tumor( for example, in the case of a lesion of the vocal cords, radiation therapy is preferred, which will preserve the voice).In the late stage, surgery involves the removal of part of the larynx or the entire larynx( partial or total laryngectomy) and often accompanied by radiotherapy.
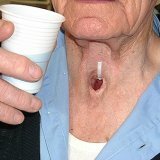
If a person completely removes the vocal folds, he remains without a voice and restores the opportunity to speak in one of 3 ways: esophageal speech, electrogut, and tracheoesophageal speech. For esophageal speech, the patient learns to take air into the esophagus when inhaling and exhale it gradually( in order to create a sound).With tracheoesophageal speech, a tracheoesophageal fistula is inserted, inserted surgically between the esophagus and the trachea and directing the air when the person breathes into the esophagus( in order to produce a sound).If the valve functions incorrectly, solid food and liquid may accidentally enter the trachea. An electricortany is also called a device acting at its location and neck as a sound source. In speech, the sounds that are produced by these methods are transformed as always( with the mouth, teeth, nose, lips and tongue), but the voice sounds weaker than normal and artificially.
If adequate treatment is provided, approximately 90% of patients with Stage I malignancy remain alive for a minimum of 5 years, and patients with Stage IV - 25%.