Urinary system: anatomy and physiology
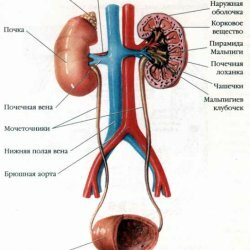
Kidneys
Kidneys are small paired organs that resemble large beans. There are kidneys on either side of the spine in the lumbar region of the abdominal cavity. The weight of the kidney of an adult is about 150 grams. The kidneys are designed to perform the function of complex biological filters. The filtering surface of both kidneys is approximately five to six square meters. Every minute, through the kidneys, more than one-fifth of the body's blood flows. The kidneys receive blood from the aorta. From the blood flowing through the kidneys, water surpluses, excess mineral salts and residual metabolic products are removed. Through the kidneys are also derived excesses of various substances, for example, drugs. After cleansing, the blood returns to the lower vena cava.
Substances that have been filtered out, dissolved in water and form urine. For a day in an adult human body forms about one and a half liters of urine, which collects in the renal pelvis and is guided along the ureters into the bladder - a saccate organ with thick muscular walls. When the muscles of the bladder contract, the urine from it is removed to the outside through the urethra.
Regulation of urinary excretion has a reflex character. The arcs of these reflexes pass through the sacral region of the spinal cord, but urination is performed arbitrarily in man, which is associated with the influence of special nerve cells of the brain, or rather, its cortex. These nerve cells inhibit or, on the contrary, activate the centers of the spinal cord, which regulate the release of urine.
Kidneys not only release harmful substances, excess for the body, kidneys help maintain a constant level of chemical composition and properties of fluids of the internal environment of the body( blood, lymph, intercellular fluid).The volume and composition of urine is determined by the volume of water and food consumed, as well as the rate of metabolic processes in the body. After eating a meal that is rich in carbohydrates, or after carrying out heavy muscular work in the urine, even a normal amount of glucose may be contained.
Kidneys synthesize many biologically active substances, they form, for example, some enzymes that cause an increase in blood pressure, chemicals that increase the body's resistance to infection and stimulate the process of hematopoietic hormone precursors.
The work of the kidneys, as other organs, is regulated by the central nervous system, and also with the help of blood elements. One way to regulate is to reduce or increase the amount of blood that flows through the kidneys. This is achieved by changing the lumen of the blood vessels that bring blood to the kidneys.
In case of kidney disease, primarily of an infectious nature, both the bladder( develops cystitis) and the urethra( developing urethritis) can suffer, which is explained by the infection of the kidneys in these organs.
Udder
The human ureter is a cylindrical tube with a diameter of 6-8 millimeters, which is located in the retroperitoneum. The length of the ureter of an adult reaches twenty-five to thirty centimeters.
Urine travels through the ureter due to rhythmic peristaltic contractions of its thick muscular membrane.
Bladder
The bladder in an adult person lies in the small pelvis behind the pubic symphysis. Its capacity can be up to half liter. The pointed tip of this organ is directed upwards, and the extended bottom is turned downwards and backwards. The bottom of the lower part of the bladder, tapering, forms the neck of the bladder, which passes into the urethra.
An empty bladder is covered with the peritoneum mainly from above, slightly laterally and posteriorly. When filling the body is rounded, the top of it rises. The bottom of the bladder in men behind and below lies in the prostate gland( prostate) and seminal vesicles, behind - to the ampoule of the rectum, in women - to the vagina and uterus. The wall of the organ is formed by the mucosa, which is involved in the inflammatory process under favorable conditions. Infection of the bladder can be transferred from the outside, for example, when sitting on a damp cold object or bathing water contaminated with microbes, and also descend from diseased kidneys and ureters. The infection can also be introduced from the prostate gland in the presence of an inflammatory process.
Urethra
The urethra or urethra is located behind the pubic symphysis. His outer hole in men is in the spongy body of the penis, and in women - on the eve of the vagina.
In men, part of the urethra passes through the prostate gland.
Prostate gland
The prostate gland is the unpaired organ of the male reproductive system, which is located on the anterior lower part of the pelvis below the bladder. In its form, the organ resembles a chestnut, which is turned upside down. This gland supports spermatogenesis, which is involved in the formation of sexual desire, so doctors call this organ the second heart of a man. In men, often in this gland develops an inflammatory process that leads to the appearance of prostatitis, which can contribute to inflammation of the bladder.
Thus, all the organs of the urinary system are closely related to each other both anatomically and physiologically. Disease of one of these organs can lead to illness of neighbors.
Stay healthy!