Osteoarthritis of joints
 Arthrosis( osteoarthritis) is a common disease of the musculoskeletal system, which affects the cartilaginous tissue of the joints. Inflammation, thinning and deformation of the hyaline cartilage disturbs the correct operation of the joint, which entails adverse consequences for a person up to disability. Many factors of our life can contribute to the development of arthrosis. Most often, the diagnosis of arthrosis is set at the age of 40 to 60 years, this is associated with a decrease in the ability of cartilage cells to synthesize a full tissue.
Arthrosis( osteoarthritis) is a common disease of the musculoskeletal system, which affects the cartilaginous tissue of the joints. Inflammation, thinning and deformation of the hyaline cartilage disturbs the correct operation of the joint, which entails adverse consequences for a person up to disability. Many factors of our life can contribute to the development of arthrosis. Most often, the diagnosis of arthrosis is set at the age of 40 to 60 years, this is associated with a decrease in the ability of cartilage cells to synthesize a full tissue.
Causes of arthrosis
- Increased physical activity and uneven loads .Risks of developing arthrosis are high both among professional athletes, and in people who have excess body weight. Under uneven load it implies not only physical exercise without warming up the joints, but also improper lifting and carrying heavy objects - for which there is a sharp pressure in the joint capsule( other than "daily" stress to which the joints are used to).People - who by virtue of the profession have to sit or stand for a long time in the performance of works are also at risk of developing arthrosis in view of the stagnation of synovial fluid inside the joint. With great caution should be approached to increased physical activity for people with excess weight, t. K on the joints already exerts additional pressure of excess weight and increased stress on the joints can lead to cartilage trauma.
-
 Heredity .If the family had cases of arthrosis, the chances that the disease will manifest in the next generation are very high. And osteoarthritis can manifest at an early age. Most often, hereditary arthrosis affects women.
Heredity .If the family had cases of arthrosis, the chances that the disease will manifest in the next generation are very high. And osteoarthritis can manifest at an early age. Most often, hereditary arthrosis affects women. - Endocrine diseases .With such diseases( diabetes, obesity, thyroid disease), there is a hormonal failure, which can make the joint cartilage more vulnerable to stress and injury. In women during menopause, the lack of estrogen adversely affects joints.
- Deformations of the musculoskeletal system .As in congenital( clubfoot, torticollis), and when the acquired deformities( a kyphosis, scoliosis) occurs uneven load on the joint surface which leads to deformation and microtraumas articular surfaces and causes premature wear of the cartilage. Classification
- primary arthrosis osteoarthritis( idiopathic) - accompanied by destruction of cartilage structure, joint capsule and changes in the tissues of the joints and connective tissue. Usually this happens at the age of over 40 years. Osteoarthritis may be exposed to multiple joints, the most frequent location on the phalanges of the fingers( Heberden's nodes or Bouchard)
- secondary arthrosis etiology is more pronounced and is a consequence of injury, metabolic disorders, inflammatory diseases of the transferred result.
The most common types of arthrosis
-
 Arthrosis of the hip joint ( coxarthrosis) is the most severe type of osteoarthritis. It affects middle-aged and elderly people, and also occurs among young people with congenital diseases of the musculoskeletal system. It is characterized by sharp pains in the region of the hip joint when walking, forcing a person to bend forward to ease the pain. Subsequently, the spine begins to curve and the person's gait changes. On the part of the gait resembles the "duck walk".
Arthrosis of the hip joint ( coxarthrosis) is the most severe type of osteoarthritis. It affects middle-aged and elderly people, and also occurs among young people with congenital diseases of the musculoskeletal system. It is characterized by sharp pains in the region of the hip joint when walking, forcing a person to bend forward to ease the pain. Subsequently, the spine begins to curve and the person's gait changes. On the part of the gait resembles the "duck walk". - knee arthrosis ( gonarthrosis). The causes of osteoarthritis of the knee were previously transferred trauma, bruises, excess weight of a person. Usually, there is a simultaneous failure of both knee joints, but the pain can be localized on one of them. External manifestations of inflammation is not under much stress ache appears on the knee.
- Osteoarthritis of the hands and fingers . The growth of bone tissue in the distal interphalangeal joints is calledZelko heberden. often occur in women during menopause, there is emerging evidence nodules on several fingers, palpation causes pain. Osteoarthritis in the proximal interphalangeal joints called Bouchard nodules, these nodules significantly reduce the amplitude of the fingers.
Symptoms of osteoarthritis
- The first stage of - after excessive or prolonged exercise, soreness and uncomfortable sensations appear in the joints. There is a process of softening, decreasing the elasticity of the cartilage. After rest all the symptoms disappear. At the same time, the volume of movements and muscle strength in the joint damaged by arthrosis remains the same. The X-ray at this stage will be of little informative, examination by a doctor will help to identify irregularities or hardening of the joint, if any already exist.
- The second stage of - progresses soreness in the joint, not only after active physical actions, but also in their absence. If at this moment to completely immobilize the joint to avoid pain, then atrophy of muscle tissue can begin, which also has a bad effect on the development of the disease. X-ray photography will allow us to see a slight narrowing of the joint gap, the formation of marginal osteophytes, cysts and osteosclerosis.
- The third stage of is acute pain while moving the joint, without abating and at rest. Significant restriction or lack of joint movement can cause the bone ankylosis - a disease in which the bone substance of the glenoid cavity and the joint head are connected. On the X-ray, significant narrowing, complete or partial absence of the joint gap, marginal osteophytes, etc. will be seen.
Diagnosis of arthrosis
Diagnosis for the detection of such a disease as arthrosis includes a comprehensive examination and a complete assessment of the state of the body. Based on the history of previous injuries or diseases, X-rays and laboratory tests, the doctor will identify the form of the disease and prescribe the most effective course of treatment and therapeutic measures.
treatment of arthrosis
-
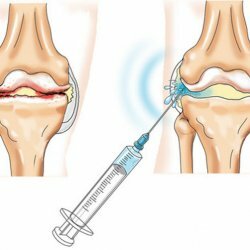 Pharmacotherapy arthritic joints is also integrated and is directed at relieving pain in the joints, removing inflammatory( NSAIDs), early restoration of the cartilaginous tissue( via chondroprotective, which are elements of the cartilage) and increasing concentrations of the synovial fluid( This is facilitated by injections of hyaluronic acid).
Pharmacotherapy arthritic joints is also integrated and is directed at relieving pain in the joints, removing inflammatory( NSAIDs), early restoration of the cartilaginous tissue( via chondroprotective, which are elements of the cartilage) and increasing concentrations of the synovial fluid( This is facilitated by injections of hyaluronic acid). - Surgical treatment is required when using the drug treatment failed to stabilize the progression of the disease, it remains a complete or partial immobility and severe pain in the affected joint. There are two types of surgery for arthrosis:
- minimally invasive arthroscopic surgery aims at removing a deformed portion of the cartilage, bone spurs. With its help, you can grind the cartilaginous tissue to restore the normal course of movement and joint work.
- Joint replacement is done when the joint is completely replaced by a metal or combined prosthesis( implant).This operation is extensive, since the surgeon has to strip the entire joint, remove the damaged parts of the cartilage and install the implant.
Preventive measures in the treatment of osteoarthritis
At the first stage of osteoarthritis should make adjustments to their lifestyle to ensure that the disease has progressed.
- Rational nutrition, the elimination of alcohol consumption helps to reduce weight and improve the metabolism of the body. This is especially important for people who are overweight, because it causes additional stress on the joints.
- moderate physical activity. Avoid prolonged physical exertion on joints such as walking, running and squats. It is necessary to do an easy gymnastics in the mornings and to adhere to the correct motor mode during the day.
In the second stage of arthrosis:
- timely administration of drugs designated by the attending physician
- physiotherapy
- eliminate long stay in the same position, lifting or moving heavy objects.
- regular therapeutic gymnastics( LFK).